H-vpls implementation, Advantages of h-vpls access, H-vpls with lsp access – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 168
157
•
In VLAN mode, packets transmitted over the PW must carry a P-Tag. For a packet from a CE, if it
contains the service delimiter, the PE keeps the P-Tag unchanged or changes the P-Tag to the VLAN
tag expected by the peer PE or to a null tag (the tag value is 0), and then adds a PW label and a
tunnel label into the packet before sending the packet out. If the packet contains no service delimiter,
the PE adds the VLAN tag expected by the peer PE or a null tag, and then a PW label and a tunnel
label into the packet before sending the packet out. For a packet to be sent downstream, the PE
rewrites, removes, or retains the service delimiter depending on your configuration.
According to the protocol, the packet encapsulation type of a PW is VLAN by default.
H-VPLS implementation
Hierarchy of VPLS (H-VPLS) can extend the VPLS access range of a service provider and reduce costs.
Advantages of H-VPLS access
•
H-VPLS has lower requirements on the multi-tenant unit switch (MTU-s). It has distinct hierarchies
which fulfill definite tasks.
•
H-VPLS reduces the logical complexity of the fully meshed network consisting of PEs and the
configuration complexity.
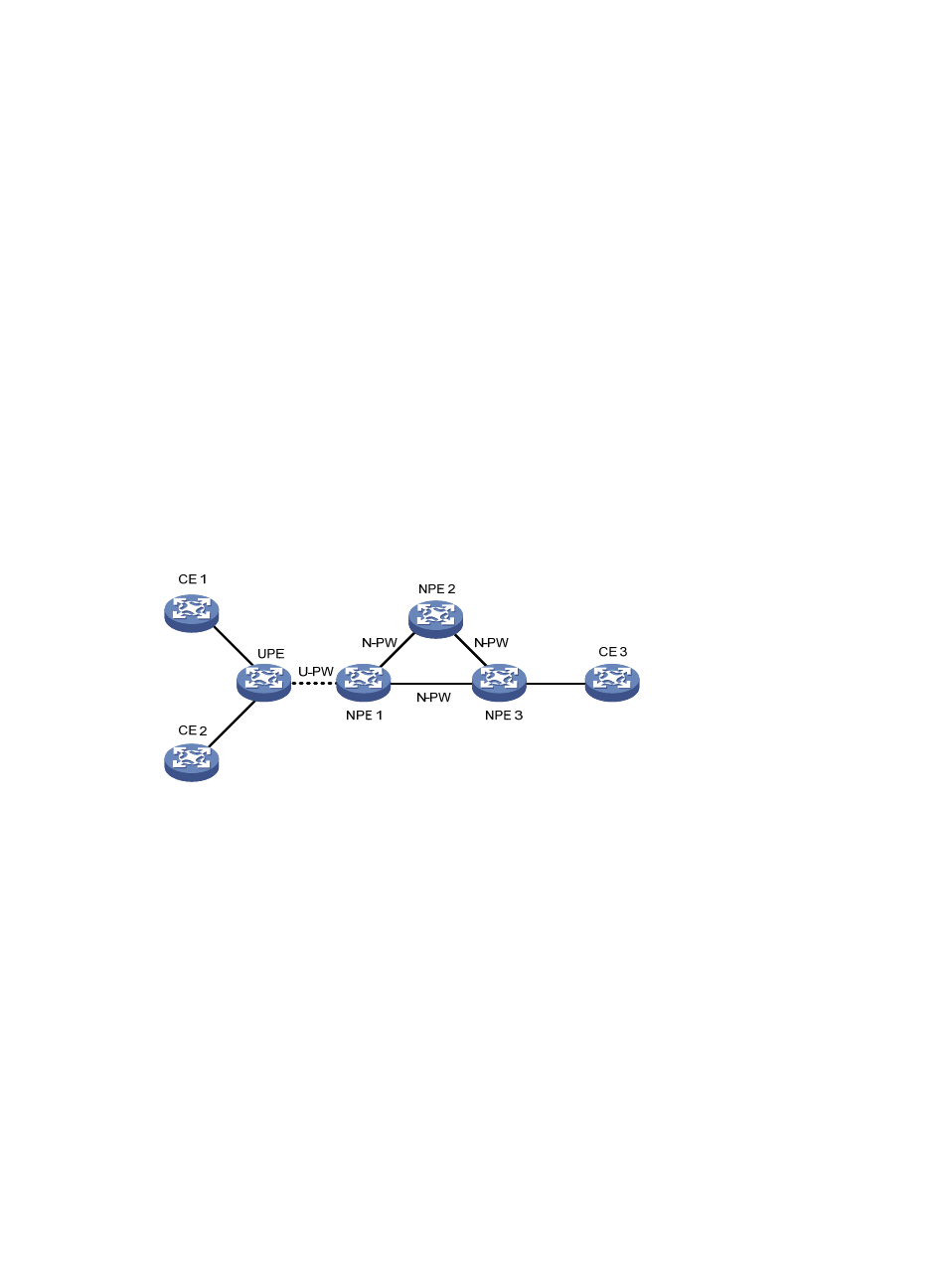
H-VPLS with LSP access
Figure 37 H-VPLS with LSP access
As shown in
, UPE functions as the convergence device MTU-s and establishes only a virtual link
U-PW with NPE 1. It does not establish virtual links with any other peers.
Data forwarding in H-VPLS with LSP access is as follows:
•
Upon receiving a packet from a CE, UPE tags the packet with the MPLS label for the U-PW, namely
the multiplex distinguishing flag, and then sends the packet to NPE 1.
•
When receiving the packet, NPE 1 determines which VSI the packet belongs to by the label and,
based on the destination MAC address of the packet, tags the packet with the multiplex
distinguishing flag for the N-PW, and forwards the packet.
•
Upon receiving the packet from the N-PW, NPE 1 tags the packet with the multiplex distinguishing
flag for the U-PW and sends the packet to UPE, which forwards the packet to the CE.
For packets to be exchanged between CE 1 and CE 2, UPE can forward them directly without NPE 1
because it holds the bridging function by itself. For the first packet with an unknown destination MAC
address or a broadcast packet, UPE broadcasts the packet to CE 2 through the bridging function and, at
the same time, forwards it through U-PW to NPE 1, which replicates the packet and sends a copy to each
peer CE.