Basic concepts in igmp snooping, Igmp snooping related ports – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 30
15
Basic concepts in IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping related ports
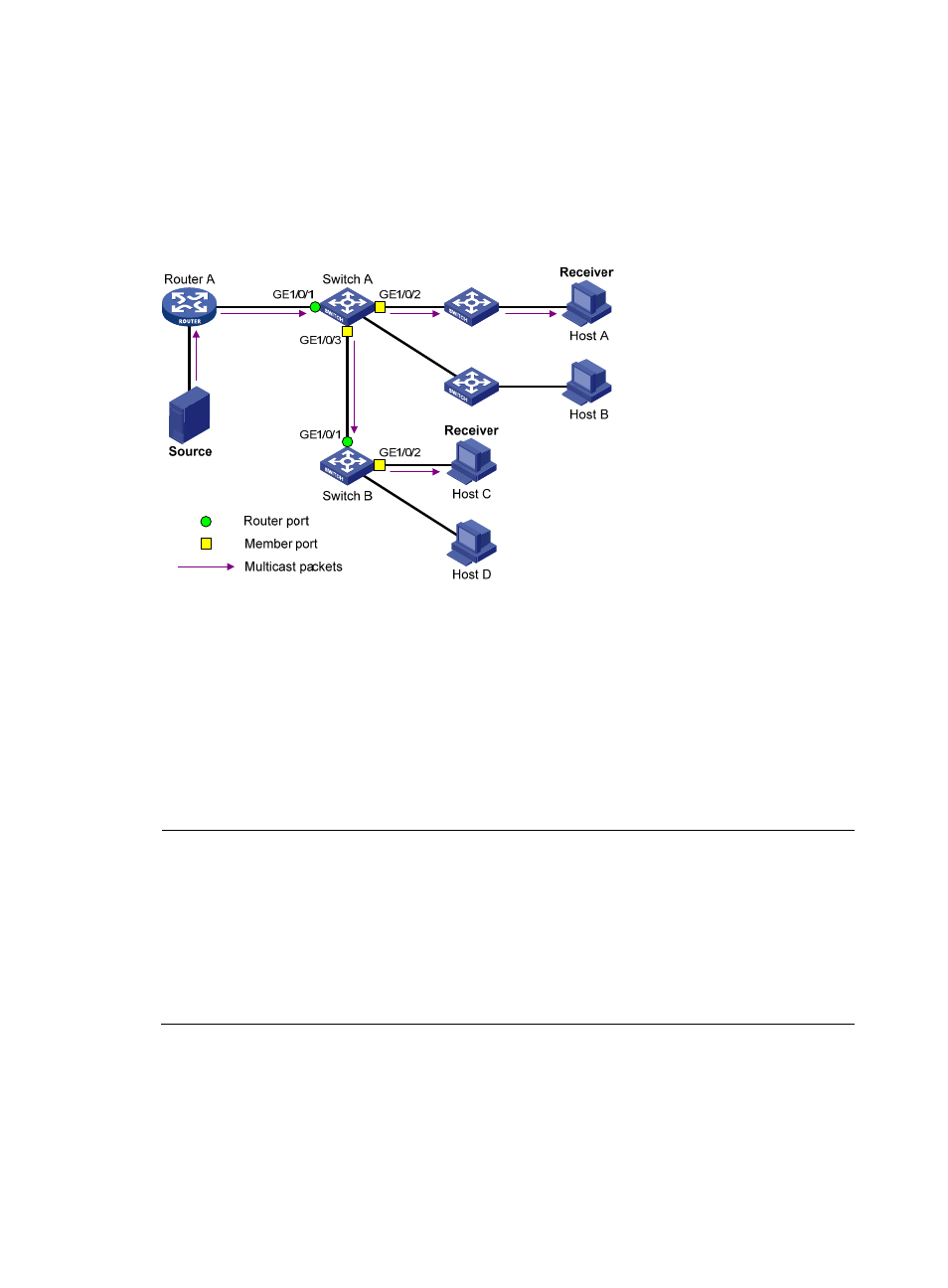
As shown in
, Router A connects to the multicast source, IGMP snooping runs on Switch A and
Switch B, and Host A and Host C are receiver hosts (namely, multicast group members).
Figure 12 IGMP snooping related ports
Ports involved in IGMP snooping, as shown in
, are described as follows:
•
Router port—A router port is a port on an Ethernet switch that leads the switch toward a Layer 3
multicast device (DR or IGMP querier). In the figure, GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Switch A and
GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Switch B are router ports. The switch registers all its local router ports in
its router port list.
•
Member port—A member port is a port on an Ethernet switch that leads the switch toward multicast
group members. In the figure, GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 of Switch A and
GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 of Switch B are member ports. The switch registers all the member ports on
the local device in its IGMP snooping forwarding table.
NOTE:
•
Whenever mentioned in this document, a router port is a port on the switch that leads the switch to a
Layer 3 multicast device, rather than a port on a router.
•
Unless otherwise specified, router/member ports mentioned in this document include static and
dynamic ports.
•
An IGMP-snooping-enabled switch deems that all its ports on which IGMP general queries with the
source IP address other than 0.0.0.0 or PIM hello messages are received are dynamic router ports. For
more information about PIM hello messages, see the chapter “PIM configuration.”