Vrrp principles, Figure 32 – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 142
131
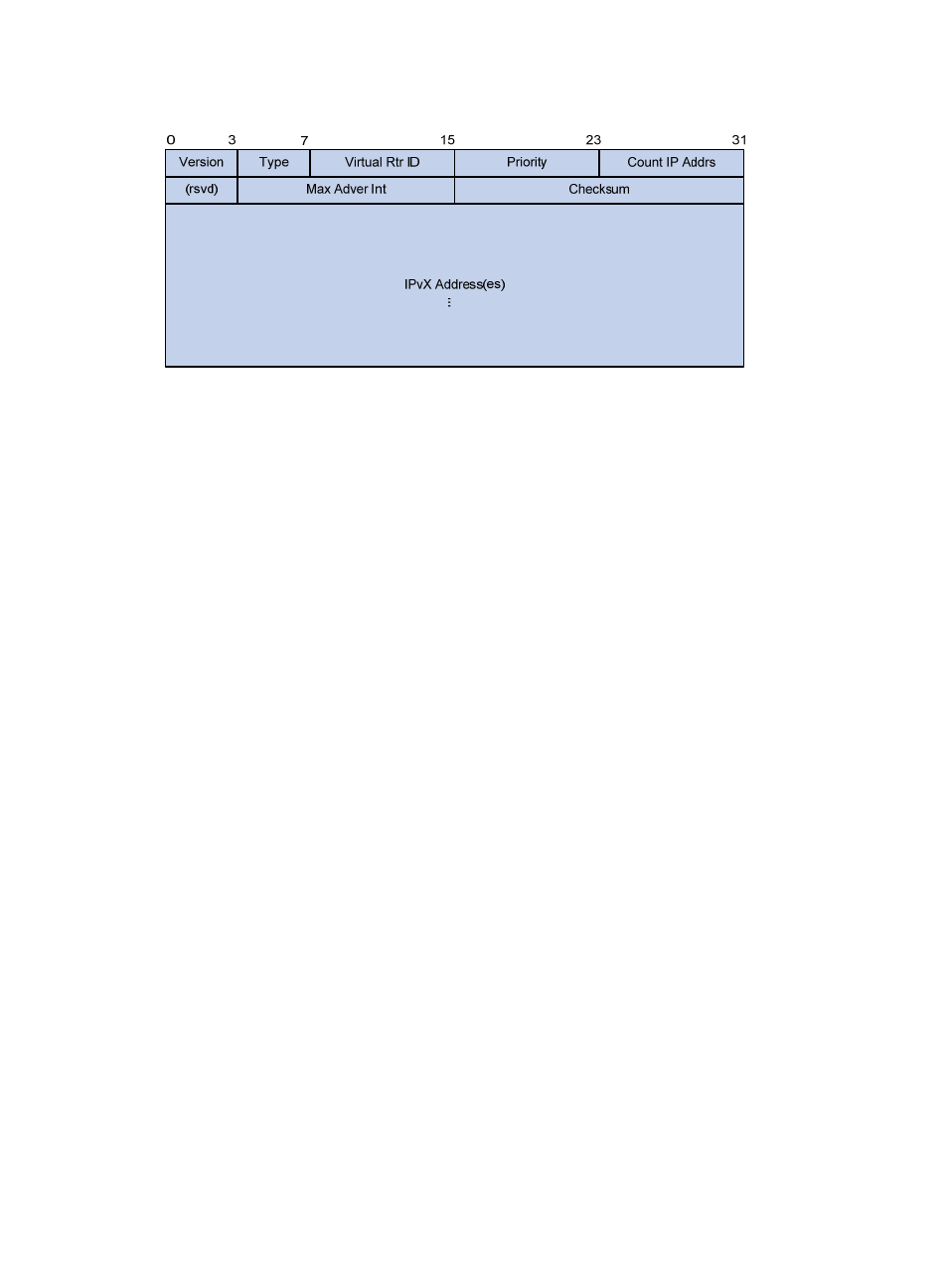
Figure 32 Format of an IPv4/IPv6 VRRPv3 packet
A VRRP packet comprises the following fields:
•
Version—Version number of the protocol, 2 for IPv4 VRRPv2 and 3 for other versions.
•
Type—Type of the VRRP packet. Only one VRRP packet type is present, that is, VRRP advertisement,
which is represented by 1.
•
Virtual Rtr ID (VRID)—ID of the virtual router, that is, ID of the VRRP group. It ranges from 1 to 255.
•
Priority—Priority of the router in the VRRP group, in the range 0 to 255. A greater value represents
a higher priority.
•
Count IP Addrs/Count IPv6 Addrs—Number of virtual IPv4 or IPv6 addresses for the VRRP group.
A VRRP group can have multiple virtual IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
•
Auth Type—Authentication type. For IPv4 VRRPv2, 0 means no authentication, 1 means simple text
authentication, and 2 means MD5 authentication. For IPv6 VRRPv2, 0 means no authentication, 1
means simple text authentication, and MD5 authentication is not supported. For IPv4/IPv6 VRRPv3,
authentication is not supported and this field is reserved.
•
Adver Int—Interval for sending advertisement packets. For IPv4 VRRPv2, the interval is in seconds
and defaults to 1. For other VRRP versions, the interval is in centiseconds and defaults to 100.
•
Checksum—16-bit checksum for validating the data in VRRP packets.
•
IP Address/IPv6 Address—Virtual IPv4 or IPv6 address entry of the VRRP group. The Count IP
Addrs or Count IPv6 Addrs field defines the number of the virtual IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
•
Authentication Data—Authentication key. This field is used only for simple authentication and is 0
for any other authentication modes. This field is not available for IPv4/IPv6 VRRPv3 packets.
VRRP principles
•
Routers in a VRRP group determine their roles by priority. The router with the highest priority is the
master, and the others are the backups. The master periodically sends VRRP advertisements to notify
the backups that it is working correctly, and each of the backups starts a timer to wait for
advertisements from the master.
•
In preemptive mode, when a backup receives a VRRP advertisement, it compares the priority in the
packet with its own priority. If the priority of the backup is higher, the backup becomes the master.
Otherwise, it remains as a backup. With the preemptive mode, a VRRP group always has a router
with the highest priority as the master for packet forwarding.
•
In non-preemptive mode, a router in the VRRP group remains as a master or backup as long as the
master does not fail. A backup does not become the master even if it is configured with a higher