3 typical main circuit wiring examples – Yaskawa Sigma-5 User Manual: Setup for Rotary Motors User Manual
Page 82
3 Wiring and Connection
3.3.3 Typical Main Circuit Wiring Examples
3-24
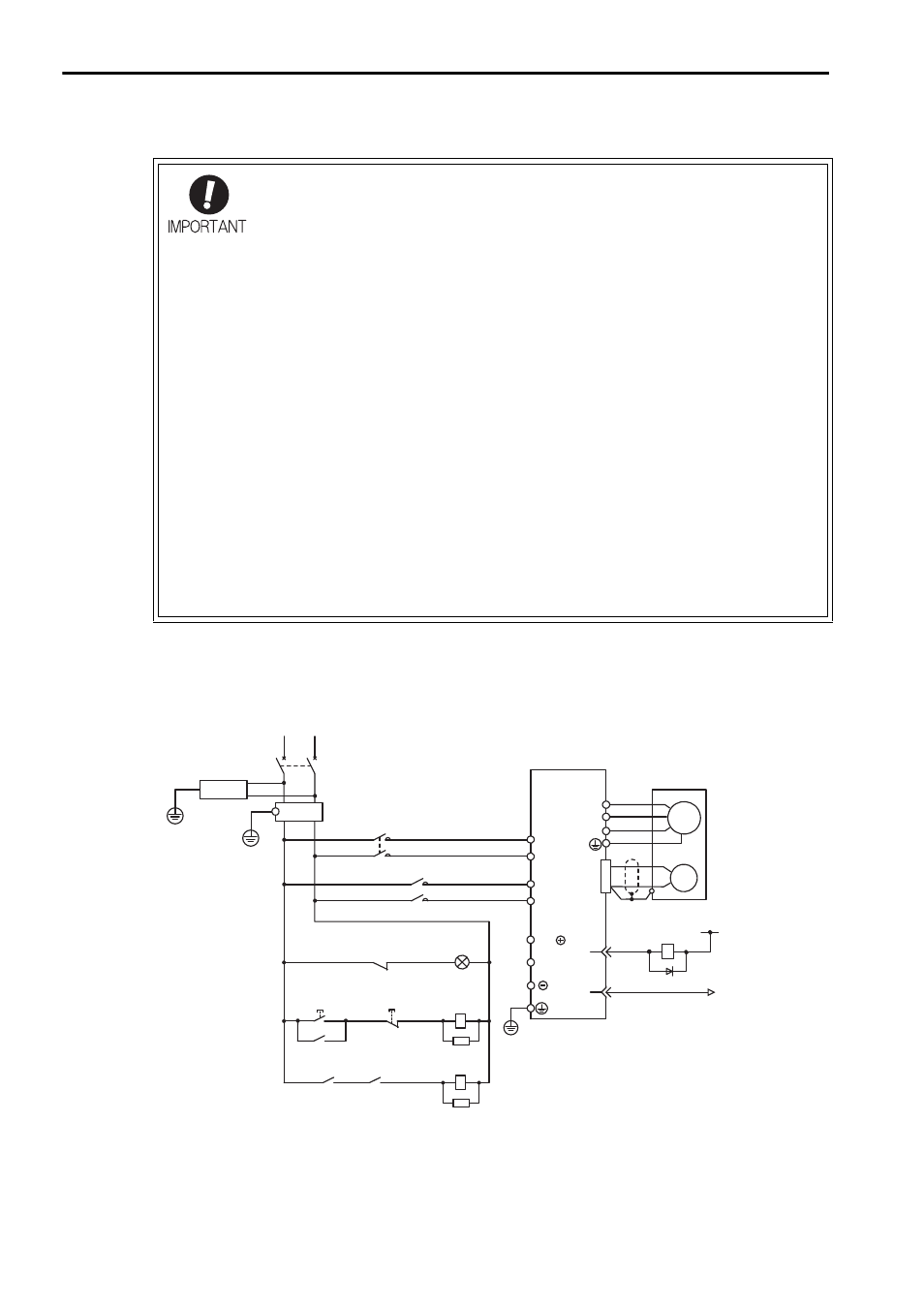
3.3.3 Typical Main Circuit Wiring Examples
The following wiring examples show the
Σ-V Series SGDV SERVOPACK (Analog
pulse model).
Single-phase 100 V, SGDV-F (SGDV-R70F, R90F, 2R1F, 2R8F)
• Use a molded-case circuit breaker (1QF) or fuse to protect the
main circuit.
The SERVOPACK connects directly to a commercial power sup-
ply; it is not isolated through a transformer or other device.
Always use a molded-case circuit breaker (1QF) or fuse to pro-
tect the servo system from accidents involving different power
system voltages or other accidents.
• Install a ground fault detector.
The SERVOPACK does not have a built-in protective circuit for
grounding.
To configure a safer system, install a ground fault detector
against overloads and short-circuiting, or install a ground fault
detector combined with a molded-case circuit breaker.
• Do not frequently turn power ON and OFF.
• Frequently turning power ON and OFF causes elements
inside the SERVOPACK to deteriorate. Do not use the servo
drive with an application that requires frequently turning power
ON and OFF.
• After the actual operation starts, the allowable interval for turn-
ing power ON and OFF is one hour or longer.
1PL: Indicator lamp
1SA: Surge absorber
2SA: Surge absorber
3SA: Surge absorber
1D: Flywheel diode
1QF: Molded-case circuit breaker
1FIL: Noise filter
1KM: Magnetic contactor (for control power supply)
2KM: Magnetic contactor (for main power supply)
1Ry: Relay
L1
ENC
SERVOPACK
SGDV-
F
U
V
W
M
0 V
1Ry
ALM+
ALM−
31
32
1D
2KM
1KM
B2
L2
CN1
1QF
R
T
1FIL
+24 V
B1/
3SA
(For servo
alarm display)
1Ry
1PL
supply ON
1KM
2KM
1SA
Servo power
supply OFF
Servo power
1KM
1Ry
1KM
2SA
L1C
L2C