Westermo MRI-128-F4G-PSE24 User Manual
Page 75
71
(STP) introduced a standard method to accomplish this. It is specified in IEEE
802.1D-1998. Later, Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) was adopted and
represents the evolution of STP, providing much faster spanning tree convergence
after a topology change. This is specified in IEEE 802.1w. In 2004, 802.1w is
included into 802.1D-2004 version. This switch supports both RSTP and STP (all
switches that support RSTP are also backward compatible with switches that
support only STP).
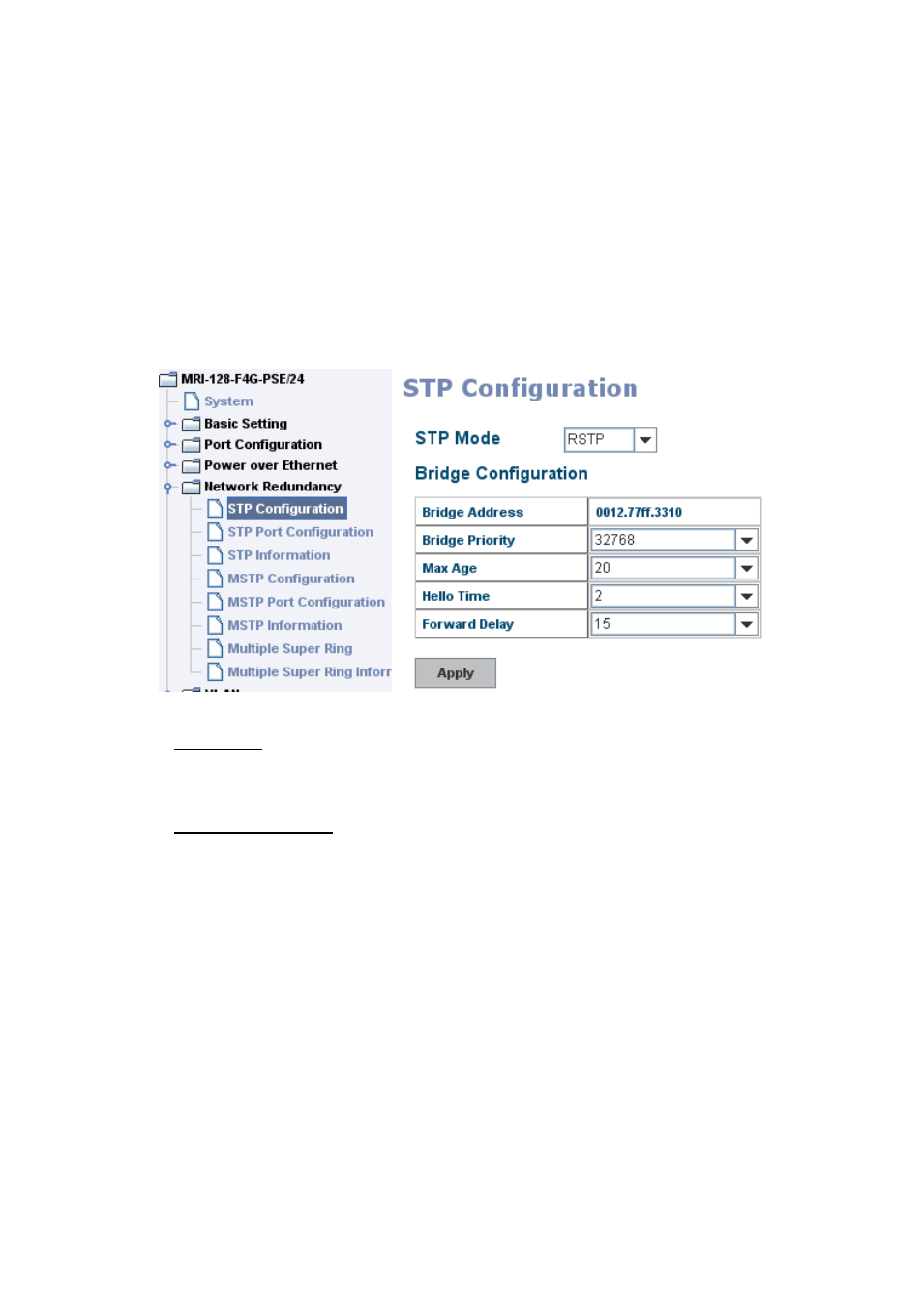
This page allows you to enable/disable RSTP, configure the global setting and port
settings.
RSTP Mode: You must first enable STP/RSTP mode, before configuring any related
parameters. Parameter settings required for both STP and RSTP are the same.
Note that 802.1d refers to STP mode, while 802.1w refers to faster RSTP mode.
Bridge Configuration
Priority (0-61440): RSTP uses bridge ID to determine the root bridge, the bridge
with the highest bridge ID becomes the root bridge. The bridge ID is composed of
bridge priority and bridge MAC address. So that the bridge with the highest
priority becomes the highest bridge ID. If all the bridge ID has the same priority,
the bridge with the lowest MAC address will then become the root bridge.
Note: The bridge priority value must be in multiples of 4096. A device with a
lower number has a higher bridge priority. Ex: 4096 is higher than 32768.
Max Age (6-40): Enter a value from 6 to 40 seconds here. This value represents
the time that a bridge will wait without receiving Spanning Tree Protocol
configuration messages before attempting to reconfigure.
If the switch is not the root bridge, and if it has not received a hello message
from the root bridge in an amount of time equal to Max Age, then it will