Ntp configuration task list, Configuring ntp operation modes – H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 44
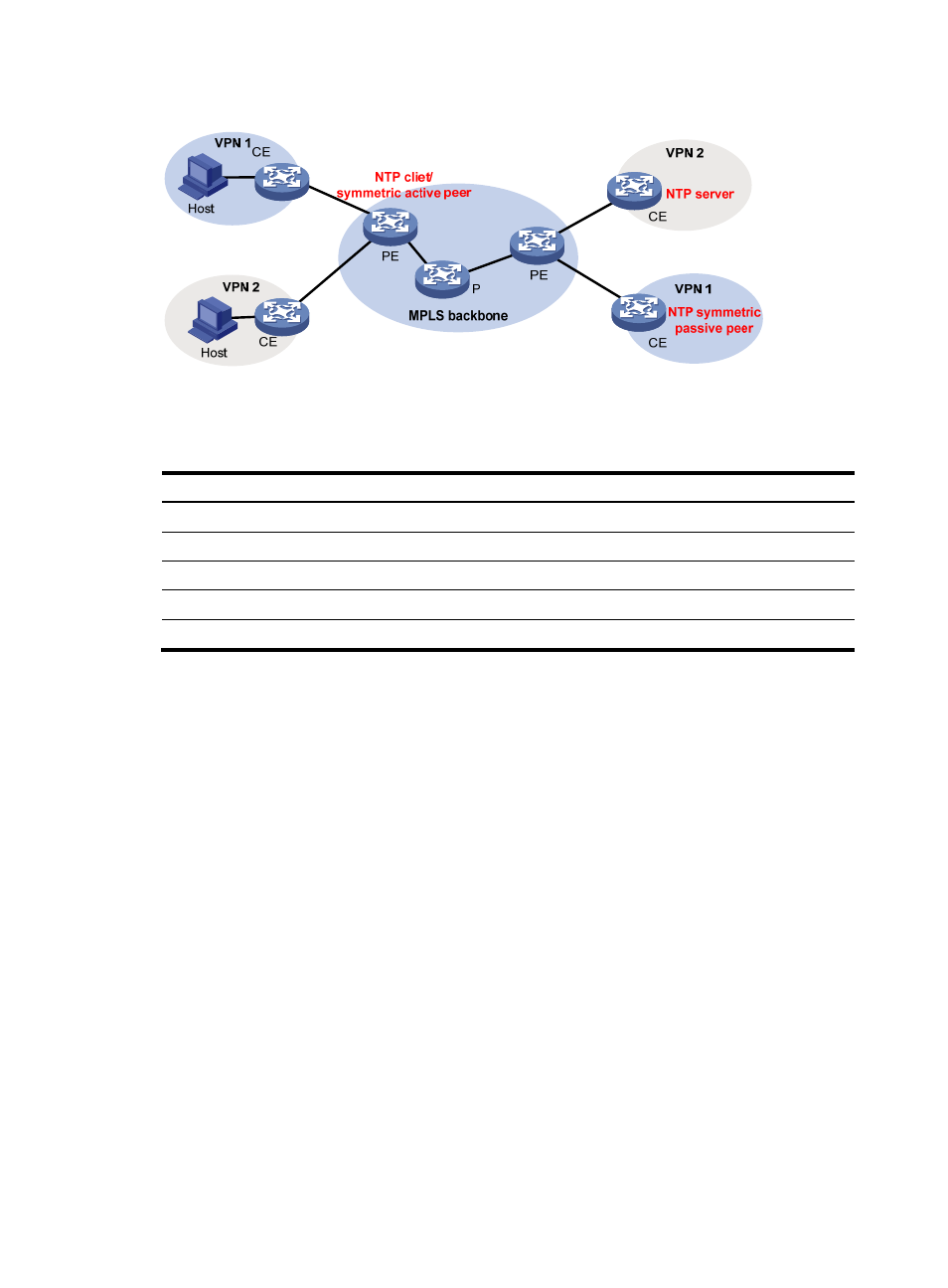
Figure 16 Network diagram
NTP configuration task list
Task Remarks
Configuring NTP operation modes
Required.
Configuring the local clock as a reference source
Optional.
Configuring optional parameters for NTP
Optional.
Configuring access-control rights
Optional.
Configuring NTP authentication
Optional.
Configuring NTP operation modes
Devices can implement clock synchronization in one of the following modes:
•
Client/server mode—Configure only clients.
•
Symmetric mode—Configure only symmetric-active peers.
•
Broadcast mode—Configure both clients and servers.
•
Multicast mode—Configure both clients and servers.
A single device can have a maximum of 128 associations at the same time, including static associations
and dynamic associations.
A static association refers to an association that a user has manually created by using an NTP command.
A dynamic association is a temporary association created by the system during operation. A dynamic
association is removed if the system fails to receive messages from it over a specific long time.
In client/server mode, for example, when you execute a command to synchronize the time to a server, the
system creates a static association, and the server just responds passively upon the receipt of a message,
rather than creating an association (static or dynamic). In symmetric mode, static associations are
created at the symmetric-active peer side, and dynamic associations are created at the symmetric-passive
peer side. In broadcast or multicast mode, static associations are created at the server side, and dynamic
associations are created at the client side.
31