PLANET WGSW-5242 User Manual
Page 97
User’s Manual of WGSW-5242
97
Figure 4-7-5
Device Roles
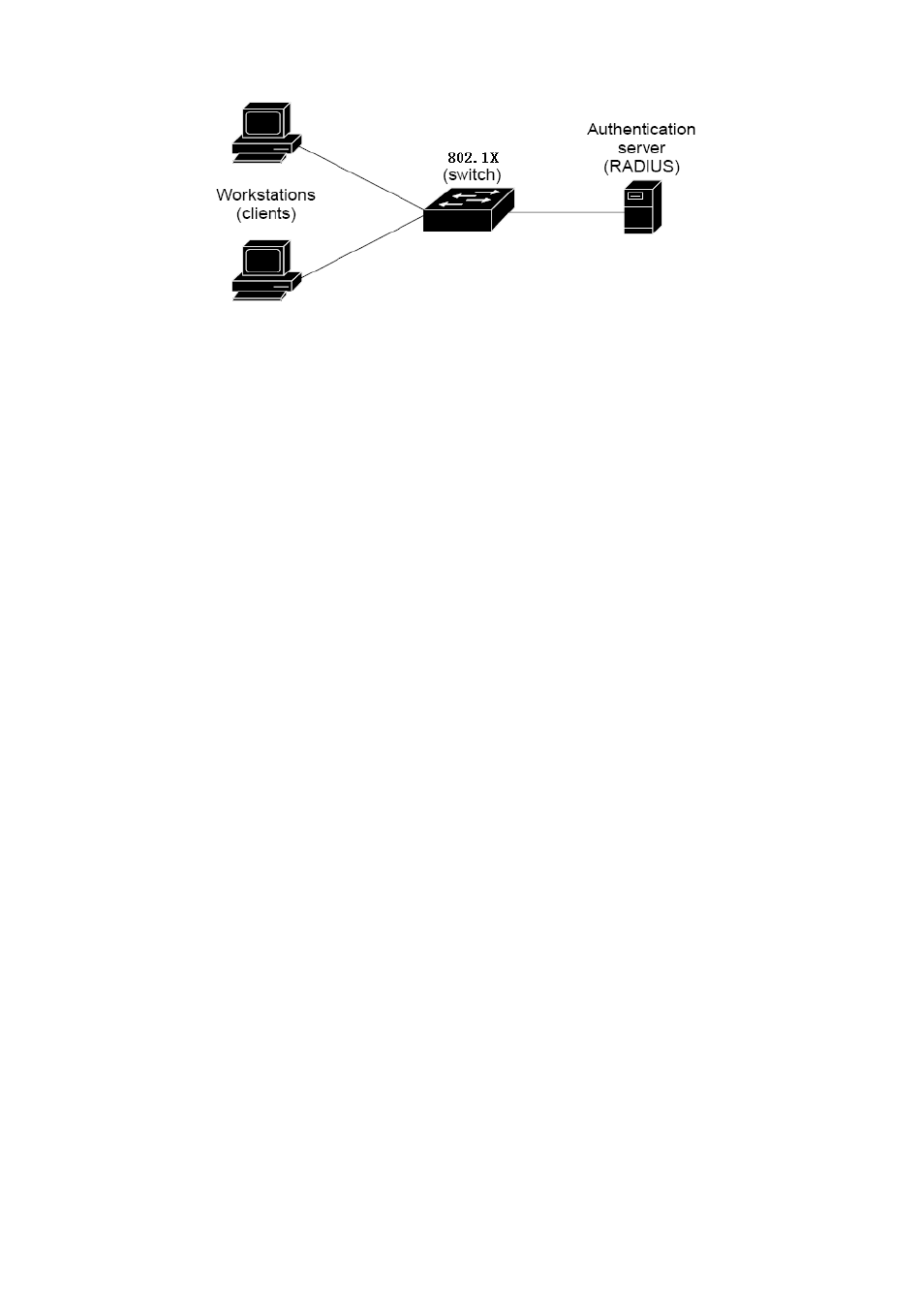
Client
—the device (workstation) that requests access to the LAN and switch services and responds to requests from
the switch. The workstation must be running 802.1X-compliant client software such as that offered in the Microsoft
Windows XP operating system. (The client is the supplicant in the IEEE 802.1X specification.)
Authentication server
—performs t he a ctual authentication of the c lient. T he authentication server v alidates t he
identity of the client and notifies the switch whether or not the client is authorized to access the LAN and switch services.
Because the switch acts as the proxy, the authentication service is transparent to the client. In this release, the Remote
Authentication D ial-In U ser Service (R ADIUS) s ecurity s ystem w ith Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
extensions is the only supported authentication server; it is available in Cisco Secure Access Control Server version 3.0.
RADIUS oper ates i n a client/server m odel i n w hich s ecure aut hentication i nformation i s ex changed be tween t he
RADIUS server and one or more RADIUS clients.
Switch (802.1X device)
—controls the physical access to the network based on the authentication status of the client.
The s witch a cts as an i ntermediary ( proxy) bet ween t he c lient and t he aut hentication s erver, r equesting i dentity
information from the client, verifying that information with the authentication server, and relaying a response to the client.
The s witch i ncludes t he R ADIUS c lient, w hich i s r esponsible f or en capsulating and d ecapsulating t he Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP)
frames and interacting with the authentication server. When the switch receives
EAPOL frames and relays them to the authentication server, the Ethernet header is stripped and the remaining EAP
frame is re-encapsulated in the RADIUS format. The EAP frames are not modified or examined during encapsulation,
and the authentication server must support EAP within the native frame format. When the switch receives frames from
the authentication server, the server's frame header is removed, leaving the EAP frame, which is then encapsulated for
Ethernet and sent to the client.
Authentication Initiation and Message Exchange
The switch or the client can initiate authentication. If you enable authentication on a port by using the dot1x port-control auto
interface configuration command, the switch must initiate authentication when it determines that the port link state transitions
from down to up. It then sends an EAP-request/identity frame to the client to request its identity (typically, the switch sends an
initial identity/request frame followed by one or more requests for authentication information). Upon receipt of the frame, the
client responds with an EAP-response/identity frame.