Configuring bfd, Bfd overview, How bfd works – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 203: Operation of bfd
192
Configuring BFD
BFD overview
Switches need to detect communication failures quickly so that measures can be taken in time to ensure
service continuity and enhance network availability.
Fault detection methods include the following:
•
Hardware detection—Detects link failures by sending hardware detection signals, such as SDH
(synchronous digital hierarchy) transmission system alarms. Hardware detection can quickly detect
failures, but is not supported by all media types.
•
Hello mechanism—Switches can use the hello mechanism of a routing protocol for failure detection,
which has a failure detection rate in seconds. However, that detection rate is too slow for voice
services and other delay-sensitive services, as well as for high-speed data transmission, such as
Gigabit data transmission, where a detection rate slower than one second will cause a large
quantity of data to be dropped. Also, this detection method is dependent on the routing protocol.
•
Other detection methods—Different protocols sometimes provide dedicated detection mechanisms.
However, such a mechanism is hard to deploy for inter-system communications.
Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) provides a single mechanism to monitor links. With BFD,
devices can quickly detect communication failures and restore communications through backup paths.
How BFD works
BFD provides a general-purpose, standard, medium- and protocol-independent fast failure detection
mechanism. It can uniformly and quickly detect the failures of the bidirectional forwarding paths between
two routers, for protocols such as routing protocols and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS).
BFD provides no neighbor discovery mechanism. Protocols that BFD services notify BFD of routers to
which it needs to establish sessions. After a session is established, if no BFD control packet is received
from the peer within the negotiated BFD interval, BFD notifies a failure to the protocol, which takes
appropriate measures.
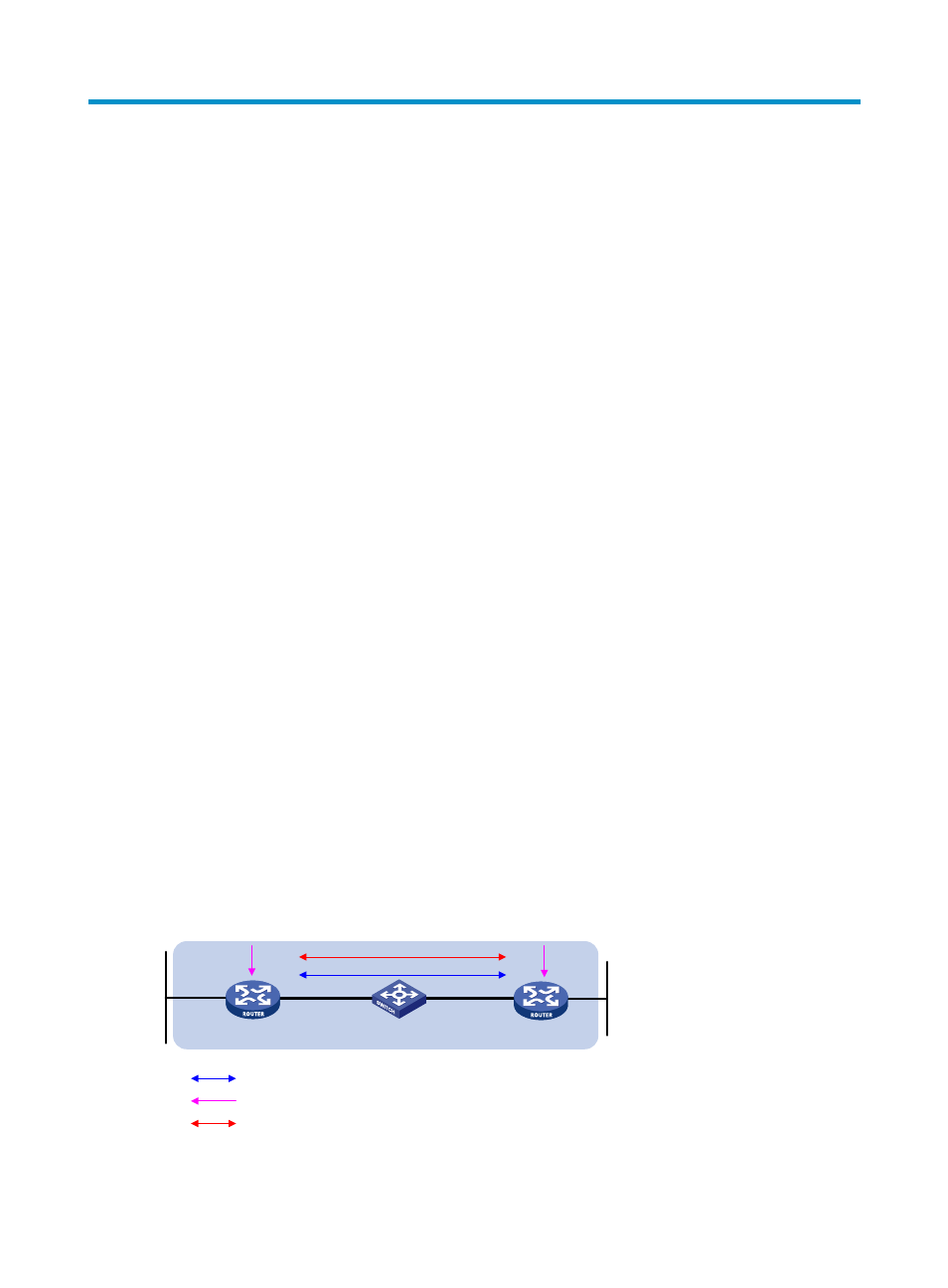
Operation of BFD
Figure 47 BFD session establishment (on OSPF routers)
BFD session establishment (as shown in
):
Router A
Router B
1
2
3
2
OSPF advertises the BFD neighbor relationship
BFD neighbors
OSPF neighbors