1 unconnected port 0, 6 non-ethercat protocols, 7 special functions of port 0 – BECKHOFF EtherCAT Technology Section I User Manual
Page 36: Unconnected port 0, Non-ethercat protocols, Special functions of port 0
Frame Processing
I-16
Slave Controller
– Technology
3.5.1
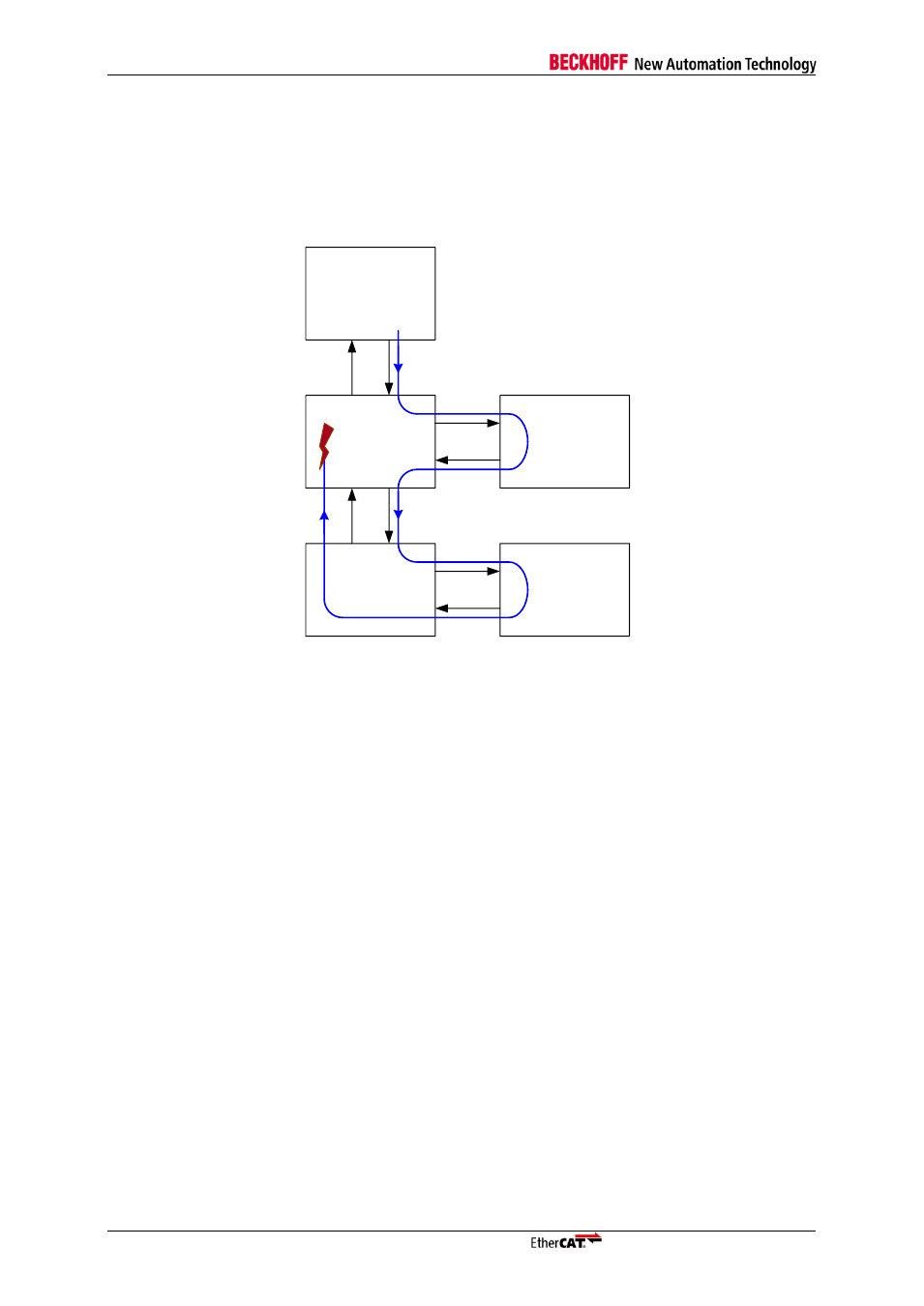
Unconnected Port 0
Port 0 must not be left intentionally unconnected (slave hardware or topology) because of the
circulating frame prevention. All frames will be dropped after they have passed an automatically
closed Port 0 for the second time, and this can prohibit any EtherCAT communication.
Example: Port 0 of slave 1 and 3 are automatically closed because nothing is connected. The
Circulating bit of each frame is set at slave 3. Slave 1 detects this and destroys the frames.
EtherCAT
master
EtherCAT
slave 1
P
o
rt
0
P
o
rt
1
EtherCAT
slave 2
P
o
rt
0
P
o
rt
0
EtherCAT
slave 3
P
o
rt
0
P
o
rt
1
EtherCAT
slave 4
P
o
rt
0
P
o
rt
0
Port 3
Port 2
Port 3
Figure 7: All frames are dropped because of Circulating Frame Prevention
In redundancy operation, only one Port 0 is automatically closed, so the communication remains
active.
3.6
Non-EtherCAT Protocols
If non-EtherCAT protocols are used, the forwarding rule in the ESC DL Control register (0x0100[0])
has to be set to forward non-EtherCAT protocols. Otherwise they are destroyed by the ESC.
3.7
Special Functions of Port 0
Port 0 of each EtherCAT is characterized by some special functions in contrast to ports 1, 2, and 3:
Port 0 leads to the master, i.e., port 0 is the upstream port, all other ports (1-3) are downstream
ports (unless an error has occurred and the network is in redundancy mode).
The link state of Port 0 influences the Circulating Frame bit, and frames are dropped at port 0 if
the bit is set and the link is automatically closed.
Port 0 loop state is open if all ports are closed (either automatically or manually).
Port 0 has a special behavior when using standard EBUS link detection.