Spanning tree, Region r – Microsens MS453490M Management Guide User Manual
Page 195
C
HAPTER
8
| Spanning Tree Algorithm
Overview
– 195 –
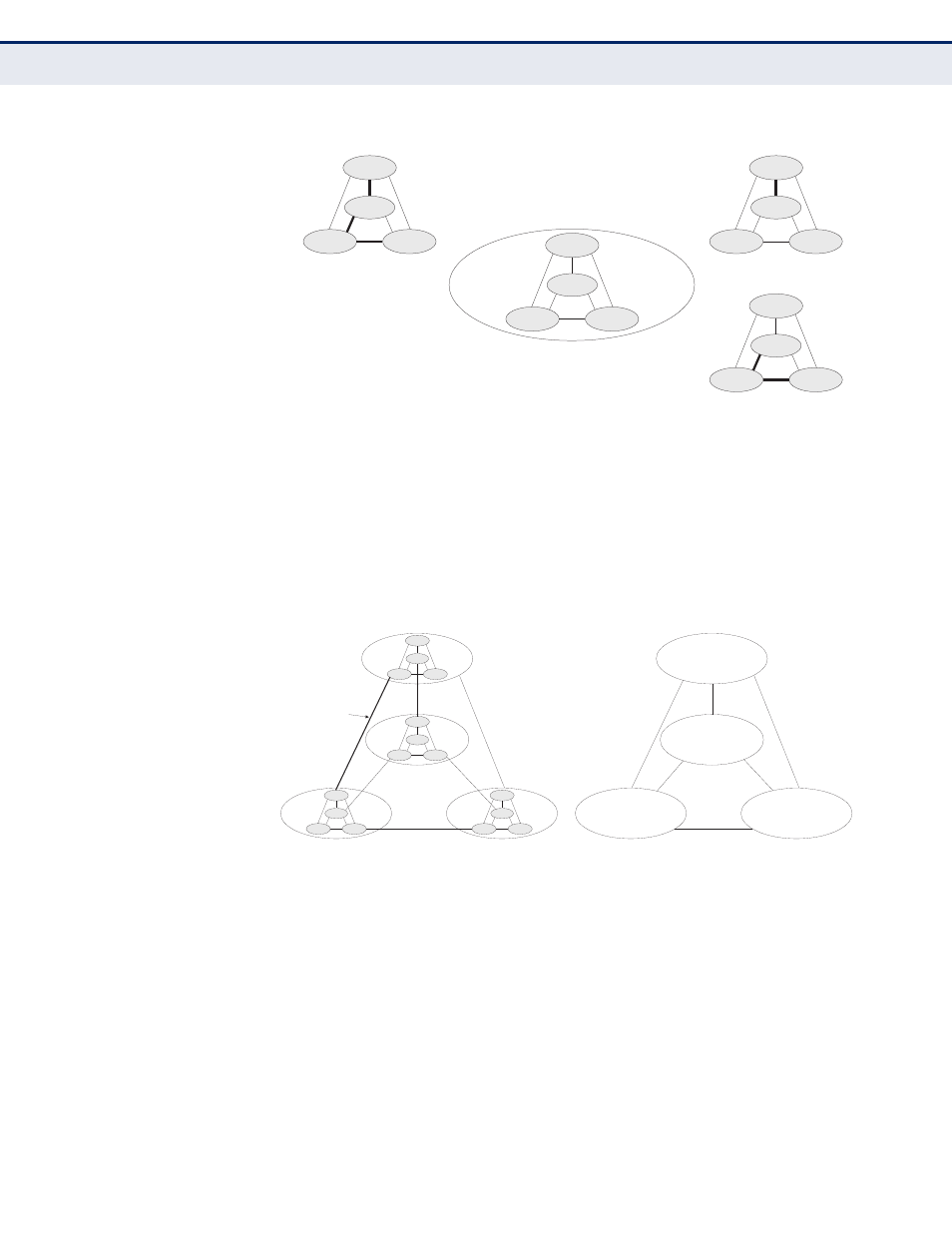
Figure 91: MSTP Region, Internal Spanning Tree, Multiple Spanning Tree
An MST Region consists of a group of interconnected bridges that have the
same MST Configuration Identifiers (including the Region Name, Revision
Level and Configuration Digest – see
"Configuring Multiple Spanning Trees"
). An MST Region may contain multiple MSTP Instances. An
Internal Spanning Tree (IST) is used to connect all the MSTP switches
within an MST region. A Common Spanning Tree (CST) interconnects all
adjacent MST Regions, and acts as a virtual bridge node for
communications with STP or RSTP nodes in the global network.
Figure 92: Common Internal Spanning Tree, Common Spanning Tree,
Internal Spanning Tree
MSTP connects all bridges and LAN segments with a single Common and
Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The CIST is formed as a result of the
running spanning tree algorithm between switches that support the STP,
RSTP, MSTP protocols.
Once you specify the VLANs to include in a Multiple Spanning Tree Instance
(MSTI), the protocol will automatically build an MSTI tree to maintain
connectivity among each of the VLANs. MSTP maintains contact with the
global network because each instance is treated as an RSTP node in the
Common Spanning Tree (CST).
Region R
IST
(for this Region)
MST 1
MST 2
Region 1
Region 4
Region 2
Region 3
CIST
IST
Region 1
Region 4
Region 2
Region 3
CST