Port modes – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 14
3
shows the structure of an FC address. The FC address is 24 bits long and contains the following
8-bit fields:
•
Domain_ID—A domain represents a switch and all N_Ports connected to the switch. For more
information about N_Ports, see "
." A domain ID, which is in the range of 1 to 239,
uniquely identifies an FC switch. Different FC switches in the same fabric have different domain IDs.
•
Area_ID—One or more N_Ports on the same node can be assigned to an area, which is identified
by an area ID.
•
Port_ID—The Port_ID field identifies an N_Port.
Figure 2 Structure of an FC address
An FC address can uniquely identify an N_Port on a node. Different N_Ports on the same node have
different FC addresses. FC switches use domain IDs to route messages between each other.
The FC protocol standardizes the FC address usage. For more information, see "
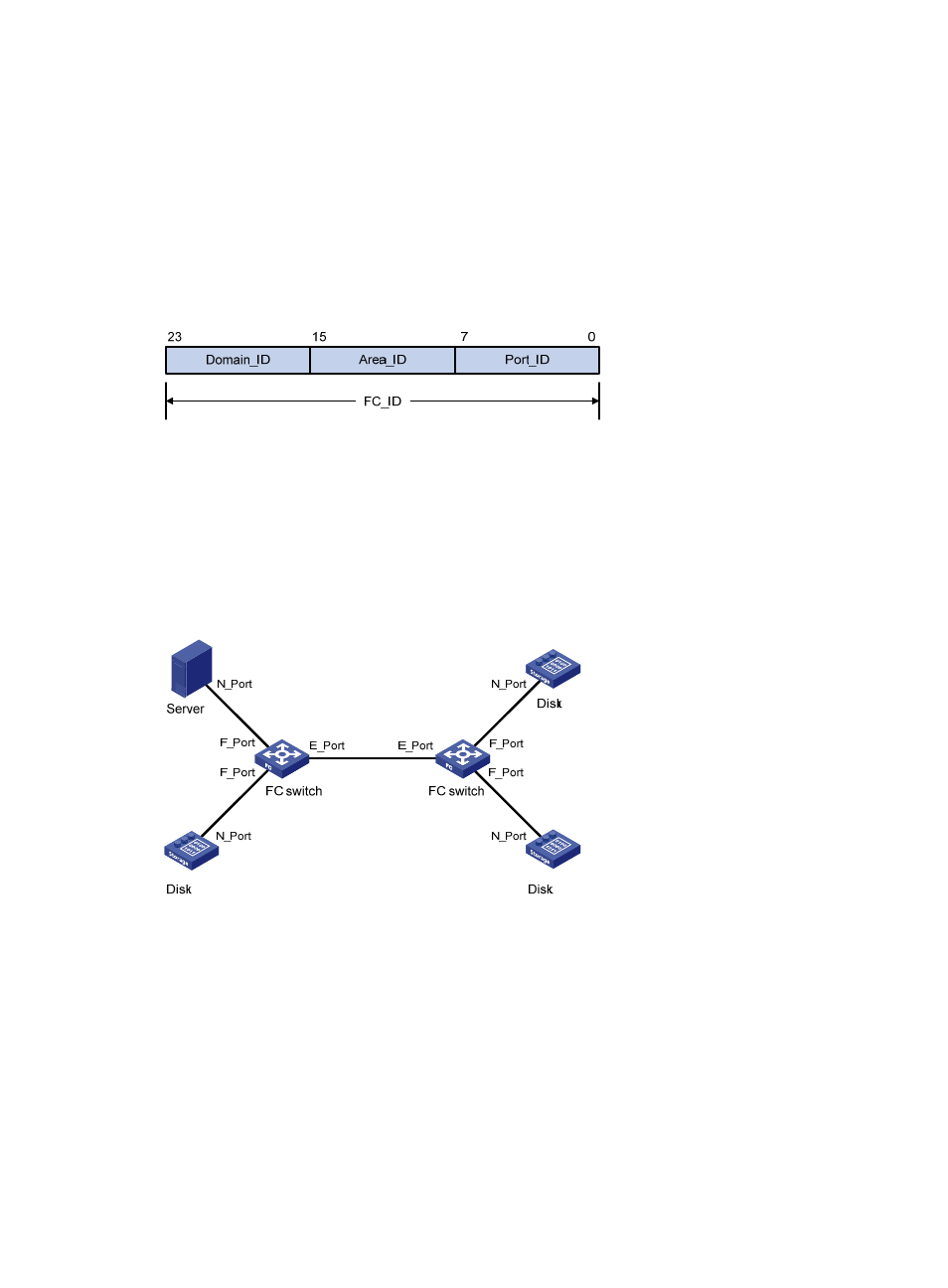
Port modes
In a switched fabric, nodes and FC switches communicate through interfaces operating in different
modes.
Figure 3 Port modes
A node supports the following port modes:
•
N_Port—Directly connects to a fabric.
•
NL_Port—Connects to a fabric through an arbitrated loop.
An FC switch provides the following port modes:
•
E_Port—Connects to an E_Port on another FC switch.
•
F_Port—Connects to an N_Port on a node or an NP_Port on another FC switch.
•
NP_Port—Connects to an F_Port on another FC switch. For more information about NP_Ports, see
"
E_Ports connect FC switches to form a fabric, and F_Ports connect the nodes to FC switches in the fabric.