Dhcp snooping, Dhcp s – Microsens MS453490M Management Guide User Manual
Page 342
C
HAPTER
14
| Security Measures
DHCP Snooping
– 342 –
W
EB
I
NTERFACE
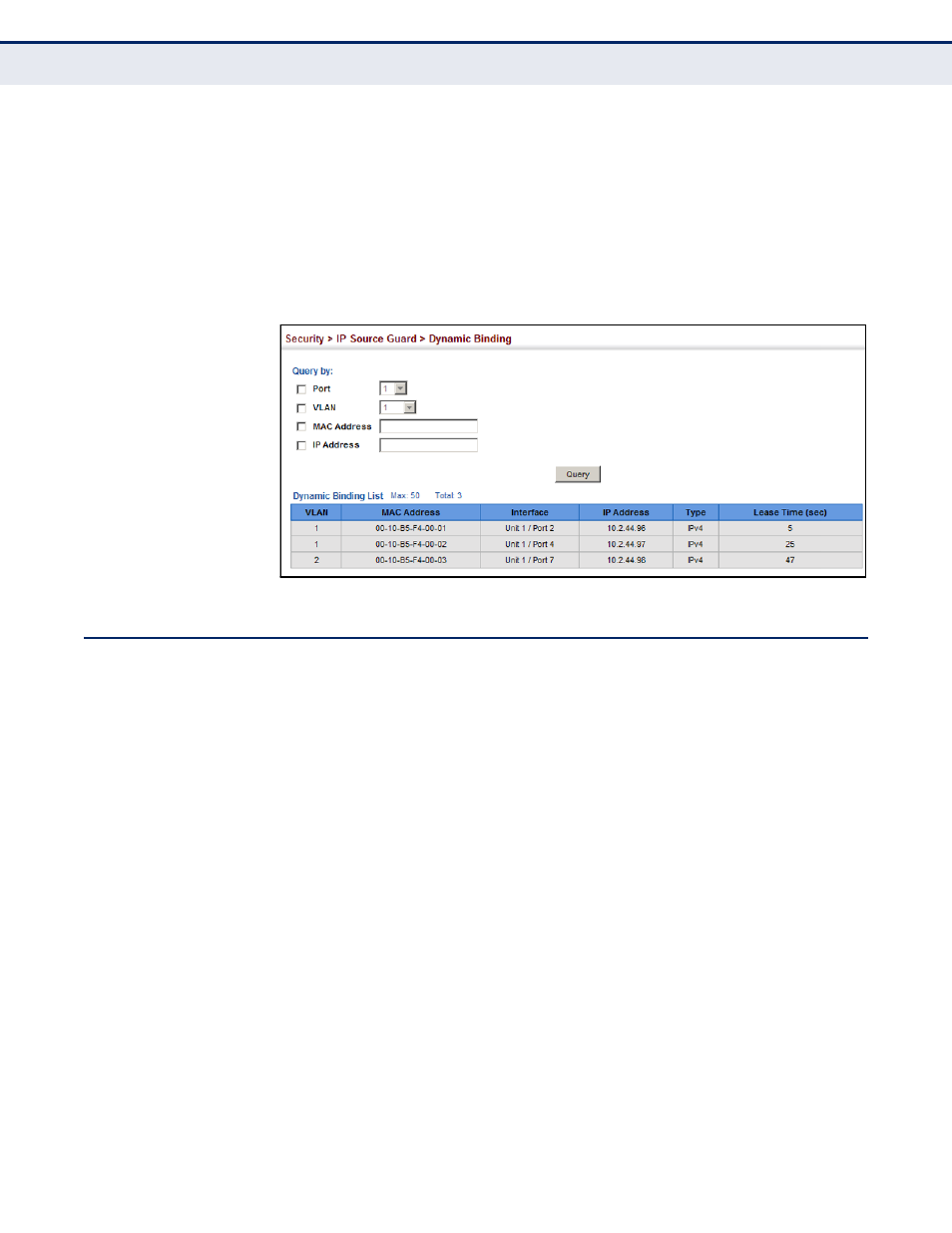
To display the binding table for IP Source Guard:
1.
Click Security, IP Source Guard, Dynamic Binding.
2.
Mark the search criteria, and enter the required values.
3.
Click Query
Figure 196: Showing the IP Source Guard Binding Table
DHCP S
NOOPING
The addresses assigned to DHCP clients on insecure ports can be carefully
controlled using the dynamic bindings registered with DHCP Snooping (or
using the static bindings configured with IP Source Guard). DHCP snooping
allows a switch to protect a network from rogue DHCP servers or other
devices which send port-related information to a DHCP server. This
information can be useful in tracking an IP address back to a physical port.
C
OMMAND
U
SAGE
DHCP Snooping Process
◆
Network traffic may be disrupted when malicious DHCP messages are
received from an outside source. DHCP snooping is used to filter DHCP
messages received on a non-secure interface from outside the network
or fire wall. When DHCP snooping is enabled globally and enabled on a
VLAN interface, DHCP messages received on an untrusted interface
from a device not listed in the DHCP snooping table will be dropped.
◆
Table entries are only learned for trusted interfaces. An entry is added
or removed dynamically to the DHCP snooping table when a client
receives or releases an IP address from a DHCP server. Each entry
includes a MAC address, IP address, lease time, VLAN identifier, and
port identifier.