Local proxy arp, Figure 40 – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade NetStream Cards User Manual
Page 138
123
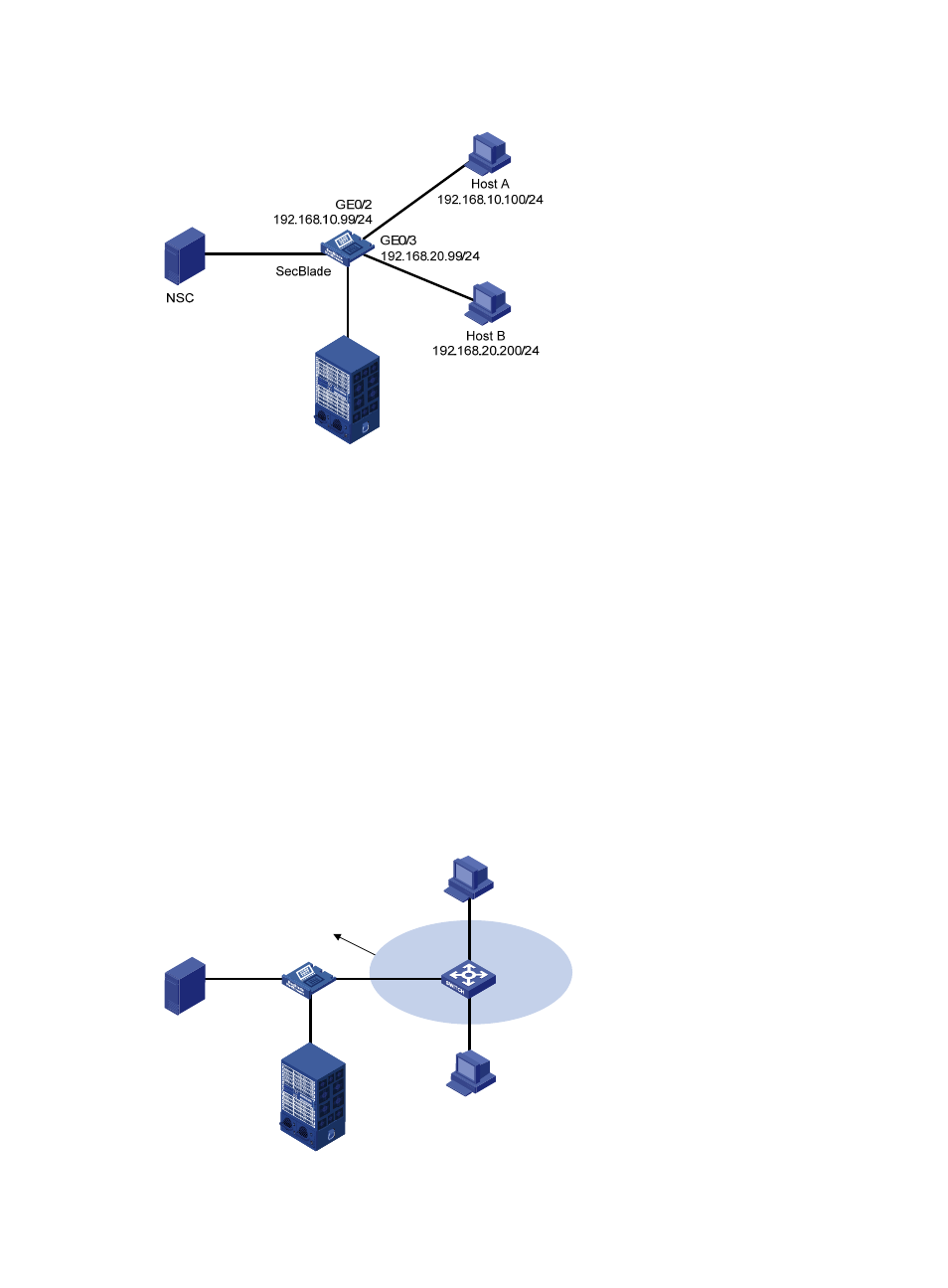
Figure 40 Application environment of proxy ARP
Because Host A considers that Host B is on the same network, it broadcasts an ARP request for the MAC
address of Host B. However, Host B cannot receive this request because it is in a different broadcast
domain.
You can enable proxy ARP on GigabitEthernet 0/2 of the SecBlade so that the SecBlade can reply to the
ARP request from Host A with the MAC address of GigabitEthernet 0/2, and forward packets sent from
Host A to Host B. In this case, the SecBlade acts as a proxy of Host B.
A main advantage of proxy ARP is that you can enable it on a single router without disturbing routing
tables of other routers in the network. Proxy ARP acts as the gateway for hosts that are not configured with
a default gateway or do not have routing capability.
Local proxy ARP
As shown in
, Host A and Host B belong to VLAN 2, but are isolated at Layer 2. Host A connects
to Ethernet 1/3 while Host B connects to Ethernet 1/1. Enable local proxy ARP on the SecBlade to allow
Layer 3 communication between the two hosts.
Figure 41 Application environment of local proxy ARP
GE0/2
VLAN 2
Vlan-int2
192.168.10.100/16
Switch B
Eth1/3
Eth1/1
Eth1/2
uplink-port
Host A
192.168.10.99/16
Host B
192.168.10.200/16
VLAN 2
port-isolate group 2
NSC
SecBlade