Ipv6 netstream operation, Ipv6 netstream key technologies, Flow aging – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 166
154
IPv6 NetStream operation
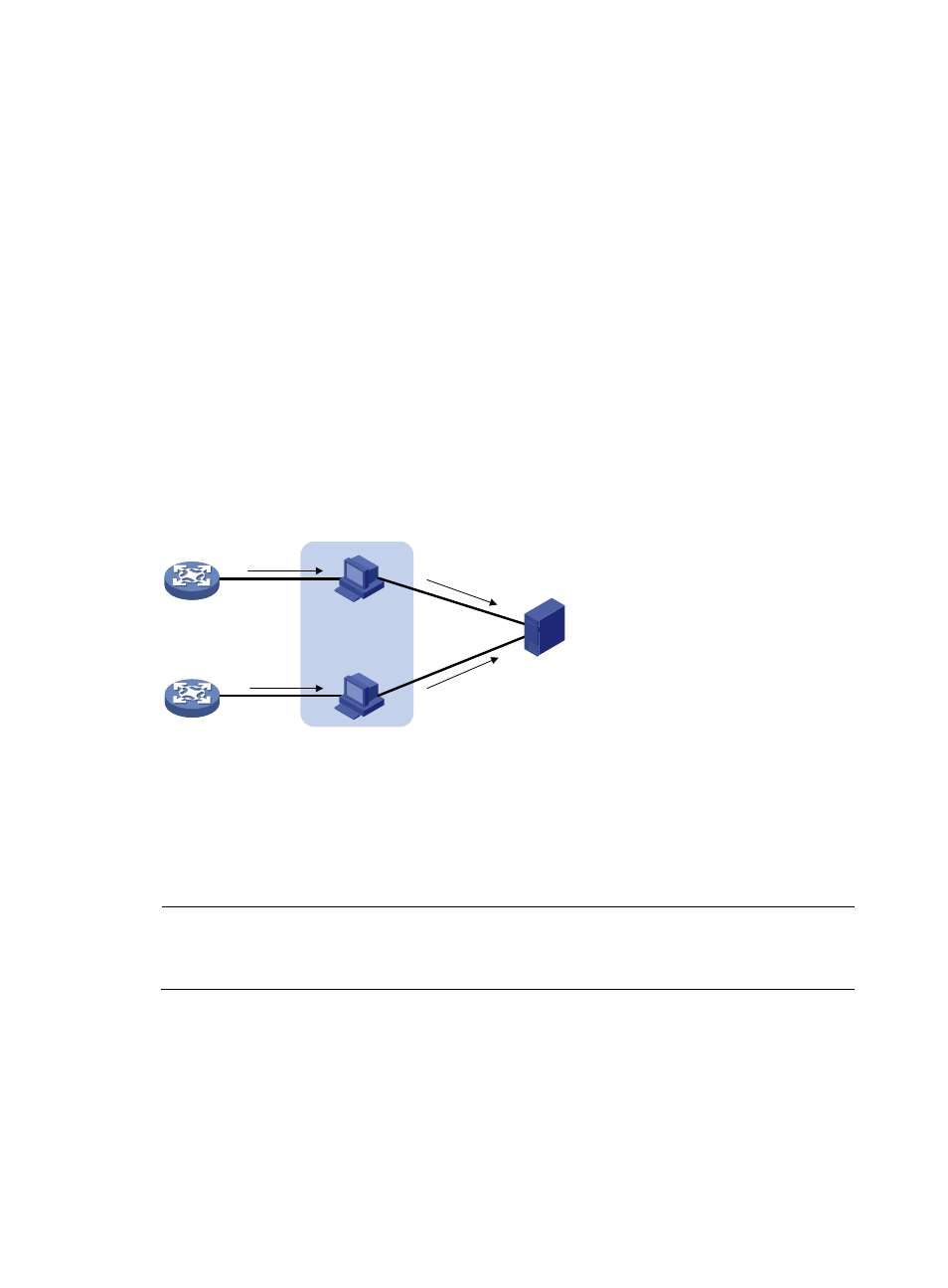
A typical IPv6 NetStream system comprises three parts: NetStream data exporter (NDE), NetStream
collector (NSC), and NetStream data analyzer (NDA).
•
NDE
The NDE analyzes traffic flows that pass through it, collects necessary data from the target flows,
and exports the data to the NSC. Before exporting data, the NDE may process the data like
aggregation. A device with IPv6 NetStream configured typically acts as an NDE.
•
NSC
The NSC is usually a program running in UNIX or Windows. It parses the packets sent from the
NDE, stores the statistics to the database for the NDA. The NSC gathers the data from multiple
NDEs.
•
NDA
The NDA is a network traffic analysis tool. It collects statistics from the NSC, and performs further
process, generates various types of reports for applications of traffic billing, network planning,
and attack detection and monitoring. Typically, the NDA features a Web-based system for users
to easily obtain, view, and gather the data.
Figure 56 IPv6 NetStream system
As shown in
, the following procedure of IPv6 NetStream data collection and analysis occurs:
1.
The NDE, that is the device configured with IPv6 NetStream, periodically delivers the collected
statistics to the NSC.
2.
The NSC processes the statistics, and then sends the results to the NDA.
3.
The NDA analyzes the statistics for accounting, network planning, and the like.
NOTE:
•
This document focuses on the description and configuration of NDE.
•
NSC and NDA are usually integrated into a NetStream server.
IPv6 NetStream key technologies
Flow aging
The flow aging in IPv6 NetStream is a means used by the NDE to export IPv6 NetStream data to the
NetStream server. IPv6 NetStream creates an IPv6 NetStream entry for each active flow in the cache of
NSC
NDA
NDE
NDE
- H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C SecPath F5020 H3C SecPath F5040 H3C VMSG VFW1000 H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module