Igmp proxying – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 102
86
As shown in
, on an SSM network, Host A, Host B and Host C are running IGMPv1, IGMPv2
and IGMPv3 respectively. To provide SSM service for all the hosts if IGMPv3 is not available on Host A
and Host B, you must configure the IGMP SSM mapping feature on Router A.
With the IGMP SSM mapping feature configured, when Router A receives an IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 report,
it checks the multicast group address G carried in the message:
•
If G is not in the SSM group range, Router A cannot provide the SSM service but can provide the
ASM service.
•
If G is in the SSM group range but no IGMP SSM mappings that correspond to the multicast group
G have been configured on Router A, Router A cannot provide SSM service and drops the message.
•
If G is in the SSM group range and the IGMP SSM mappings have been configured on Router A for
multicast group G, Router A translates the (*, G) information in the IGMP report into (G, INCLUDE,
(S1, S2...)) information based on the configured IGMP SSM mappings and provides SSM service
accordingly.
NOTE:
The IGMP SSM mapping feature does not process IGMPv3 reports.
For more information about the SSM group range, see "Configuring PIM."
IGMP proxying
In a simple tree-shaped topology, it is not necessary to configure multicast routing protocols, such as PIM,
on edge devices. Instead, you can configure IGMP proxying on these devices. With IGMP proxying
configured, the device serves as a proxy for the downstream hosts to send IGMP messages, maintain
group memberships, and implement multicast forwarding based on the memberships. In this case, each
edge device is a host but no longer a PIM neighbor to the upstream device.
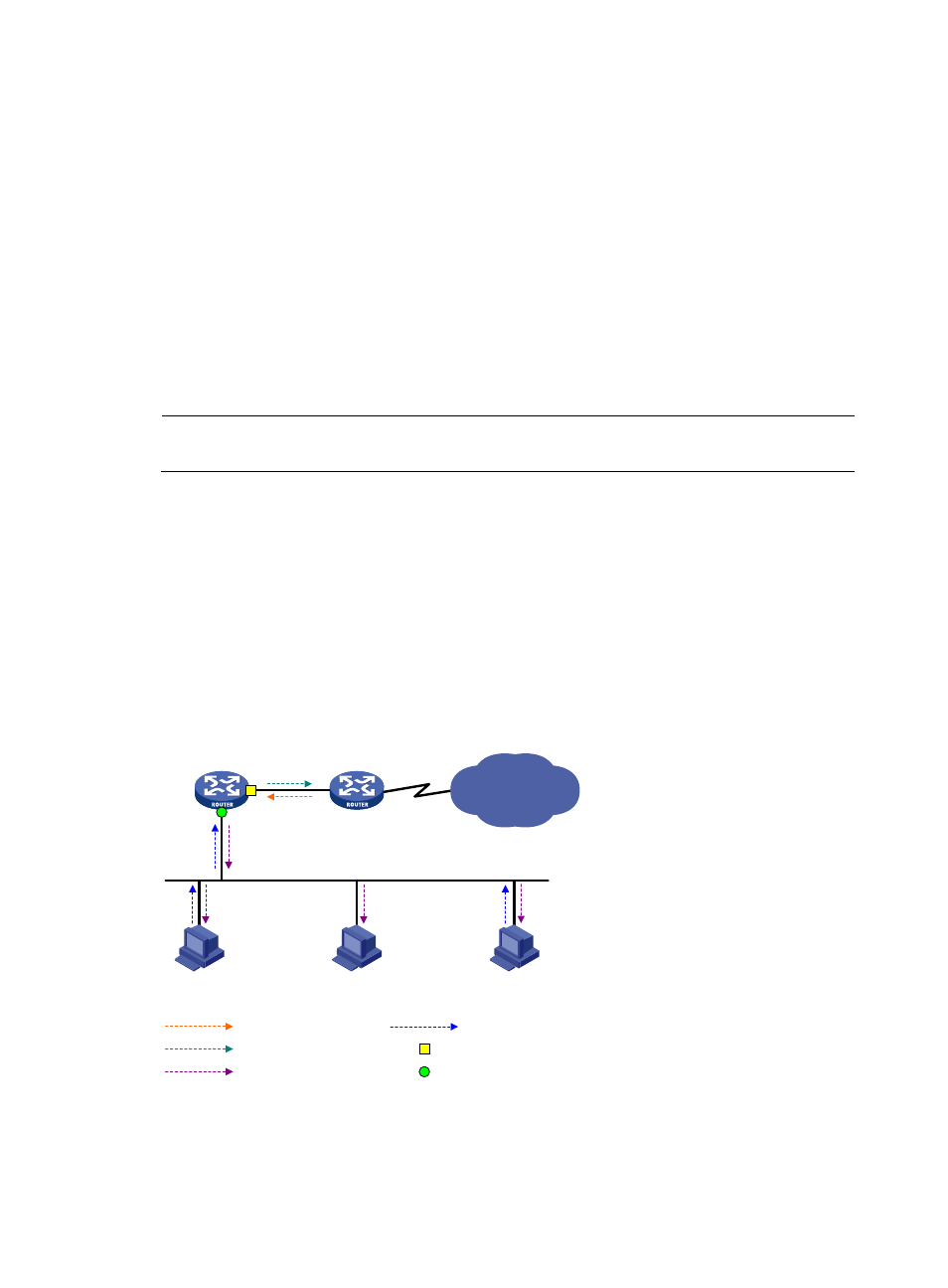
Figure 33 Network diagram
As shown in
, the following types of interfaces are defined on an IGMP proxy device:
•
Upstream interface—Also called the "proxy interface." A proxy interface is an interface on which
IGMP proxying is configured. It is in the direction toward the root of the multicast forwarding tree.
Query from Router A
Report from Router B
Ethernet
Router interface
Host interface
Proxy & Querier
Router B
Querier
Router A
Host B
Receiver
Host A
Receiver
Host C
Query from Router B
Report from Host
PIM domain