Network address translation (nat), Nat details screen, Network address translation (nat) -70 – Verilink WANsuite 7205 (34-00317.B) Product Manual User Manual
Page 100: Nat details screen -70
3-70
W A N s u i t e 7 2 0 5
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT is a method of connecting multiple computers to the Internet (or any
other IP network) using one IP address. This lets users cost-effectively and
efficiently connect their networks to the Internet.
Whether on a global or local port, NAT provides translation only upon receipt
of a packet, which NAT will translate, not translate, or filter, depending on
the user-specified parameters (further described below). If the decision is
made to “translate,” the packet will be modified internally, and eventually
sent on to the IP Gateway to be processed. If the decision is made not to
“translate,” the packet will not be modified in any way. If the decision is
made to “filter,” the packet will be discarded without any further action
required.
NOTICE:
You must Save and Restart for any changes in NAT configuration
parameters to take effect.
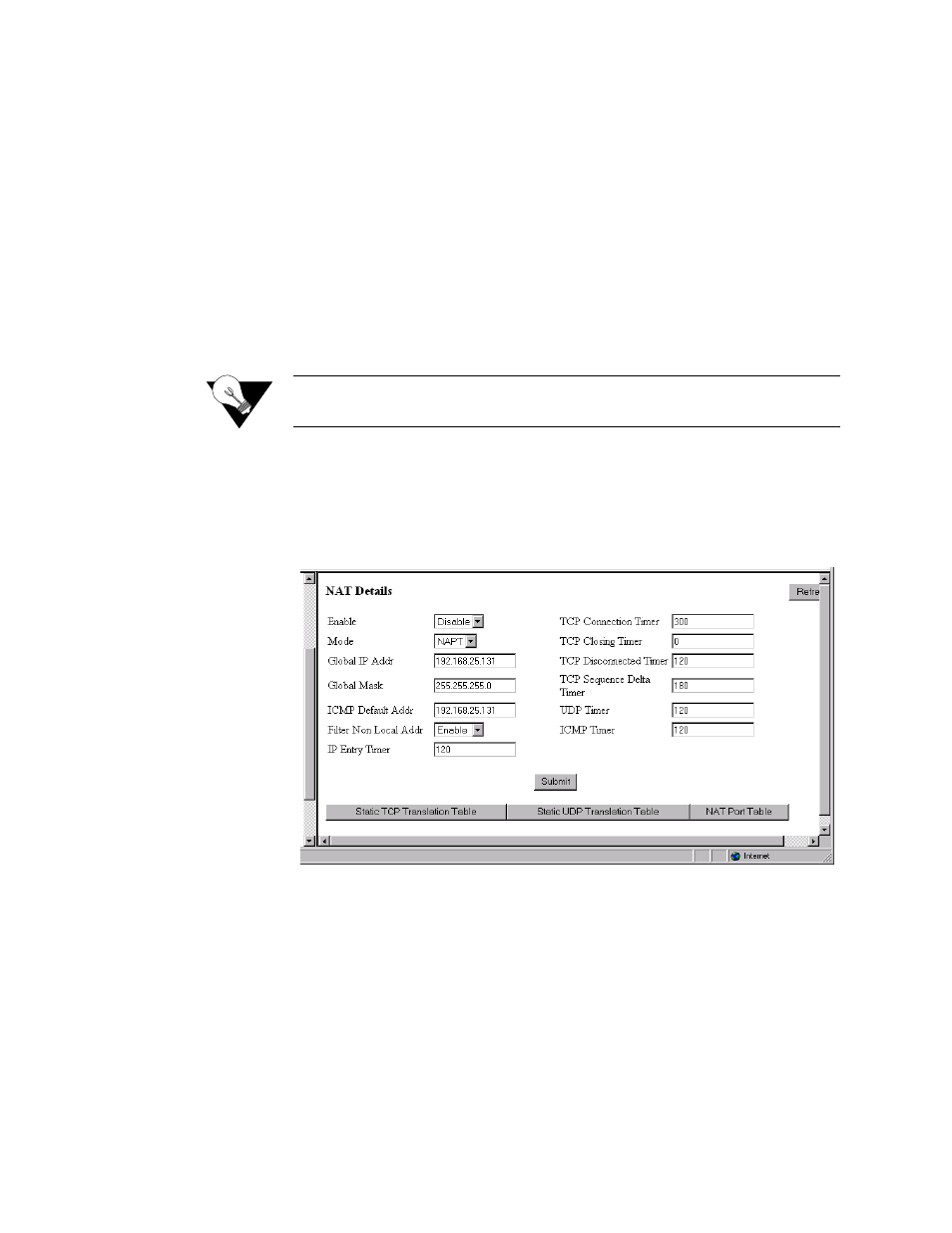
NAT Details Screen
The NAT Details screen (Figure 3.60) lets the user configure the NAT global
parameters described below.
Figure 3.60
NAT Details Screen
Enable
Enables or disables NAT. Default is “Disable.”
Mode
Selects the Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) mode or the Basic
NAT mode. In NAPT mode, all hosts on the Global (public) side view all
hosts on the Local (private) side as a single internet host (one IP address). In
Basic NAT mode, the Global IP address is assigned as a Class C host address
(Mask of 255.255.255.0). Each private IP address on the Local side is mapped
to a Class C public address on the Global side. In other words, if there are 30
hosts on the private (Local) side, 30 public (Global) addresses are required.
The default is NAPT.