RIGOL MSO/DS1000Z Series User Manual
Page 64
RIGOL
Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System
3-4
MSO1000Z/DS1000Z User’s Guide
According to sinθ=A/B or C/D (wherein, θ is the phase deviation angle between
the two channels and the definitions of A, B, C and D are as shown in the figure
above), the phase deviation angle is obtained, that is:
θ=±arcsin (A/B) or ±arcsin (C/D)
If the principal axis of the ellipse is within quadrant I and III, the phase deviation
angle obtained should be within quadrant I and IV, namely within (0 to π/2) or (3π/2
to 2π). If the principal axis of the ellipse is within quadrant II and IV, the phase
deviation angle obtained should be within quadrant II and III, namely within (π/2 to
π) or (π to 3π/2).
The XY function can be used to measure the phase deviation occurred when the
signal under test passes through a circuit network. Connect the oscilloscope to the
circuit to monitor the input and output signals of the circuit.
Application example: measure the phase deviation of the input signals of two
channels.
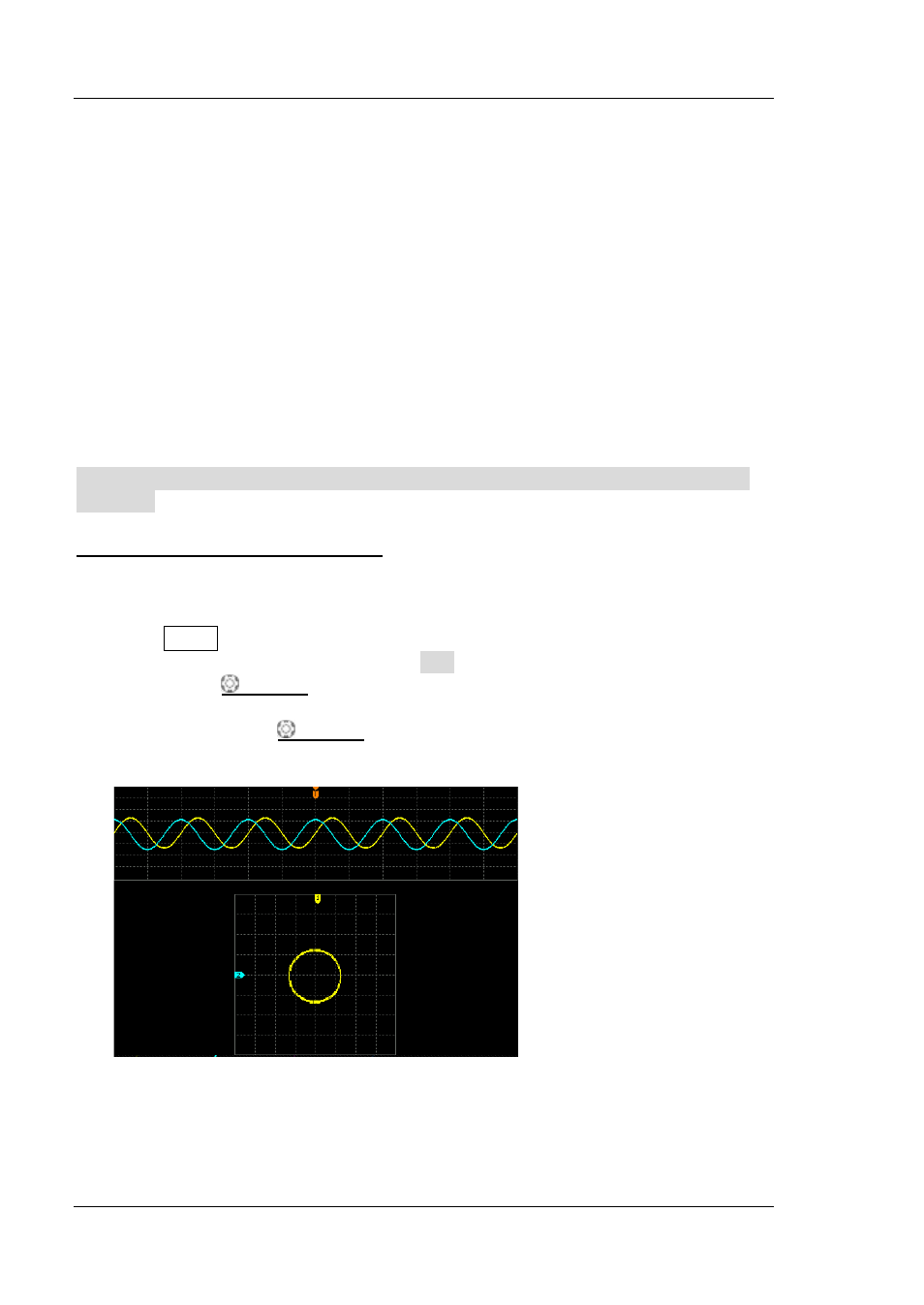
Method 1: Use Lissajous method
1. Connect a sine signal to CH1 and then connect a sine signal with the same
frequency and amplitude but a 90° phase deviation to CH2.
2. Press AUTO and then adjust the vertical positions of CH1 and CH2 to 0 V.
3. Set the time base mode to XY, press X-Y and select "CH1-CH2". Rotate
Horizontal SCALE to adjust the sample rate properly to get better
Lissajous figure for better observation and measurement.
4. Rotate VERTICAL SCALE of CH1 and CH2 to make the signals easy to
observe. At this point, the circle as shown in the figure below should be
displayed.
5. Observe the measurement result shown in the figure above. According to the
measurement schematic diagram of the phase deviation (as shown in Figure
3-2), A/B (C/D) = 1. Thus, the phase deviation angle θ=±arcsin1=90°.