1 ethercat slave controller overview, Ethercat slave controller overview, Table 1: esc main features – BECKHOFF EtherCAT Technology Section I User Manual
Page 21: Figure 1: ethercat slave controller block diagram
EtherCAT Slave Controller Overview
Slave Controller
– Technology
I-1
1
EtherCAT Slave Controller Overview
An EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC) takes care of the EtherCAT communication as an interface
between the EtherCAT fieldbus and the slave application. This document covers the following
Beckhoff ESCs: ASIC implementations (ET1100, ET1200), functionally fixed binary configurations for
FPGAs (ESC20), and configurable IP Cores for FPGAs (ET1810/ET1815).
Table 1: ESC Main Features
Feature
ET1200
ET1100
IP Core
ESC20
Ports
2-3 (each
EBUS/MII,
max. 1xMII)
2-4 (each
EBUS/MII)
1-3 MII/
1-3 RGMII/
1-2 RMII
2 MII
FMMUs
3
8
0-8
4
SyncManagers
4
8
0-8
4
RAM [Kbyte]
1
8
0-60
4
Distributed Clocks
64 bit
64 bit
32/64 bit
32 bit
Process Data Interfaces
Digital I/O
16 bit
32 bit
8-32 bit
32 bit
SPI Slave
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
8/16 bit µController
-
Async/Sync
Async
Async
On-chip bus
-
-
Yes
-
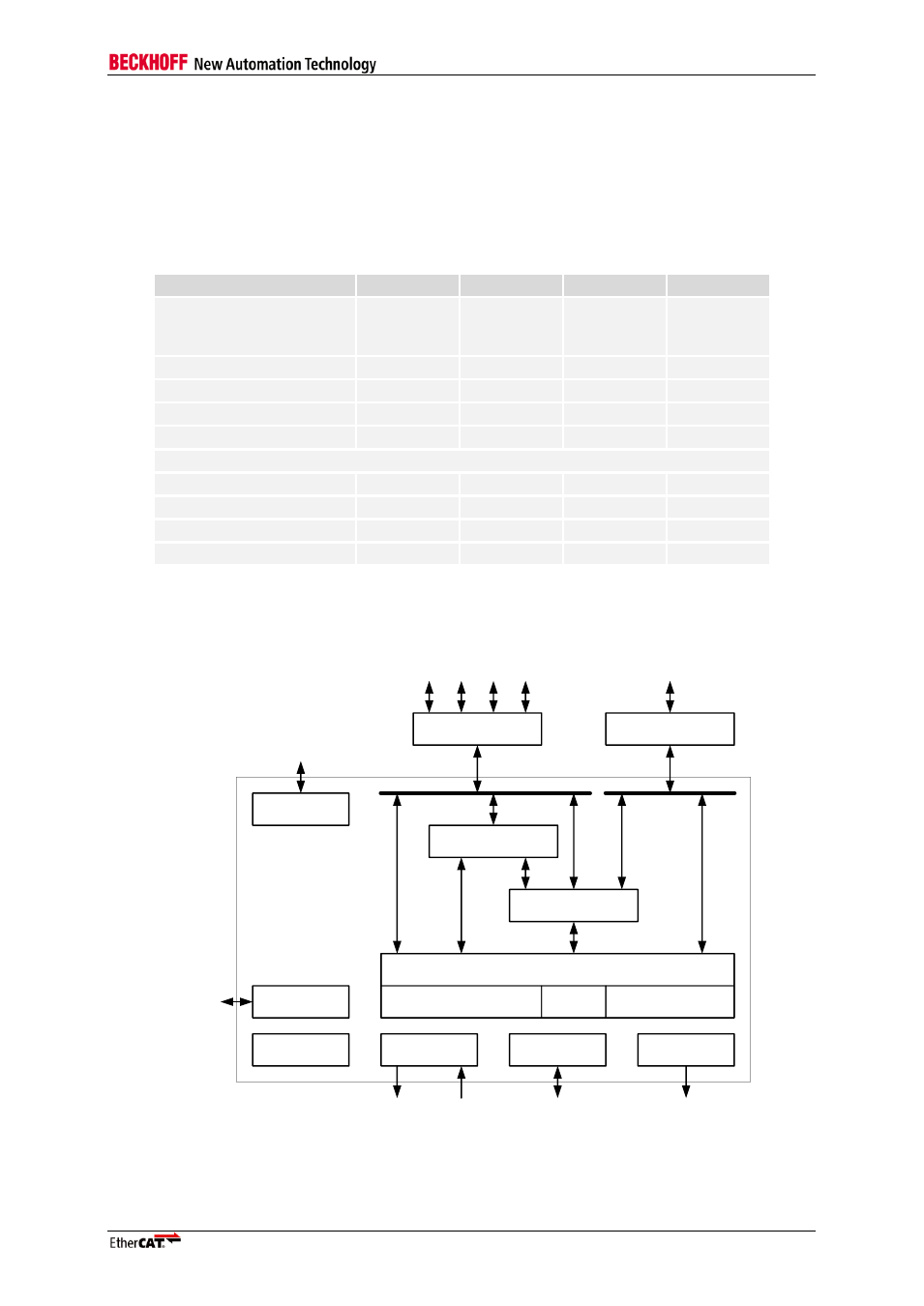
The general functionality of an ESC is shown in Figure 1:
ECAT
Processing
Unit
AutoForwarder +
Loopback
SyncManager
FMMU
ESC address space
User RAM
Registers
Process RAM
EEPROM
Distributed
Clocks
Monitoring
Status
Reset
PHY
Management
Reset
SYNC
LEDs
I²C EEPROM
PHY MI
SPI / µC parallel /
Digital I/O / On-chip bus
0
1
2
3
Ports (Ethernet/EBUS)
LATCH
PDI
ECAT Interface
PDI Interface
Figure 1: EtherCAT Slave Controller Block Diagram