Multicast protocols, Layer 3 multicast protocols – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 25
9
•
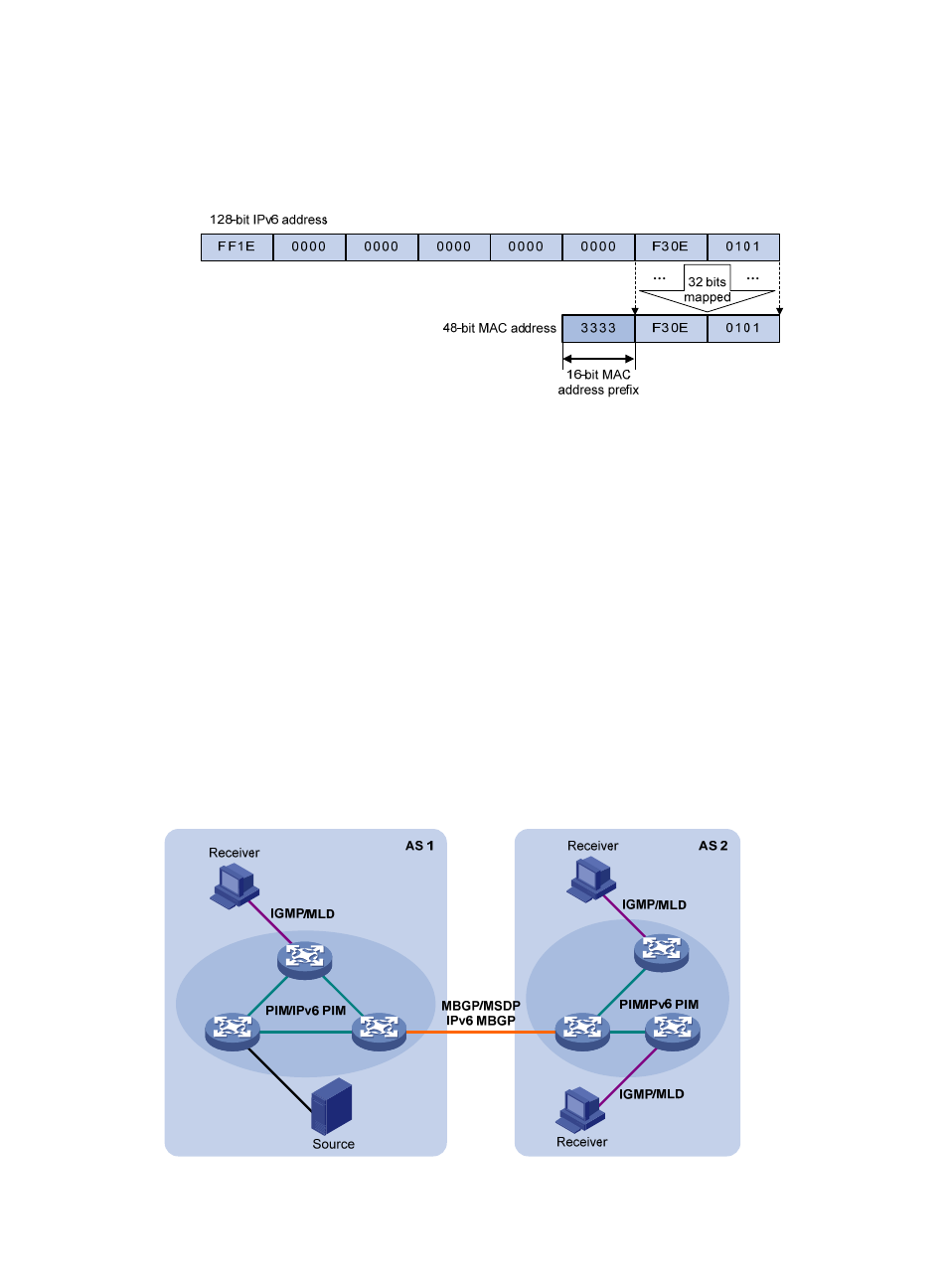
IPv6 multicast MAC addresses:
The most significant 16 bits of an IPv6 multicast MAC address are 0x3333. The least significant
32 bits are the least significant 32 bits of a multicast IPv6 address.
Figure 7 An example of IPv6-to-MAC address mapping
Multicast protocols
Generally, Layer 3 multicast refers to IP multicast working at the network layer. The corresponding
multicast protocols are Layer 3 multicast protocols, which include IGMP, MLD, PIM, IPv6 PIM, MSDP,
MBGP, IPv6 MBGP. Layer 2 multicast refers to IP multicast working at the data link layer. The
corresponding multicast protocols are Layer 2 multicast protocols, which include IGMP snooping, MLD
snooping, PIM snooping, IPv6 PIM snooping, multicast VLAN, and IPv6 multicast VLAN.
IGMP snooping, PIM snooping, multicast VLAN, IGMP, PIM, MSDP, and MBGP are for IPv4, and MLD
snooping, IPv6 PIM snooping, IPv6 multicast VLAN, MLD, IPv6 PIM, and IPv6 MBGP are for IPv6.
This section provides only general descriptions about applications and functions of the Layer 2 and Layer
3 multicast protocols in a network. For more information about these protocols, see the related chapters.
Layer 3 multicast protocols
Layer 3 multicast protocols include multicast group management protocols and multicast routing
protocols.
Figure 8 Positions of Layer 3 multicast protocols