H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 265
249
remote PE device and transmitted in that VPN site. VPN multicast data flows are forwarded across the
public network differently in the following circumstances:
1.
If PIM-DM or PIM-SSM is running in the VPN, the multicast source forwards multicast data to the
receivers along the VPN SPT across the public network.
2.
When PIM-SM is running in the VPN:
{
Before SPT switchover, if the multicast source and the VPN RP are in different sites, the multicast
source forwards VPN multicast data to the VPN RP along the VPN SPT across the public network.
If the VPN RP and the receiver are in different sites, the VPN RP forwards VPN multicast traffic
to the receiver along the VPN RPT over the public network.
{
After SPT switchover, if the multicast source and the receiver are in different sites, the multicast
source forwards VPN multicast data to the receiver along the VPN SPT across the public
network.
3.
When BIDIR-PIM is running in the VPN, if the multicast source and the VPN RP are in different sites,
the multicast source sends multicast data to the VPN RP across the public network along the
source-side RPT. If the VPN RP and the receivers are in different sites, the VPN RP forwards the
multicast data to the receivers across the public network along the receiver-side RPT.
For more information about RPT-to-SPT switchover, see "Configuring PIM."
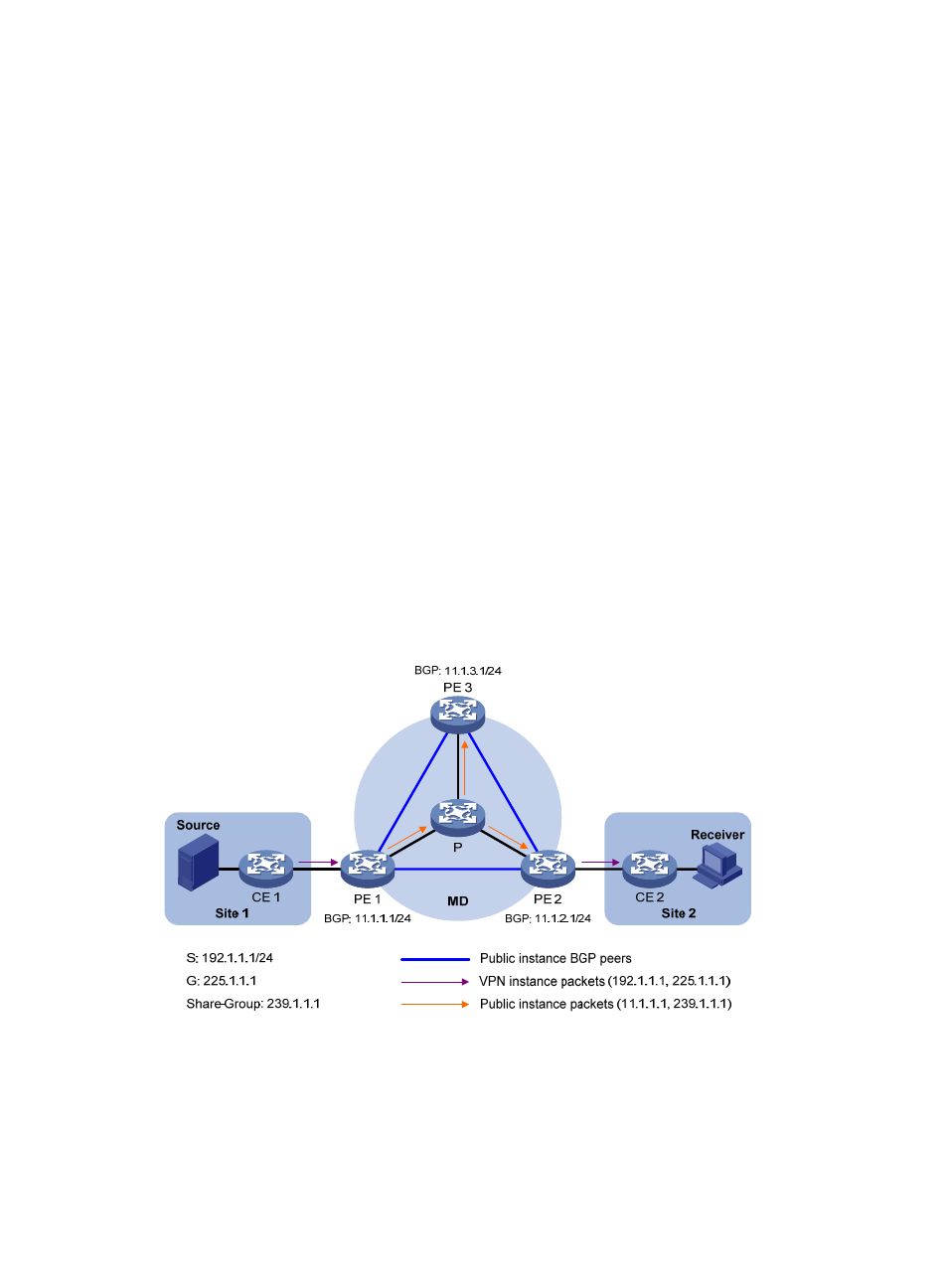
The following example explains how multicast data packets are delivered based on the share-MDT when
PIM-DM is running in both the public network and the VPN network.
As shown in
, PIM-DM is running in both the public network and the VPN sites, Receiver of the
VPN multicast group G 225.1.1.1 in Site 2 is attached to CE 2, and Source in Site 1 sends multicast data
to multicast group G; the share-group address used to forward public network multicast data is 239.1.1.1.
Figure 73 Delivery of multicast data packets
The VPN multicast traffic is delivered across the public network as follows.
4.
Source sends customer multicast data (192.1.1.1, 225.1.1.1) to CE 1.
5.
CE 1 forwards the VPN multicast data along an SPT to CE 1, and the VPN instance on PE 1 checks
the MVRF. If the outgoing interface list of the forwarding entry contains an MTI, PE 1 processes the
VPN multicast data.. Now, the VPN instance on PE 1 considers that the VPN multicast data has
been sent out of the MTI.