Displaying static lsps, Static lsp configuration example, Network requirements – H3C Technologies H3C S6800 Series Switches User Manual
Page 26
13
Step Command
Remarks
2.
Configure the
ingress node of the
static LSP.
static-lsp ingress lsp-name destination
dest-addr { mask | mask-length } { nexthop
next-hop-addr | outgoing-interface
interface-type interface-number } out-label
out-label
If you specify a next hop for the
static LSP, make sure the ingress
node has an active route to the
specified next hop address.
3.
Configure the
transit node of the
static LSP.
static-lsp transit lsp-name in-label in-label
{ nexthop next-hop-addr |
outgoing-interface interface-type
interface-number } out-label out-label
If you specify a next hop for the
static LSP, make sure the transit
node has an active route to the
specified next hop address.
4.
Configure the
egress node of the
static LSP.
static-lsp egress lsp-name in-label in-label
You do not need to configure this
command if the outgoing label
configured on the penultimate hop
of the static LSP is 0 or 3.
Displaying static LSPs
Execute display commands in any view.
Task Command
Display static LSP information.
display mpls static-lsp [ lsp-name lsp-name ]
Static LSP configuration example
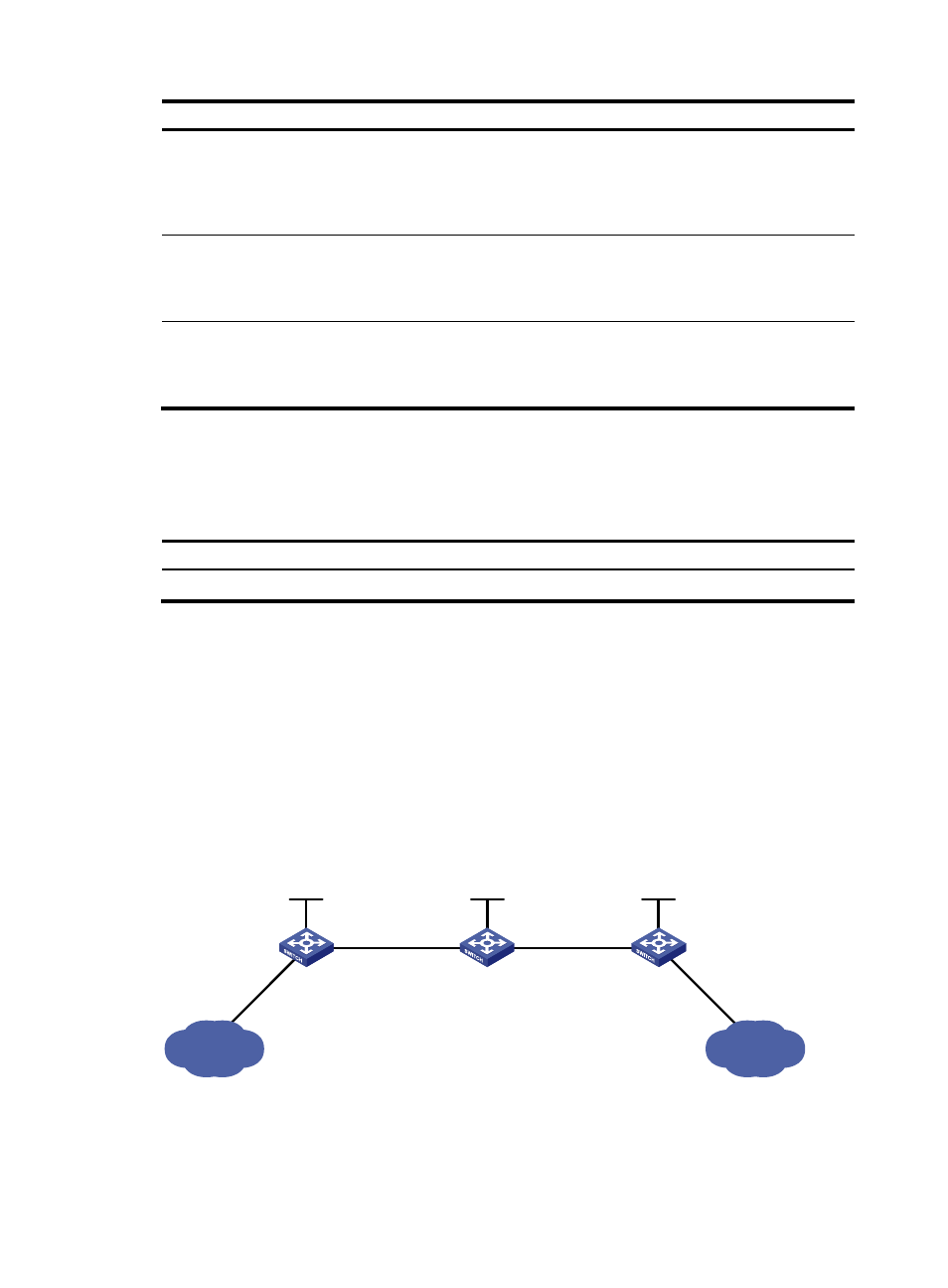
Network requirements
Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C all support MPLS.
Establish static LSPs between Switch A and Switch C, so that subnets 11.1.1.0/24 and 21.1.1.0/24 can
access each other over MPLS.
Figure 8 Network diagram
Loop0
2.2.2.9/32
Vlan-int3
20.1.1.1/24
Loop0
3.3.3.9/32
Loop0
1.1.1.9/32
Vlan-int2
10.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int2
10.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int3
20.1.1.2/24
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
11.1.1.0/24
21.1.1.0/24
Vlan-int4
11.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int5
21.1.1.1/24