2 demodulator faults – Comtech EF Data SDM-100A User Manual
Page 64
Operation
SDM-100A Satellite Modem
3–30
Rev.
0
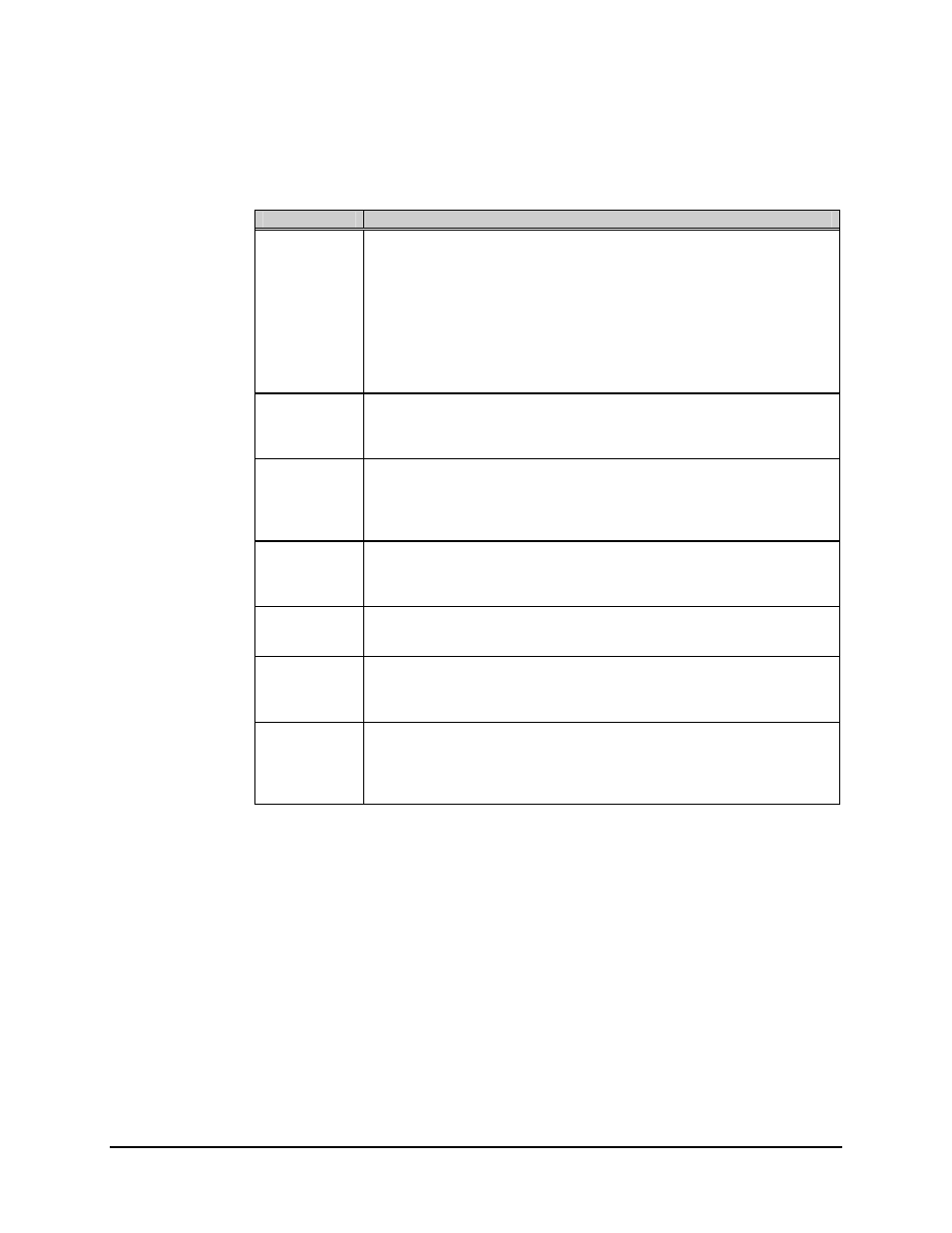
3.2.1.3.2 Demodulator Faults
Fault/Alarm
Possible Problem and Action
Carrier Detect
Carrier detect fault. Indicates the decoder is not locked.
This is the most common fault displayed in the modem. Any problem from
the input data on the modulator end of the circuit to the output of the
decoder can cause this alarm.
First, check to see that the demodulator has an RF input at the proper
frequency and power level. Check to see that the demodulator data rate is
properly programmed. Verify the frequency of the data transmitted from the
modulator is within 100 PPM. Use IF Loopback to verify the modem will lock.
IF Synthesizer
Demodulator IF synthesizer fault. Indicates the demodulator IF synthesizer
is not locked.
This fault is a hardware failure. Return the modem for repair.
I Channel
Indicates loss of activity in the I channel of the quadrature demodulator.
Typically indicates a problem in the modulator side of the circuit. Check for
proper RF input to the demodulator. If the input to the demodulator is
correct, then the problem is in the baseband processing.
Q Channel
Q channel activity fault. Indicates a loss of activity in the Q channel of the
quadrature demodulator.
Follow the same procedure as with the I channel fault.
Descrambler
Descrambler Alarm. Indicates loss of activity in the descrambler.
Typically indicates a loss of decoder program.
BER Threshold Indication that the preset BER threshold has been exceeded.
Setting of this alarm is done in the Utility menu. This alarm is based on the
corrected BER reading on the front panel.
Module
Demodulator/decoder module fault. Typically indicates that the
demod/decoder module is missing or will not program.
This could indicate a problem in the M&C or in the interface between the
demodulator and M&C. Return the modem for repair.