Configuring the as-path attribute – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 232
217
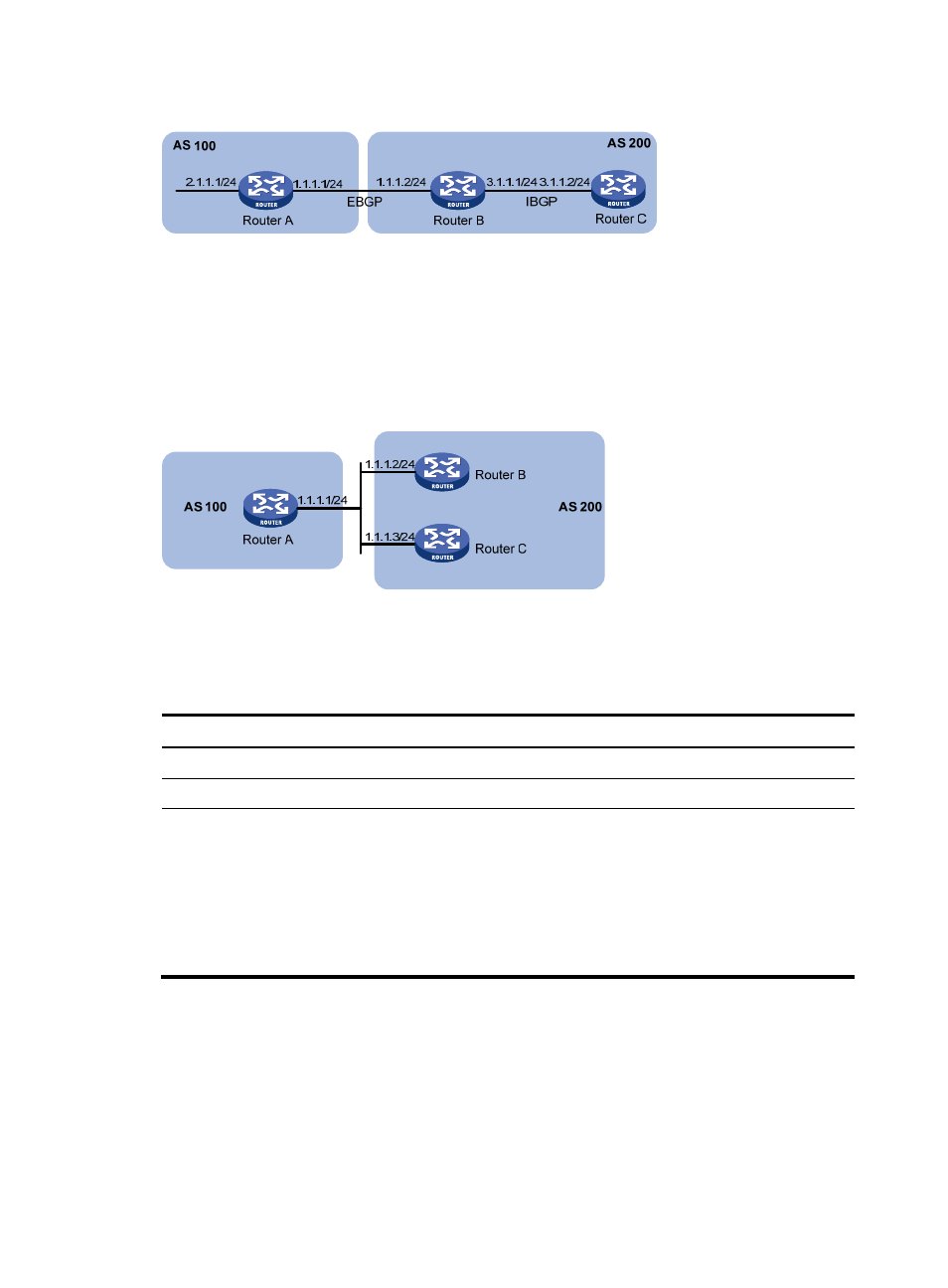
Figure 87 Next hop attribute configuration 1
If a BGP router has two peers on a common broadcast network, it does not set itself as the next hop for
routes sent to an eBGP peer by default. As shown in
, Router A and Router B establish an eBGP
neighbor relationship, and Router B and Router C establish an iBGP neighbor relationship. They are on
the same broadcast network 1.1.1.0/24. When Router B sends eBGP routes to Router A, it does not set
itself as the next hop by default. However, you can configure Router B to set it as the next hop (1.1.1.2/24)
for routes sent to Router A by using the peer next-hop-local command as needed.
Figure 88 Next hop attribute configuration 2
If you have configured BGP load balancing on a BGP router, the router will set it as the next hop for routes
sent to an iBGP peer or peer group. This is done regardless of whether the peer next-hop-local command
is configured.
Follow these steps to configure the next hop attribute:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enter BGP view
bgp as-number
—
Specify the router as the next hop of routes
sent to a peer or peer group
peer { group-name | ip-address }
next-hop-local
Optional
By default, the router sets it
as the next hop for routes
sent to an eBGP peer or peer
group, but does not set it as
the next hop for routes sent
to an iBGP peer or peer
group.
Configuring the AS-PATH attribute
Permit local AS number to appear in routes from a peer or peer group
BGP checks whether the AS_PATH attribute of a route from a peer contains the local AS number. If so, it
discards the route to avoid routing loops.
Follow these steps to permit local AS number to appear in routes from a peer or peer group and specify
the appearance times.