Modbus on tcp/ip – Basler Electric DGC-2020HD Modbus Protocol User Manual
Page 9
9469300991 Rev A
3
DGC-2020HD Modbus
™ Protocol
General Information
and can be either odd or even. The transmission baud rate is user-selectable, and can be set at
installation and altered during real-time operation. DGC-2020HD Modbus supports baud rates up to
115200. The factory default baud rate is 19200.
DGC-2020HD systems support RS-485 compatible serial interfaces. This interface is accessible from the
left side panel of the DGC-2020HD.
Message Framing and Timing Considerations
When receiving a message via the RS-485 communication port, the DGC-2020HD requires an inter-byte
latency of 3.5 character times before considering the message complete.
Once a valid query is received, the DGC-2020HD waits a specified amount of time before responding.
This time delay is set on the Modbus Setup screen under Communications in BESTCOMSPlus
®
. This
parameter contains a value from 10 - 10,000 milliseconds. The default value is 10 milliseconds.
Table 1 provides the response message transmission time (in seconds) and 3.5 character times (in
milliseconds) for various message lengths and baud rates.
Table 1. Timing Considerations
Baud Rate
3.5 Character Time
(ms)
Message Tx Time(s)
128 Bytes
256 Bytes
2400
16.04
0.59
1.17
4800
8.021
0.29
0.59
9600
4.0104
0.15
0.29
19200
2.0052
0.07
0.15
Modbus on TCP/IP
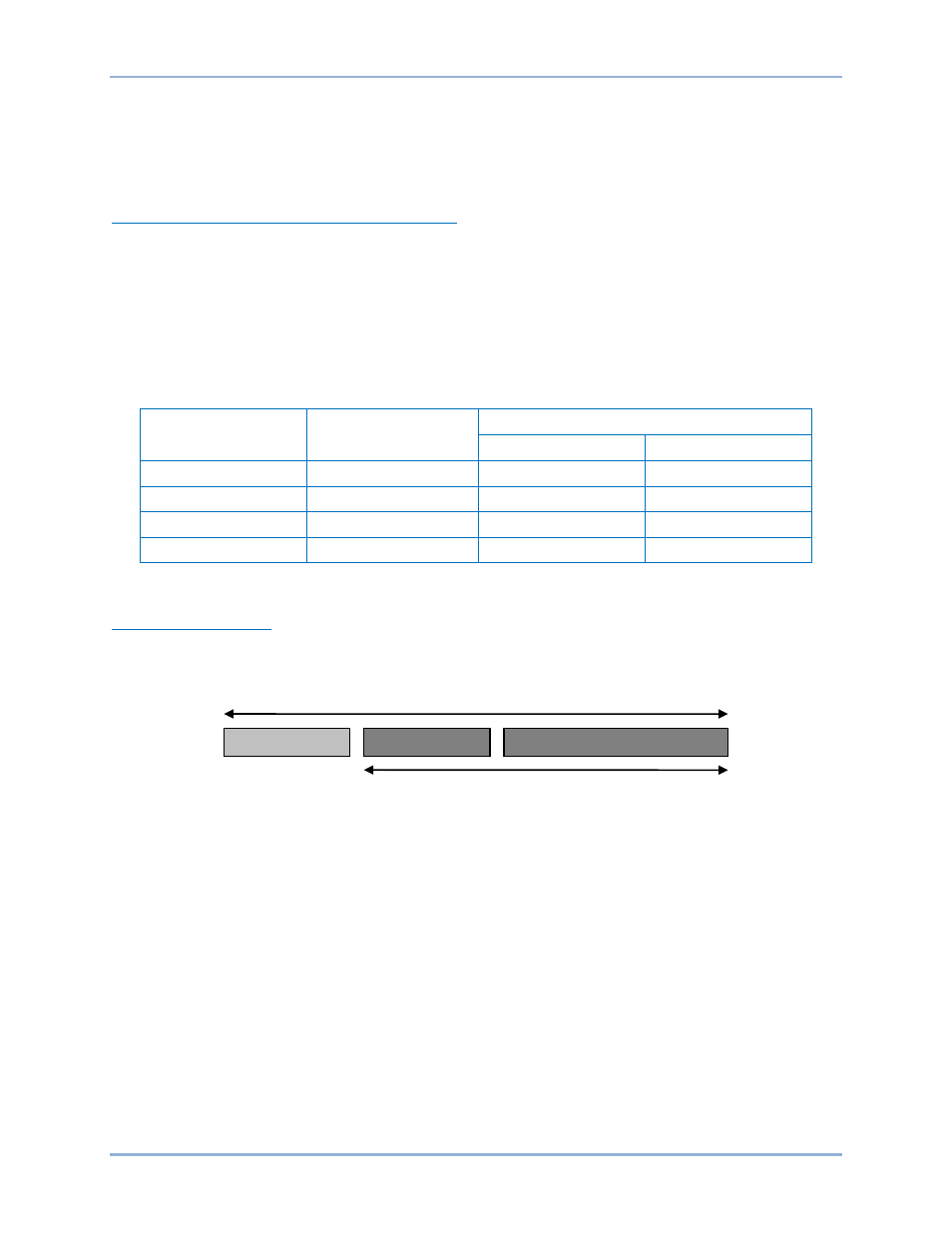
Application Data Unit
The following describes the encapsulation of a Modbus request or response when it is carried on a
Modbus TCP/IP network. See Figure 2.
Figure 2. Modbus Request/Response Over TCP/IP
A dedicated header is used on TCP/IP to identify the Modbus Application Data Unit. It is called the MBAP
header (Modbus Application Protocol header).
This header provides some differences compared to the Modbus RTU application data unit used on a
serial line:
•
The Modbus ‘slave address’ field usually used on Modbus Serial Line is replaced by a single byte
‘Unit Identifier’ within the MBAP header. The ‘Unit Identifier’ is used to communicate via devices
such as bridges, routers, and gateways that use a single IP address to support multiple
independent Modbus end units.
•
All Modbus requests and responses are designed in such a way that the recipient can verify that
a message is finished. For function codes where the Modbus PDU has a fixed length, the function
code alone is sufficient. For function codes carrying a variable amount of data in the request or
response, the data field includes a byte count.
•
When Modbus is carried over TCP, additional length information is carried in the MBAP header to
allow the recipient to recognize message boundaries even if the message has been split into
multiple packets for transmission. The existence of explicit and implicit length rules and use of a
PDU
Modbus TCP/IP ADU
Function code
Data
MBAP Header