H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 96
84
Dual Stack Lite (DS-Lite) combines the IPv4 over IPv6 tunneling and network address translation
(NAT) to connect IPv4 networks over IPv6 networks without sacrificing the benefits of NAT.
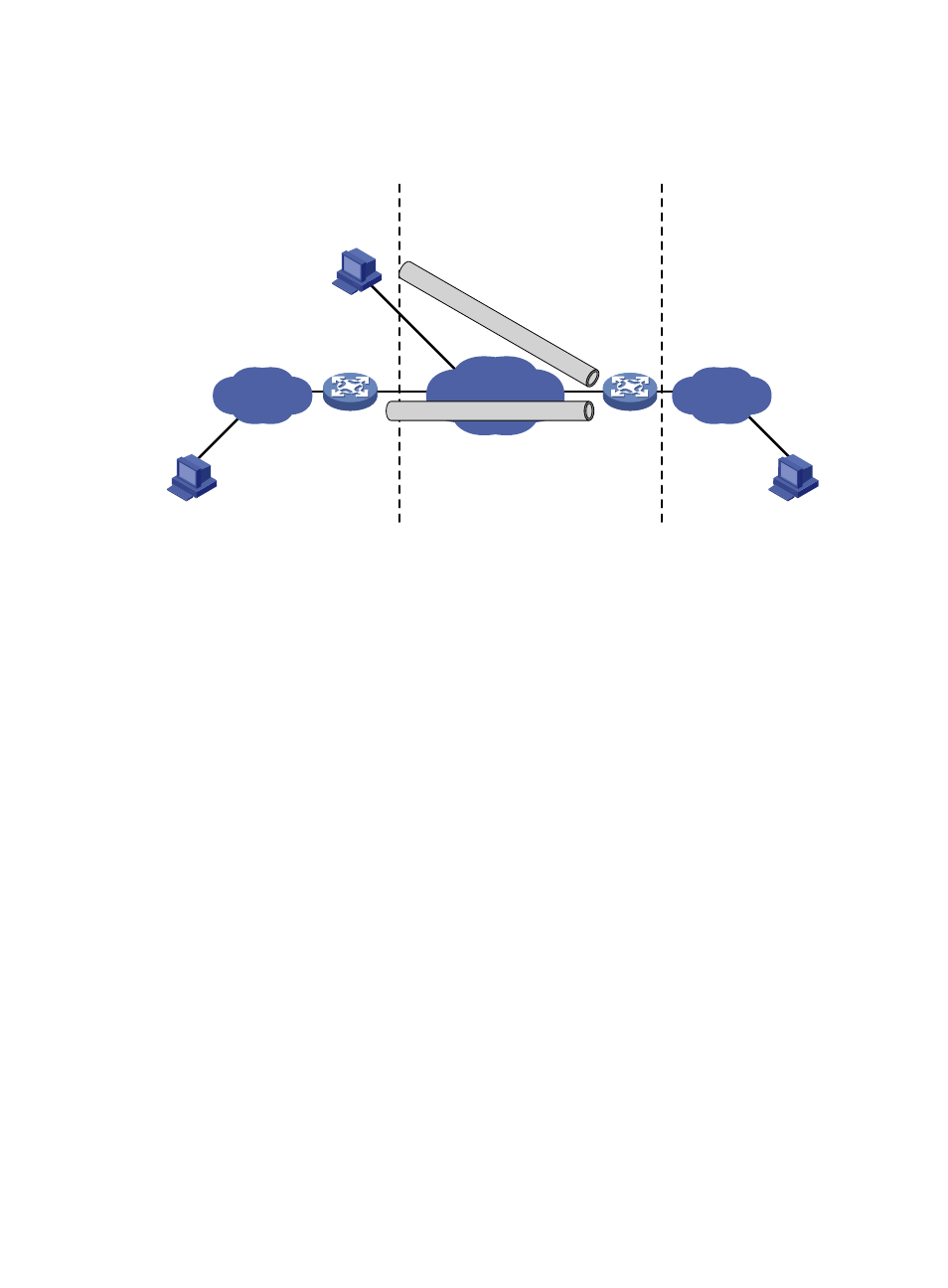
Figure 69 Network diagram
As shown in
, a DS-Lite network involves the following parts:
•
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)—Resides at the customer's premise, connects the customer's
network to an Internet Service Provider (ISP) network, and usually serves as the gateway of the
customer's network. As a tunnel end, the CPE encapsulates IPv4 packets of the customer's network
into IPv6 packets and sends them to the other end of the tunnel, and de-encapsulates IPv6 packets
into IPv4 packets and sends them to the customer's network. Some hosts can serve as the CPE. Such
hosts are referred to as DS-Lite hosts.
•
Address Family Transition Router (AFTR)—Resides in the ISP network and serves as both an IPv4
over IPv6 tunnel end and the NAT device. After IPv6 packets are de-encapsulated into IPv4 packets,
the AFTR translates the source private IPv4 address of each packet into a public IPv4 address and
sends the packet to the destination IPv4 host. The AFTR also translates the destination public IPv4
address of each response packet into a private IPv4 address, encapsulates the packet into an IPv6
packet, and forwards the packet to the CPE. In addition, the AFTR records the NAT entries and the
IPv6 address of each CPE so that IPv4 networks connected to different CPEs can use the same
address space.
•
DS-Lite tunnel—The IPv4 over IPv6 tunnel between the CPE and AFTR which carries IPv4 packets
over an IPv6 network.
Private
IPv4 network
DS-lite tunnel
IPv4 network
IPv4 host
IPv4 host
CPE
AFTR
IPv6 network
DS
-lite
tun
nel
DS-lite host
Subscriber network
ISP core network
Internet
- H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS