H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 126
116
8.
The security policy server exchanges security check information with the authentication client to
check whether the authentication client meets the security requirements.
9.
Based on the security check result, the security policy server authorizes the user to access certain
resources, and sends the authorization information to the access device. The access device then
controls access of the user based on the authorization information.
Re-DHCP authentication process (with CHAP/PAP authentication)
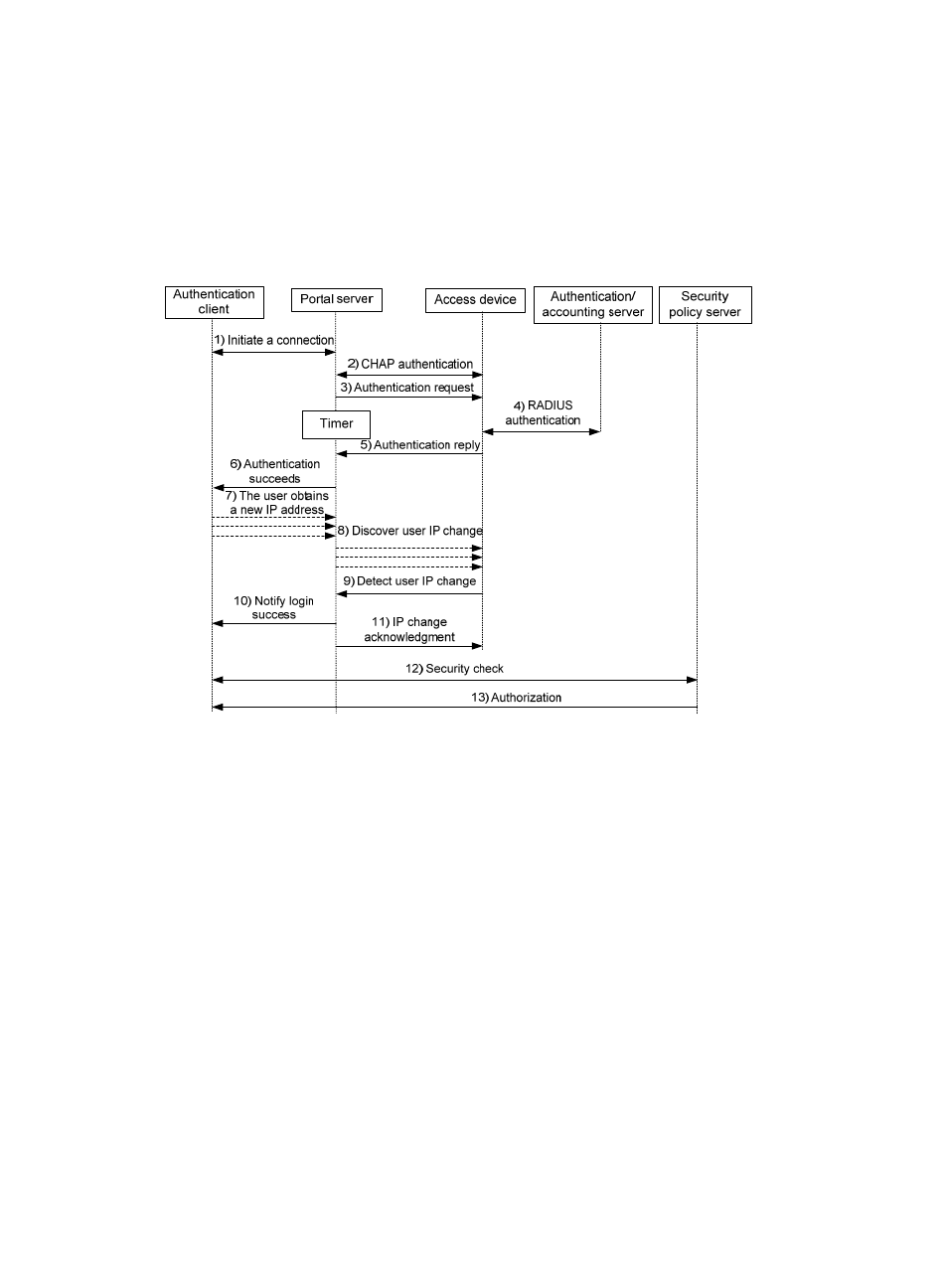
Figure 111 Re-DHCP authentication process
The re-DHCP authentication takes the following procedure:
1.
The first steps are the same as those in the direct authentication/cross-subnet authentication
process.
2.
After receiving the authentication success message, the authentication client obtains a new public
IP address through DHCP and notifies the portal server that it has obtained a public IP address.
3.
The portal server notifies the access device that the authentication client has obtained a new public
IP address.
4.
Detecting the change of the IP address by examining ARP packets received, the access device
notifies the portal server of the change.
5.
The portal server notifies the authentication client of logon success.
6.
The portal server sends a user IP address change acknowledgment message to the access device.
With extended portal functions, the process includes additional steps:
7.
The security policy server exchanges security check information with the authentication client to
check whether the authentication client meets the security requirements.
8.
Based on the security check result, the security policy server authorizes the user to access certain
resources, and sends the authorization information to the access device. The access device then
controls access of the user based on the authorization information.