Mpls l3vpn networking schemes, Basic vpn networking scheme – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 237
226
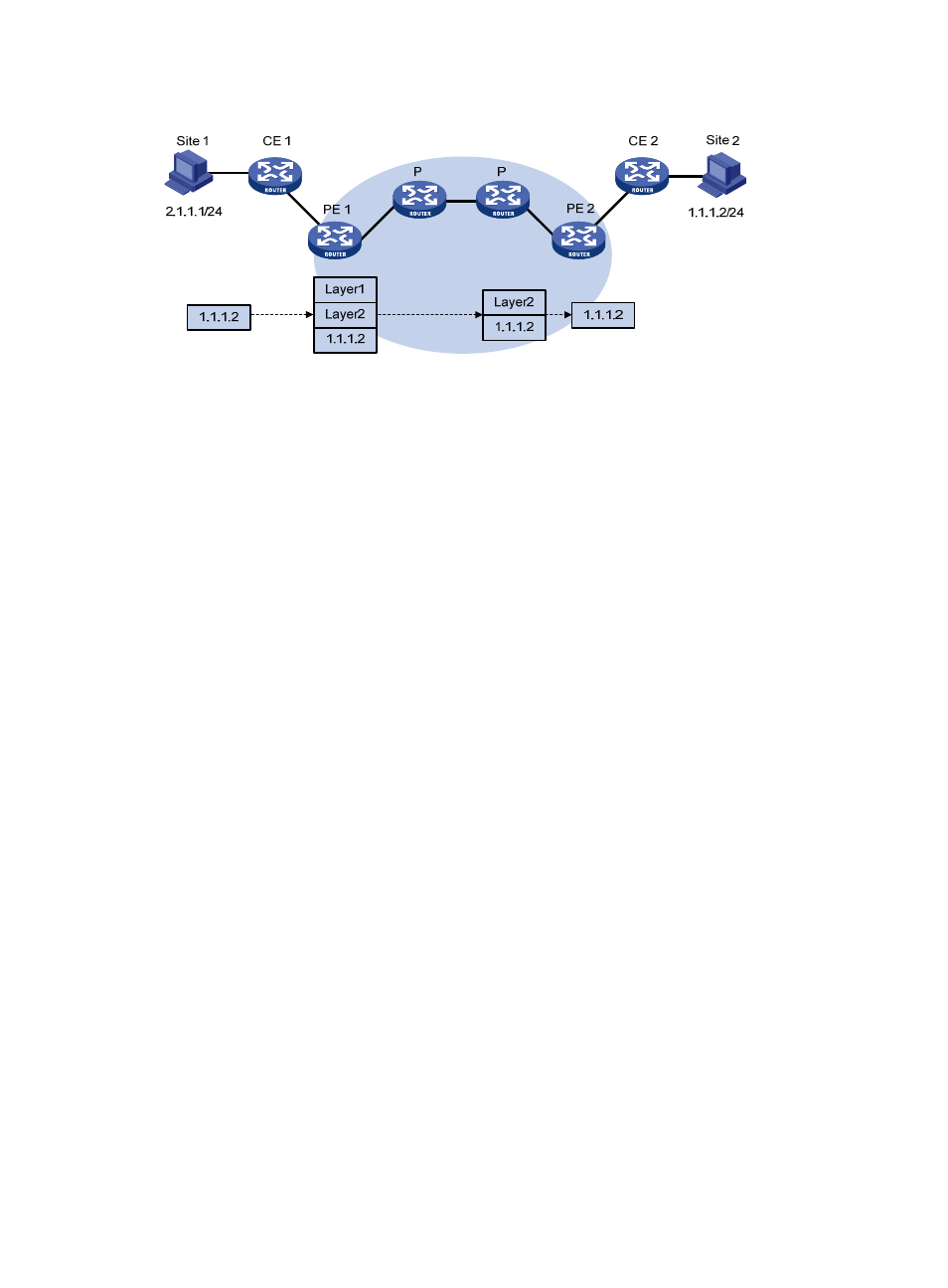
Figure 57 VPN packet forwarding
1.
Site 1 sends an IP packet with the destination address of 1.1.1.2. CE 1 transmits the packet to PE
1.
2.
PE 1 searches VPN instance entries based on the inbound interface and destination address of the
packet. Once finding a matching entry, PE 1 labels the packet with both inner and outer labels and
forwards the packet out.
3.
The MPLS backbone transmits the packet to PE 2 by outer label. The outer label is removed from
the packet at the penultimate hop.
4.
PE 2 searches VPN instance entries according to the inner label and destination address of the
packet to determine the outbound interface and then forwards the packet out the interface to CE 2.
5.
CE 2 transmits the packet to the destination by IP forwarding.
MPLS L3VPN networking schemes
In MPLS L3VPNs, VPN target attributes are used to control the advertisement and reception of VPN routes
between sites. They work independently and can be configured with multiple values to support flexible
VPN access control and implement multiple types of VPN networking schemes.
Basic VPN networking scheme
In the simplest case, all users in a VPN form a closed user group. They can forward traffic to each other
but cannot communicate with any user outside the VPN.
For this networking scheme, the basic VPN networking scheme, you need to assign a VPN target to each
VPN for identifying the export target attribute and import target attribute of the VPN. Moreover, this VPN
target cannot be used by any other VPNs.