Lsr packet – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 81
66
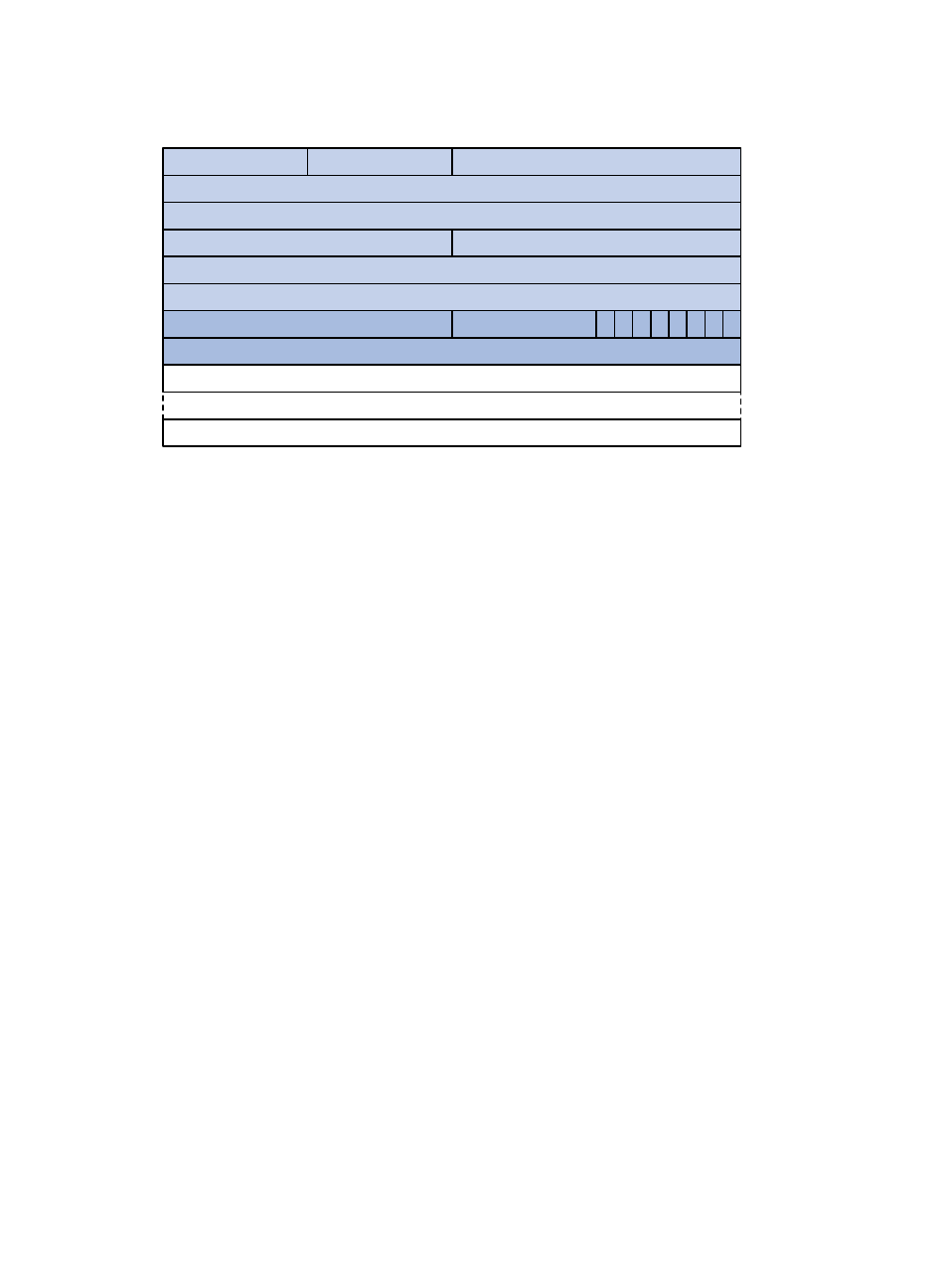
Figure 27 DD packet format
...
Version
2
Router ID
Area ID
Checksum
AuType
Packet length
Authentication
Authentication
Interface MTU
DD sequence number
LSA header
Options
0 0 0 0 0
I
M
M
S
0
7
15
31
LSA header
Major fields of the DD packets are as follows:
•
Interface MTU: Specifies the largest IP datagram in bytes that the interface can send without
fragmentation.
•
I (Initial) The Init bit, which is set to 1 if the packet is the first DD packet. It is set to 0 if not.
•
M (More): The More bit, which is set to 0 if the packet is the last DD packet. It is set to 1 if more DD
packets are to follow.
•
MS (Master/Slave): The Master/Slave bit. When set to 1, it indicates that the router is the master
during the database exchange process; otherwise, the router is the slave router.
•
DD sequence number: Used to sequence the collection of DD packets. The initial value is set by the
master. The DD sequence number then increments until the complete database description has been
sent.
LSR packet
After exchanging DD packets, two routers know which LSAs of the peer are missing from the local LSDB.
Then, they send (link state request) LSR packets to request the missing LSAs. An LSR packet contains the
brief of the missing LSAs.