Ptp domain, Clock node and ptp port – H3C Technologies H3C S6300 Series Switches User Manual
Page 66
53
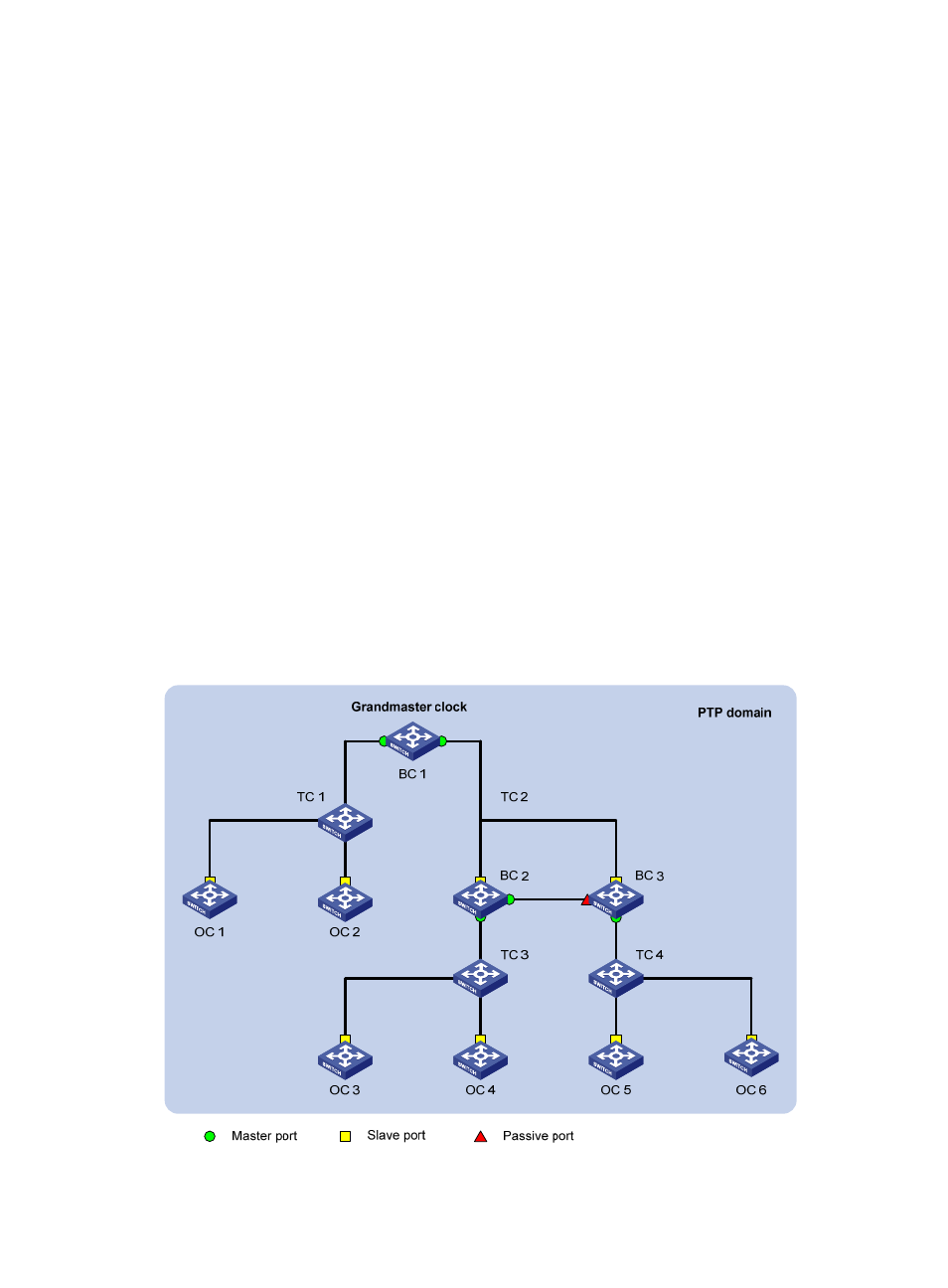
PTP domain
A PTP domain refers to a network enabled with PTP. A PTP domain has only one synchronization clock.
All devices in the domain synchronize time with the clock.
Clock node and PTP port
A node in a PTP domain is a clock node. A port enabled with PTP is a PTP port. PTP defines the following
three types of basic clock nodes:
•
Ordinary Clock (OC)—A PTP clock with a single PTP port in a PTP domain for time synchronization.
It synchronizes time from its upstream clock node through the port. If a clock node serves as the
clock source and sends synchronization time through a single PTP port to its downstream clock node,
it is also called an "OC."
•
Boundary Clock (BC)—A clock with more than one PTP port in a PTP domain for time
synchronization. A BC uses one of the ports to synchronize time from its upstream clock node, and
uses the other ports to synchronize time to the relevant upstream clock nodes. If a clock node serves
as the clock source and synchronizes time through multiple PTP ports to its downstream clock nodes,
it is also called a "BC," such as BC 1 in
•
Transparent Clock (TC)—A TC does not need to keep time consistency with other clock nodes. A TC
has multiple PTP ports. It only forwards PTP messages among these ports and performs delay
corrections of the messages, instead of performing time synchronization. TCs fall into the following
two types: End-to-End Transparent Clock (E2ETC), which forwards non-P2P packets in the network
and calculates the delay of the entire link; Peer-to-Peer Transparent Clock (P2PTC), which forwards
only Sync, Follow_Up, and Announce messages, terminates other PTP messages, and calculates the
delay of each link segment.
shows the positions of these three types of clock nodes in a PTP domain.
Figure 19 Clock nodes in a PTP domain