Ripv2 authentication message format, Supported rip features – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 39
24
Differences from RIPv1:
•
Version–Version of RIP. For RIPv2 the value is 0x02.
•
Route tag
•
IP address—Destination IP address. It can be a natural network address, subnet address, or host
address.
•
Subnet mask—Mask of the destination address. Unlike RIPv1, RIPv2 can carry subnet information.
•
Next hop—If set to 0.0.0.0, it indicates that the originator of the route is the best next hop.
Otherwise, it indicates a next hop better than the originator of the route.
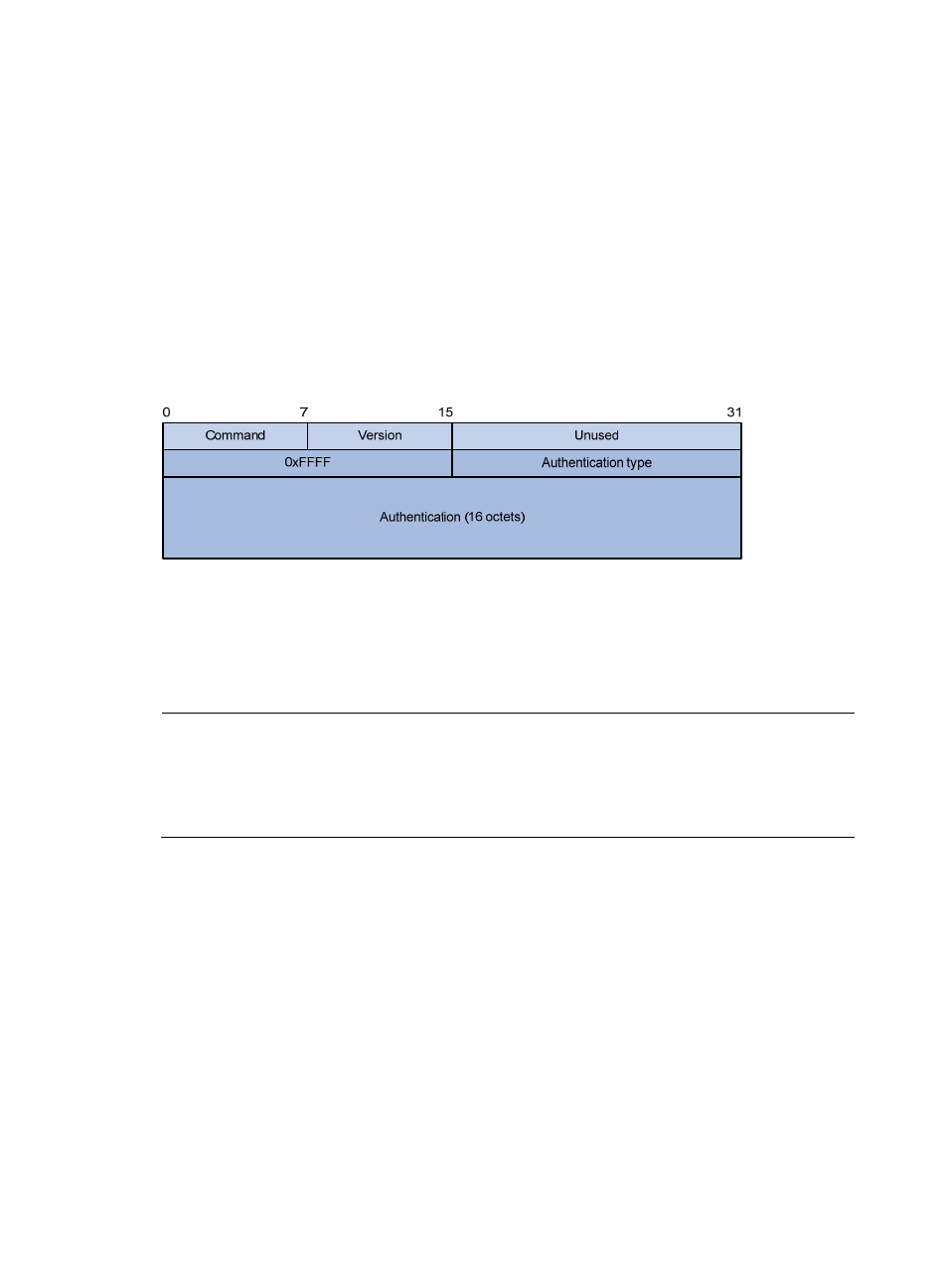
RIPv2 authentication message format
RIPv2 sets the AFI field of the first route entry to 0xFFFF to identify authentication information.
Figure 8 RIPv2 authentication message
•
Authentication Type—A value of 2 represents plain text authentication; a value of 3 represents
MD5.
•
Authentication—Authentication data, including password information when plain text
authentication is adopted or including key ID, MD5 authentication data length and sequence
number when MD5 authentication is adopted.
NOTE:
•
RFC 1723 only defines plain text authentication. For more information about MD5 authentication, see
RFC 2453,
RIP Version 2.
•
With RIPv1, you can configure the authentication mode in interface view; however, the configuration will
not take effect because RIPv1 does not support authentication.
Supported RIP features
The current implementation supports the following RIP features:
•
RIPv1 and RIPv2
•
RIP support for multi-VPN-instance
RIP can serve as the IGP running between CE and PE on a BGP/MPLS VPN network. For related
information, see MPLS Configuration Guide.
•
RIP FRR
•
BFD
RIP periodically sends route update requests to neighbors. If no route update response for a route is
received within the specified interval, RIP considers the route unreachable. This mechanism cannot detect