Bfd detection methods, Bfd session modes – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 204
193
1.
A protocol sends Hello messages to discover neighbors and establish neighborships.
2.
After establishing neighborships, the protocol notifies BFD of the neighbor information, including
destination and source addresses.
3.
BFD uses the information to establish BFD sessions.
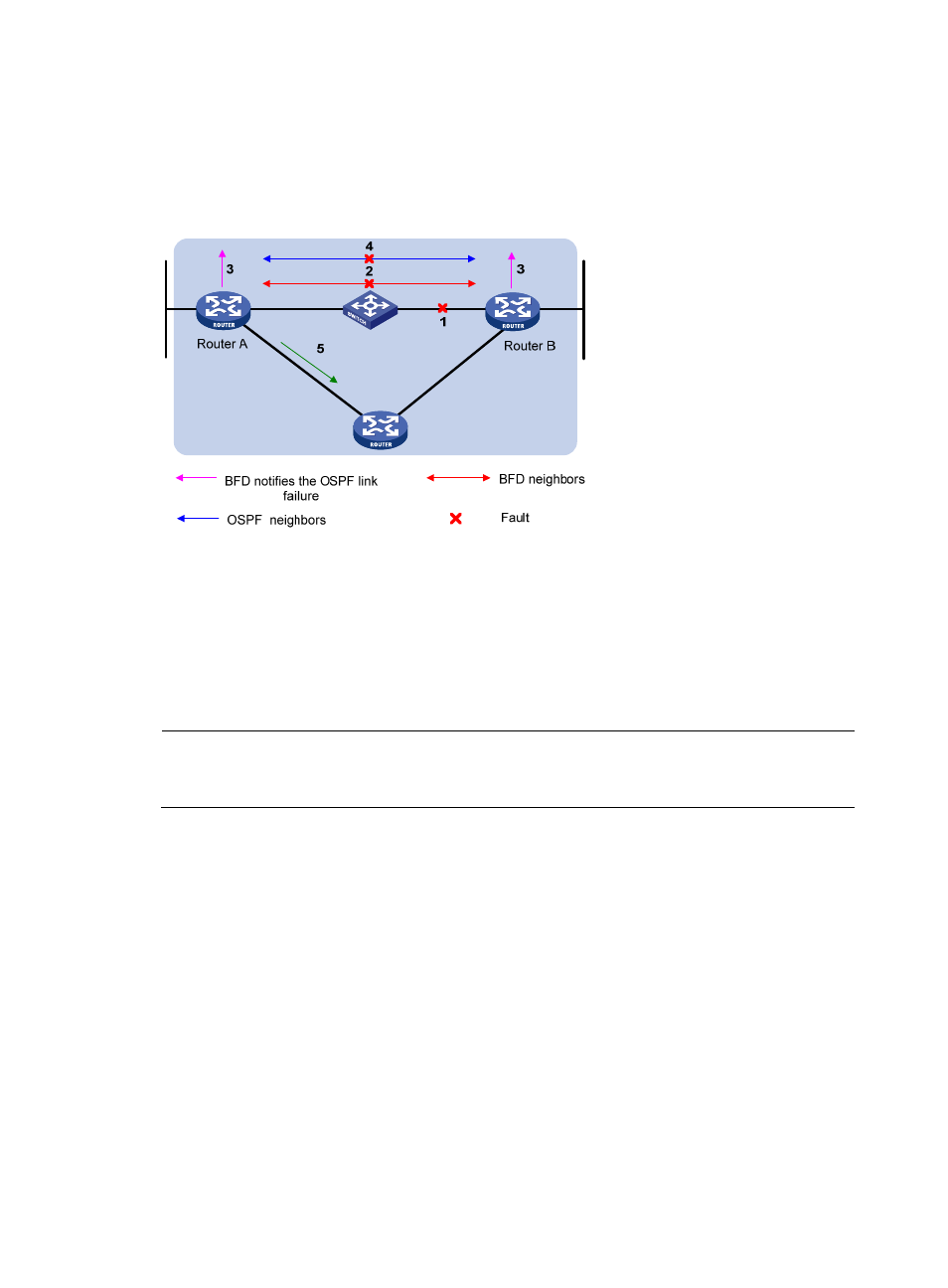
Figure 48 BFD fault detection (on OSPF routers)
BFD fault detection (as shown in
):
4.
BFD detects a link failure.
5.
BFD clears the neighbor session.
6.
BFD notifies the protocol of the failure.
7.
The protocol terminates the neighborship on the link.
8.
If a backup link is available, the protocol will use it to forward packets.
NOTE:
No detection time resolution is defined in the BFD draft. At present, most switches supporting BFD provide
detection measured in milliseconds.
BFD detection methods
•
Single-hop detection—Detects the IP connectivity between two directly connected systems.
•
Multi-hop detection—Detects any of the paths between two systems. These paths have multiple
hops and might overlap.
•
Bidirectional detection—Sends detection packets at two sides of a bidirectional link to detect the
bidirectional link status and find link failures in milliseconds. (BFD LSP detection is a special case,
in which BFD control packets are sent in one direction, and the peer switch reports the link status
through other links.)
BFD session modes
•
Control packet mode—Both ends of the link exchange BFD control packets to monitor link status.
•
Echo mode—One end of the link sends Echo packets to the other end, which then forwards the
packets back to the originating end, thereby monitoring link status in both directions.