Altera Arria 10 Avalon-ST User Manual
Page 210
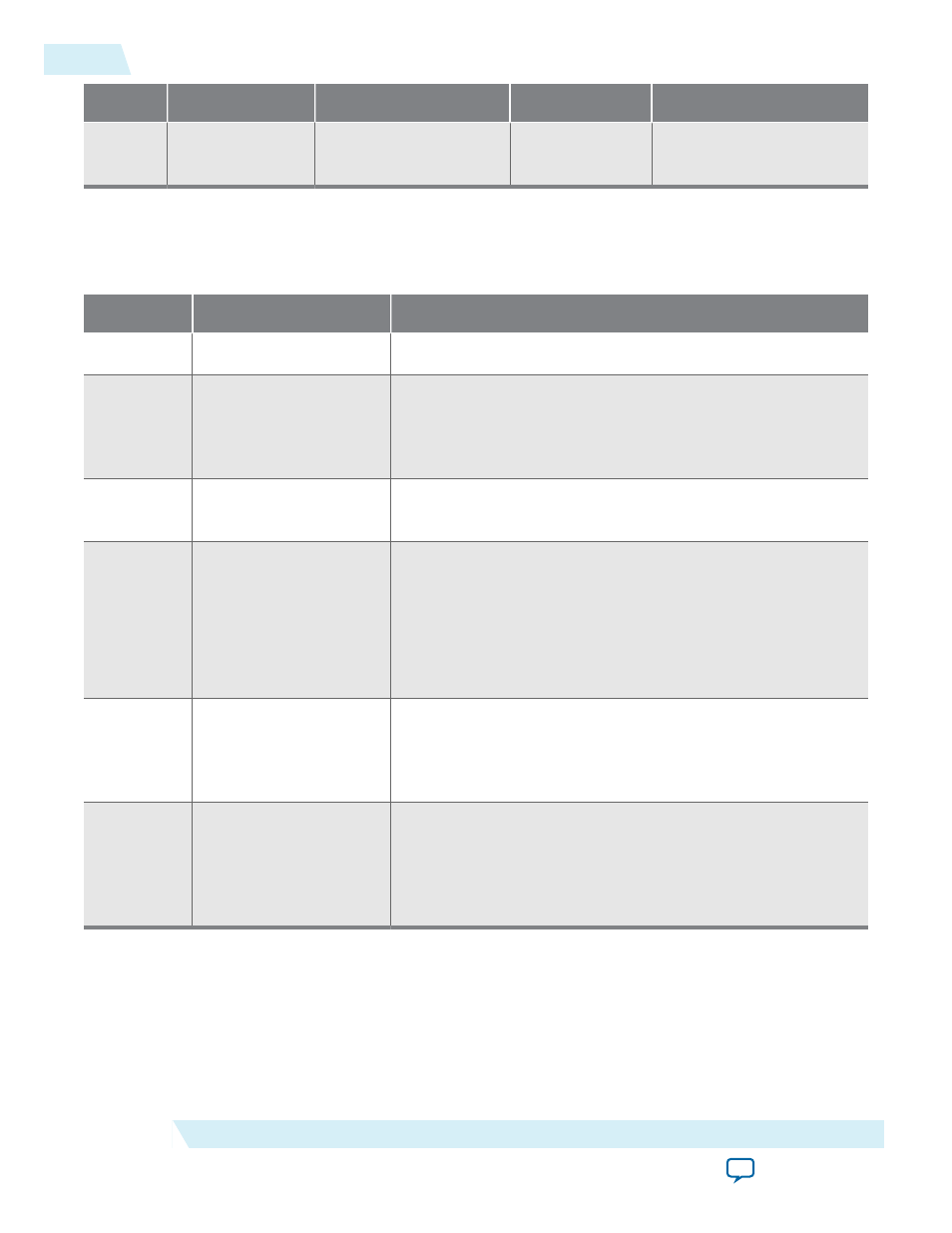
Addr
Register Name
Bits[31:]24
Bit[23:16]
Bit[15:0]
0x1C
DMA Rd Cntl DW3
Reserved
Reserved
RCLAST–Idx of the last
descriptor to process
The following table describes the control fields of the of the DMA read and DMA write control registers.
Table 17-3: Bit Definitions for the Control Field in the DMA Write Control Register and DMA Read Control
Register
Bit
Field
Description
16
Reserved
—
17
MSI_ENA
Enables interrupts of all descriptors. When 1, the Endpoint
DMA module issues an interrupt using MSI to the RC when
each descriptor is completed. Your software application or BFM
driver can use this interrupt to monitor the DMA transfer status.
18
EPLAST_ENA
Enables the Endpoint DMA module to write the number of each
descriptor back to the EPLAST field in the descriptor table.
[24:20]
MSI Number
When your RC reads the MSI capabilities of the Endpoint, these
register bits map to the back-end MSI signals
app_msi_num
[4:0]. If there is more than one MSI, the default mapping if all
the MSIs are available, is:
• MSI 0 = Read
• MSI 1 = Write
[30:28]
MSI Traffic Class
When the RC application software reads the MSI capabilities of
the Endpoint, this value is assigned by default to MSI traffic class
0. These register bits map to the back-end signal
app_msi_
tc
[2:0].
31
DT RC Last Sync
When 0, the DMA engine stops transfers when the last
descriptor has been executed. When 1, the DMA engine loops
infinitely restarting with the first descriptor when the last
descriptor is completed. To stop the infinite loop, set this bit to
0.
The following table defines the DMA status registers. These registers are read only. In this table, Addr
specifies the Endpoint byte address offset from BAR2 or BAR3.
17-10
Chaining DMA Control and Status Registers
UG-01145_avst
2015.05.04
Altera Corporation
Testbench and Design Example