ATL Telecom AM30 User Manual
Page 75
ATL Telecom User Guide
AM30
7
5
public IP addresses that the private addresses should be
translated to. Or, type the same address in both fields (if you
also specified a single address in step 4).
6.
Follow steps 8-12 under "The NAPT rule" on page 68 to
submit your changes.
The Filter rule: Configuring a BASIC rule with additional criteria
Like the BASIC flavor, the Filter flavor translates public and private IP addresses on a one-to-
one basis. The Filter flavor extends the capability of the BASIC rule. Refer to “The BASIC
Rule” on page 74 for a general description.
You can use the Filter rule if you want an address translation to occur only when your LAN
computers initiate access to specific destinations. The destinations can be identified by their
IP addresses, port type (which identifies it as a FTP or Web server, for example), or both.
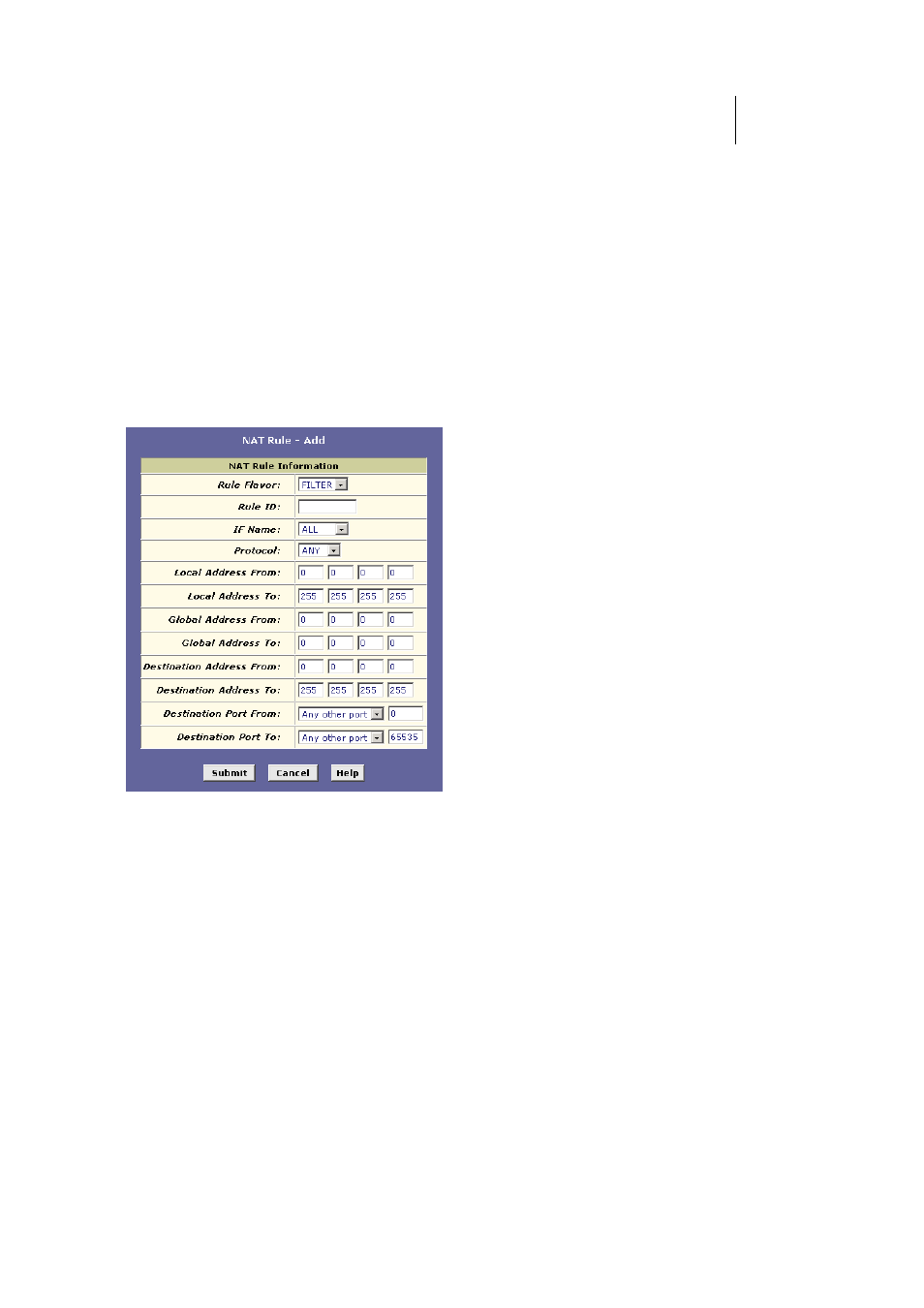
Figure 37 shows the fields used to establish a Filter rule.
Figure 37. NAT Rule
Add Page (Filter Flavor)
Follow these instructions to add a Filter rule (see steps 1-4 under "The NAPT rule" on page
68 for specific instructions corresponding to steps 1 and 2 below):
1.
Display the NAT Rule – Add Page, select FILTER as the
Rule Flavor, and enter a Rule ID.
2.
Select the interface on which this rule will be effective.
3.
Select a protocol to which this rule applies, or choose ANY.
This selection specifies which type of Internet
communication will be subject to this translation rule.
You can select ANY if the rule applies to all data. Or,
select TCP, UDP, ICMP, or a number from 1-255 that
represents the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA)-specified protocol number.
4.
In the Local Address From and Local Address To fields, type
the starting and ending IP addresses that identify the range