Ethernet hub, Ethernet cabling – Yaskawa SmartTrac AC1 User Manual
Page 49
SMART TRAC AC1
Technical Manual TM 3554-000 Networking the Smart Trac AC1
••
5-3
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Cat-5 Twisted Pair
Ethernet Cable
Laptop computer
Hub
IBM Compatible
Laser printer
SMART
TRAC
AC 1
SMART
TRAC
AC 1
SMART
TRAC
AC 1
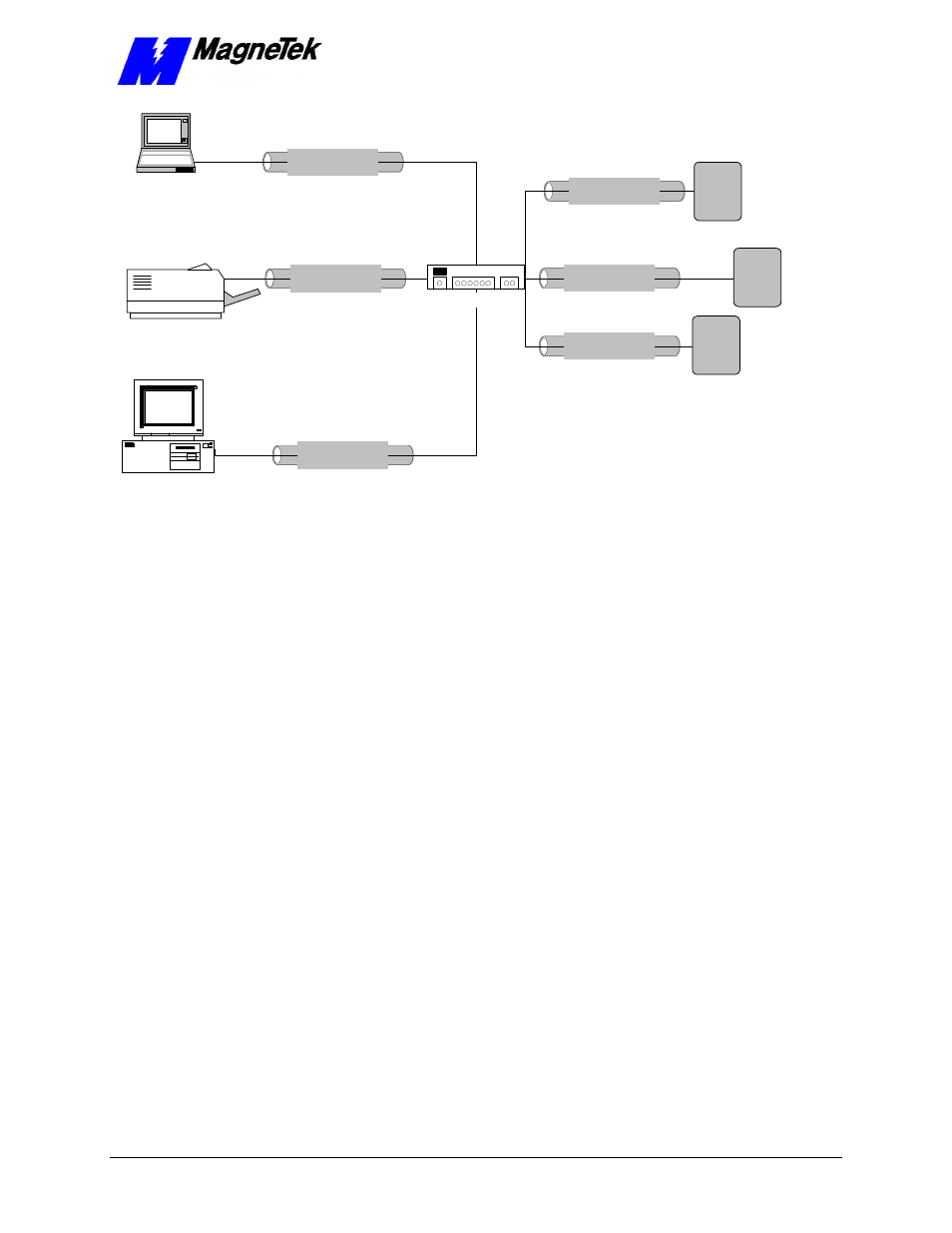
Figure 6.
A typical local area network used for PC-based operation of Smart
Trac AC1s.
Ethernet Hub
An ethernet hub is required if connecting more than two devices (more than one
Smart Trac AC1 and one computer). If only connecting a single Smart Trac with
a single computer, you need only a special "crossover" or "uplink" Ethernet
cable. (Contact your MagneTek representative for cable information).
Ethernet cabling
Two Ethernet cabling standards are commonly used with Smart Trac AC1
systems, each intended for different purposes:
•
10Base-T (Twisted-pair Ethernet) – The most widely used ethernet
cabling, it supports network speeds of 100Mbps. Uses 22- or 26-AWG
UTP cabling to transmit baseband signals on maximum 100-meter
segments. RJ-45 jacks connect separate cables between device and hub.
Each device must be at least 2 feet apart and no more than 328 feet
from the hub. Bridges or routers may be used to accommodate a larger
network. There is no limit on network length. It permits a maximum of
1,024 segments and 1,024 nodes. See IEEE standard 802.3i.
•
10Base-2 (Thin Ethernet) – Supports network speeds of 10Mbps. Uses
RG-58 coaxial cable with "T"-shaped connectors to transmit baseband
signals on 200-meter segments. Total network length can be 925
meters. One end of each linear bus cable must be terminated using a 50
ohm resistor. Transceivers reside on the NIC at each connection of the
trunk cable to a device, simplifying connections. The cable, thinner
than 10Base-5, is more flexible for easier handling. See IEEE standard
802.3a.