Ip gateway, Ip gateway -48 – Verilink T1 Access Router (34-00327) Product Manual User Manual
Page 76
3-48
T 1 A c c e s s R o u t e r
address listed, the report displays the number of Rx frames, Rx octets, Tx
frames, and Tx octets that have been passed across it. In addition, the
Timestamp field indicates the time at which a packet was examined for the
specified IP address.
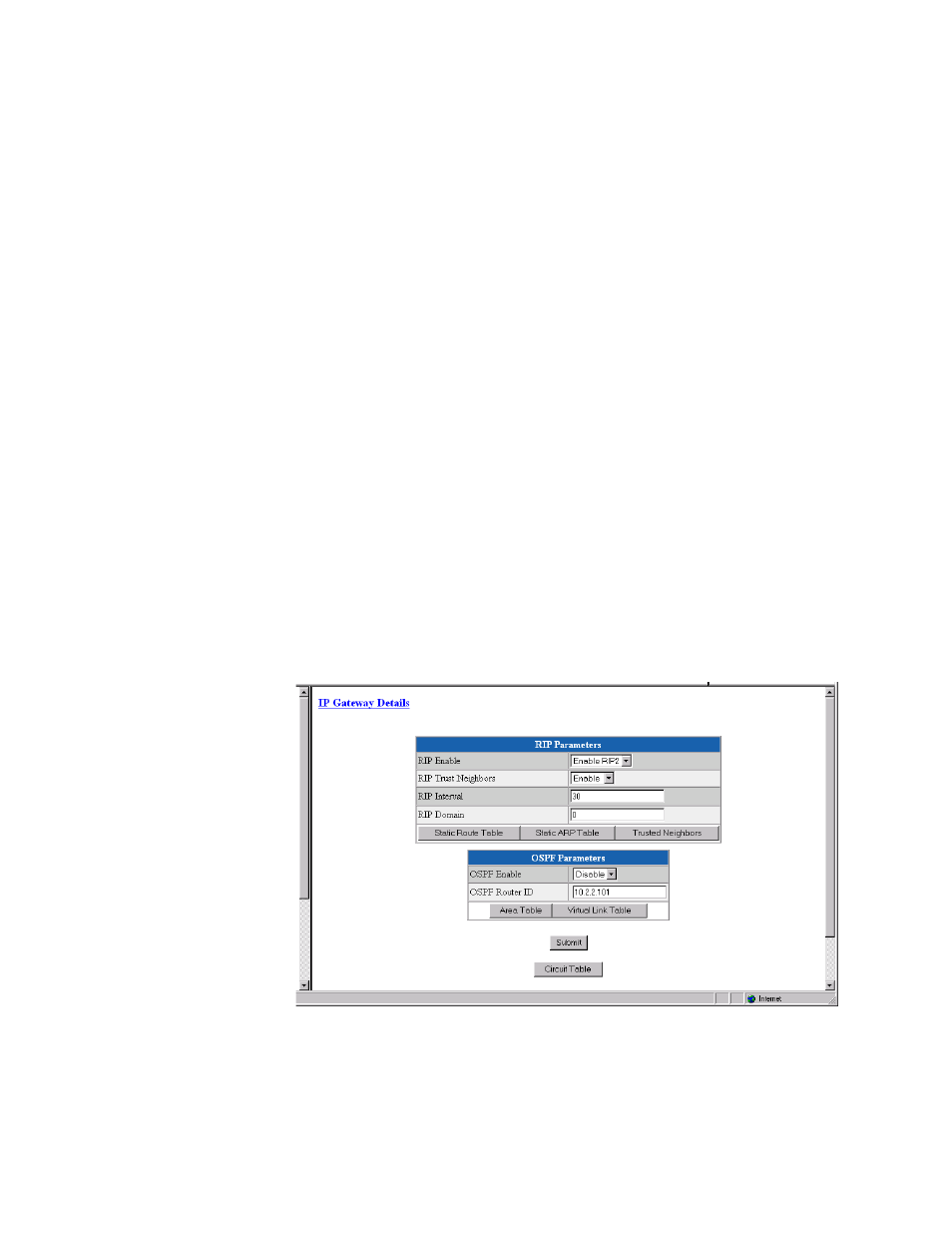
IP Gateway
The IP Gateway is a feature of the T1 Access Router that allows routing of IP
packets from one network to another using static routes configuration and/or
dynamic routing. The IP Gateway uses Routing Information Protocol (RIP) 1
or RIP 2 or Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing.
RIP 1 and RIP 2 are protocols that allow exchange of routing information
between two routers. With that information exchange, a router can build its
own routing tables that later can be used for “routing” IP packets.
OSPF is a shortest path first (SPF) or link-state protocol. OSPF is also an
internal gateway protocol (IGP) that distributes routing information between
routers in a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF chooses the least cost path
as the best path.
While RIP is ideal for small- to medium-sized networks, OSPF is more
suitable for complex networks with a large number of routers. OSPF provides
equal cost multipath routing where packets to a single destination can be sent
via more than one interface simultaneously.
The IP Gateway also supports unnumbered networks. An unnumbered
network is a point-to-point connection without an assigned IP address This
feature reduces the number of IP addresses required.
Figure 3.38
IP Gateway Details Screen