H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 223
23-6
Four authentication ways, namely EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS (transport layer security), EAP-TTLS (tunneled
transport layer security), and PEAP (protected extensible authentication protocol), are available in the
EAP relay mode.
z
EAP-MD5 authenticates the supplicant system. The RADIUS server sends MD5 keys (contained in
EAP-request/MD5 challenge packets) to the supplicant system, which in turn encrypts the
passwords using the MD5 keys.
z
EAP-TLS allows the supplicant system and the RADIUS server to check each other’s security
certificate and authenticate each other’s identity, guaranteeing that data is transferred to the right
destination and preventing data from being intercepted.
z
EAP-TTLS is a kind of extended EAP-TLS. EAP-TLS implements bidirectional authentication
between the client and authentication server. EAP-TTLS transmit message using a tunnel
established using TLS.
z
PEAP creates and uses TLS security channels to ensure data integrity and then performs new EAP
negotiations to verify supplicant systems.
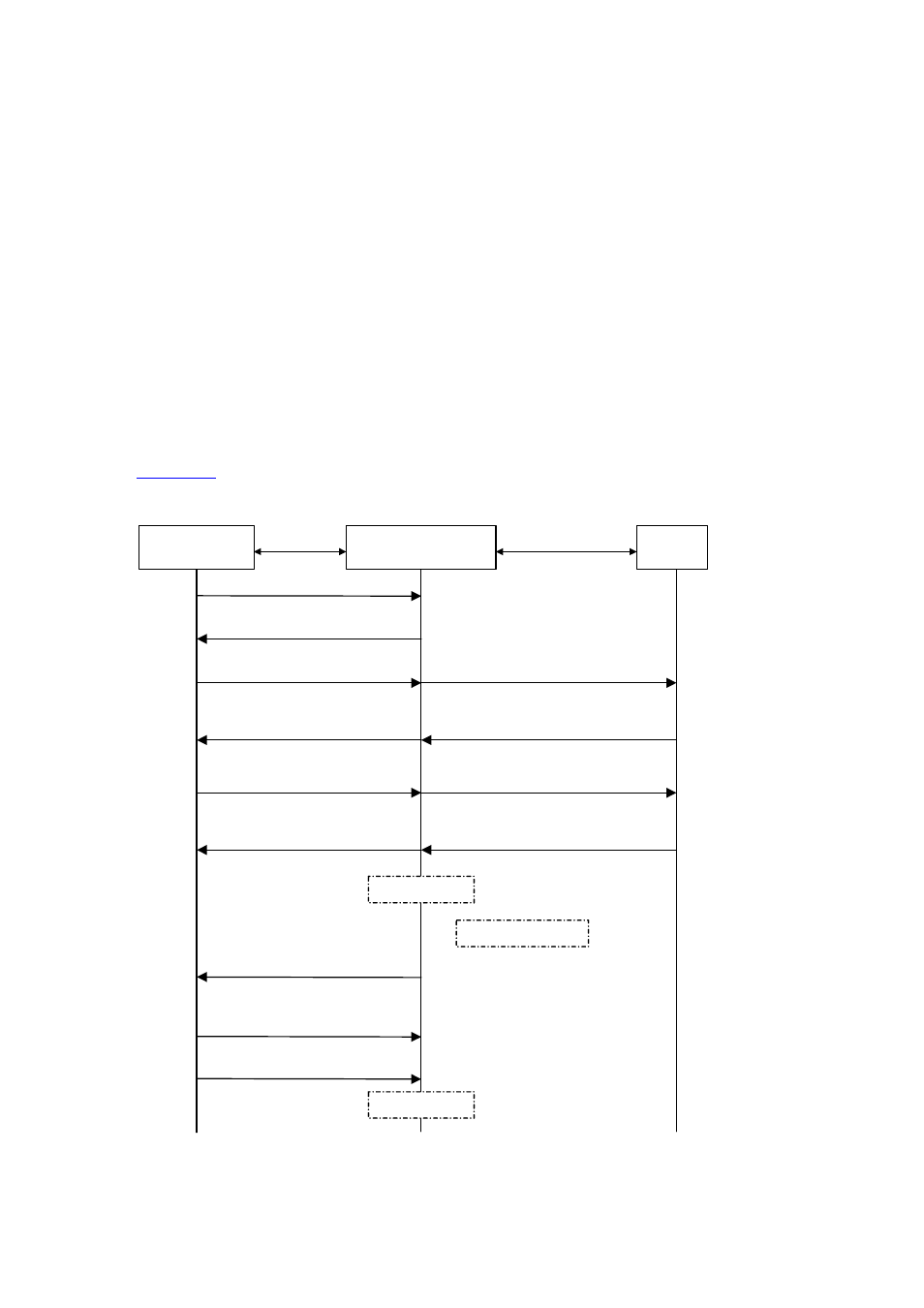
describes the basic EAP-MD5 authentication procedure.
Figure 23-8
802.1x authentication procedure (in EAP relay mode)
Supplicant System
PAE
RADUIS
server
EAPOL
EAPOR
EAPOL-Start
EAP-Request / Identity
EAP-Response / Identity
EAP-Request / MD5 challenge
EAP-Success
EAP-Response / MD5 challenge
RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response / Identity)
RADIUS Access-Challenge
(EAP-Request / MD5 challenge)
RADIUS Access-Accept
(EAP-Success)
RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response / MD5 challenge)
Port authorized
Handshake timer
Handshake request
[ EAP-Request / Identity ]
Handshake response
[ EAP-Response / Identity ]
EAPOL-Logoff
......
Port unauthorized
Authenticator System
PAE
The detailed procedure is as follows: