Special case ip addresses, Subnetting and masking, 2 subnetting and masking – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches User Manual
Page 293
30-2
Table 30-1
IP address classes and ranges
Class
Address range
Remarks
A
0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
Address 0.0.0.0 means this host no this network. This
address is used by a host at bootstrap when it does not
know its IP address. This address is never a valid
destination address.
Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback
test. Packets destined to these addresses are processed
locally as input packets rather than sent to the link.
B
128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
––
C
192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
––
D
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Multicast address.
E
240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Reserved for future use except for the broadcast address
255.255.255.255.
Special Case IP Addresses
The following IP addresses are for special use, and they cannot be used as host IP addresses:
z
IP address with an all-zeros net ID: Identifies a host on the local network. For example, IP address
0.0.0.16 indicates the host with a host ID of 16 on the local network.
z
IP address with an all-zeros host ID: Identifies a network.
z
IP address with an all-ones host ID: Identifies a directed broadcast address. For example, a packet
with the destination address of 192.168.1.255 will be broadcasted to all the hosts on the network
192.168.1.0.
Subnetting and Masking
Subnetting was developed to address the risk of IP address exhaustion resulting from fast expansion of
the Internet. The idea is to break a network down into smaller networks called subnets by using some
bits of the host ID to create a subnet ID. To identify the boundary between the host ID and the
combination of net ID and subnet ID, masking is used.
Each subnet mask comprises 32 bits related to the corresponding bits in an IP address. In a subnet
mask, the part containing consecutive ones identifies the combination of net ID and subnet ID whereas
the part containing consecutive zeros identifies the host ID.
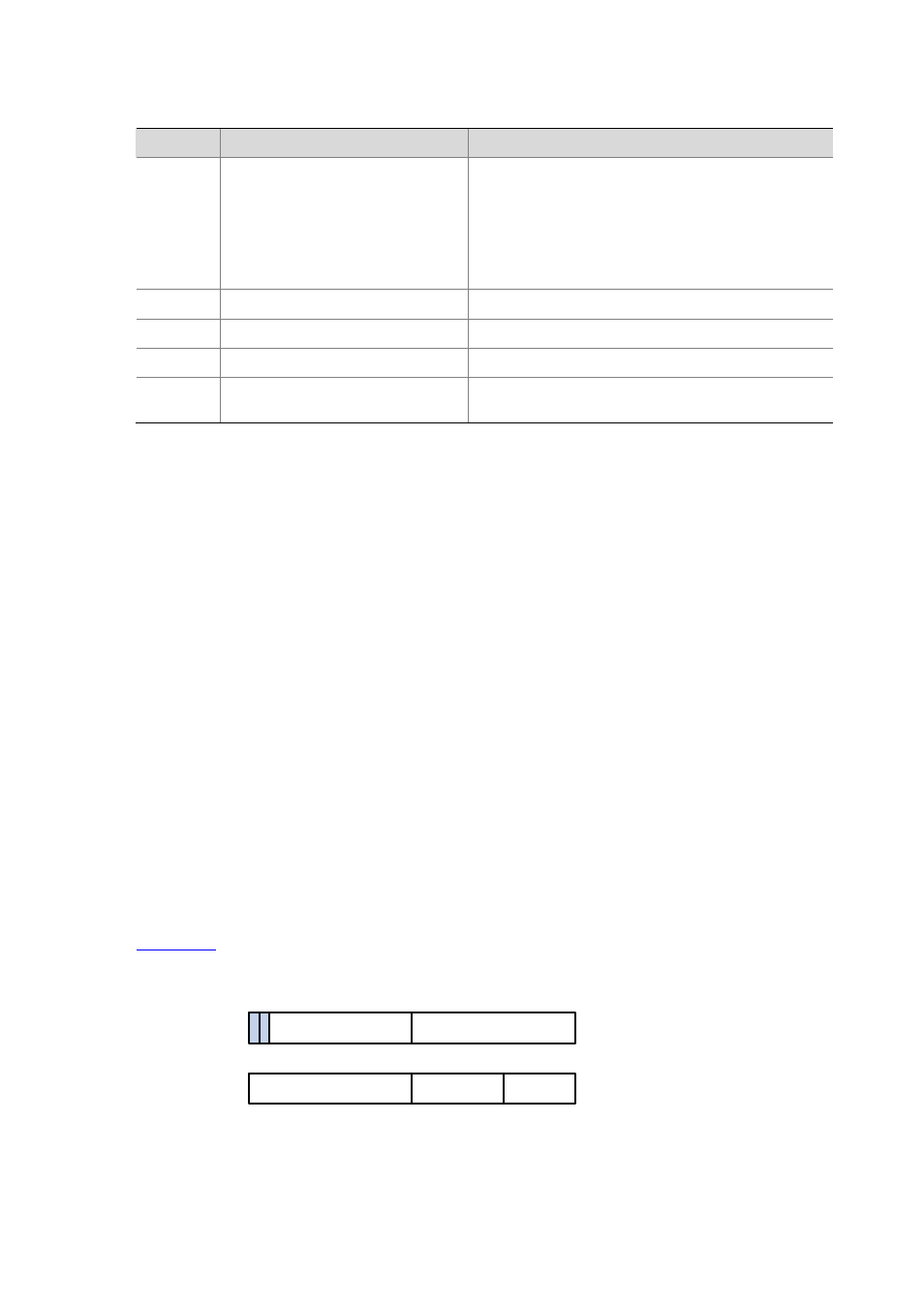
shows how a Class B network is subnetted.
Figure 30-2
Subnet a Class B network
1
Net-id
Host-id
0
Class B address
0
7
15
23
31
Mask
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Net-id
Host-id
Subnetting
Mask
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Subnet-id