Usage of bgp path attributes – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 209
194
Name Category
CLUSTER_LIST Optional
non-transitive
Usage of BGP path attributes
1.
ORIGIN
ORIGIN is a well-known mandatory attribute that defines the origin of routing information (how a route
became a BGP route). This attribute has the following types:
•
IGP—Has the highest priority. Routes added to the BGP routing table using the network command
have the IGP attribute.
•
EGP—Has the second highest priority. Routes obtained via EGP have the EGP attribute.
•
INCOMPLETE—Has the lowest priority. The source of routes with this attribute is unknown, which
does not mean such routes are unreachable. The routes redistributed from other routing protocols
have the INCOMPLETE attribute.
2.
AS_PATH
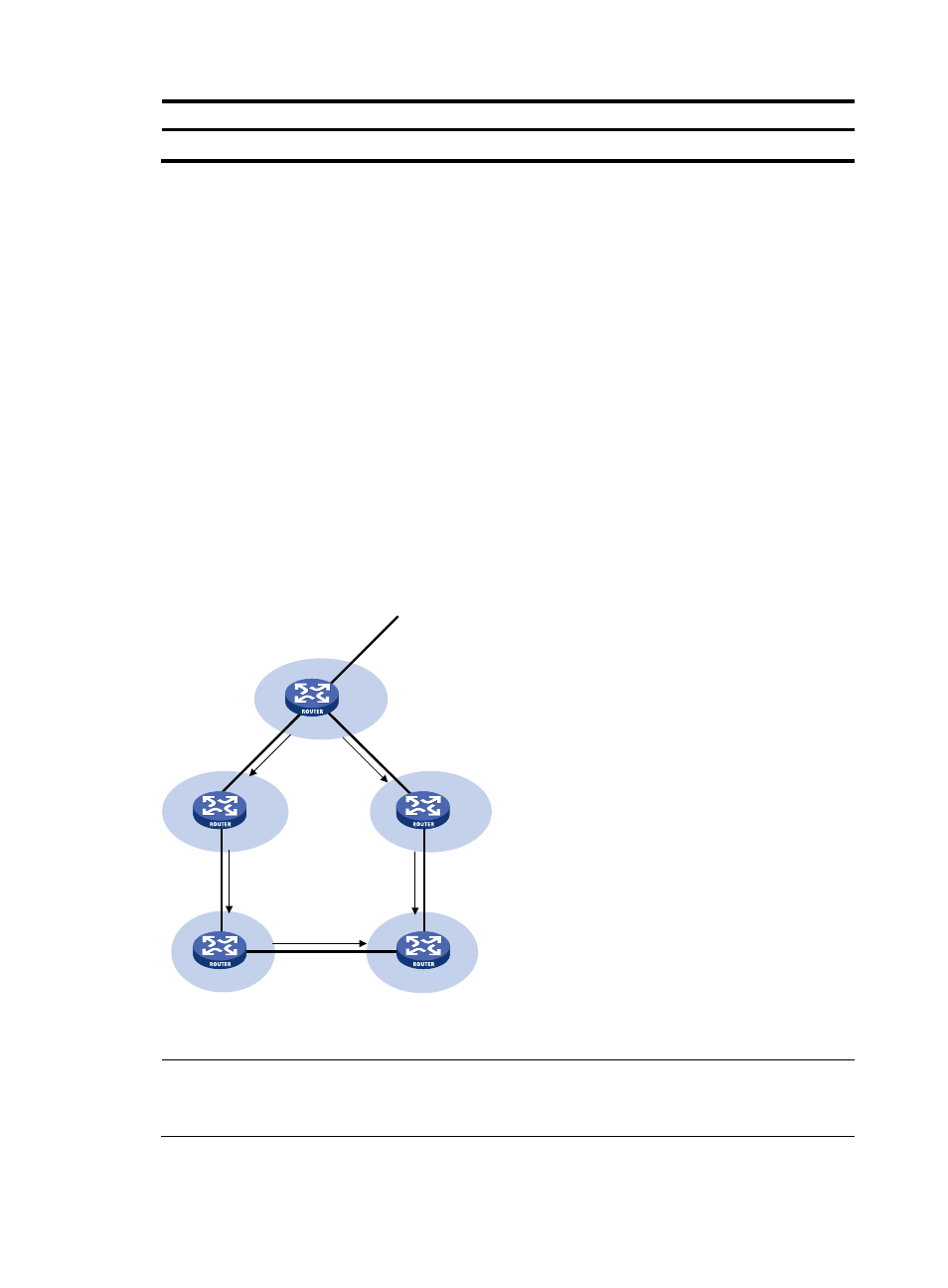
AS_PATH is a well-known mandatory attribute. This attribute identifies the autonomous systems through
which routing information carried in this Update message has passed. When a route is advertised from
the local AS to another AS, each passed AS number is added into the AS_PATH attribute, so the receiver
can determine ASs to route the message back. The number of the AS closest to the receiver’s AS is
leftmost, as shown in
:
Figure 76 AS_PATH attribute
8.0.0.0
AS 10
D = 8.0.0.0
(10)
D = 8.0.0.0
(10)
AS 20
AS 40
D = 8.0.0.0
(20,10)
AS 30
AS 50
D = 8.0.0.0
(30,20,10)
D = 8.0.0.0
(40,10)
Generally, a BGP router does not receive routes containing the local AS number to avoid routing loops.
NOTE:
The current implementation supports using the peer allow-as-loop command to receive routes containing
the local AS number in order to meet special requirements.