Path cost, How stp works – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 168
1-3
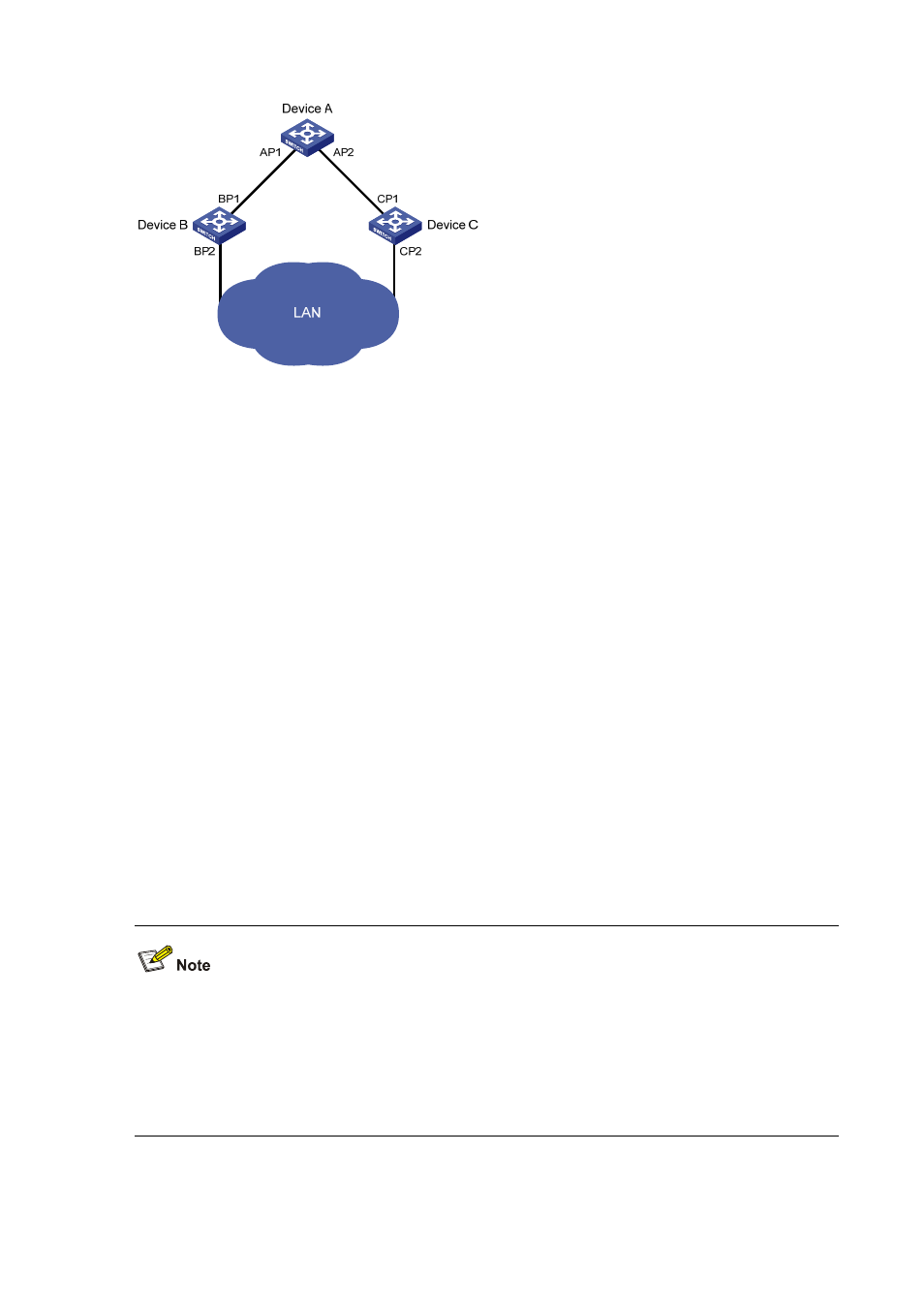
Figure 1-1
A schematic diagram of designated bridges and designated ports
Path cost
Path cost is a reference value used for link selection in STP. By calculating path costs, STP selects
relatively robust links and blocks redundant links, and finally prunes the network into a loop-free tree.
How STP works
The devices on a network exchange BPDUs to identify the network topology. Configuration BPDUs
contain sufficient information for the network devices to complete spanning tree calculation. Important
fields in a configuration BPDU include:
z
Root bridge ID: consisting of the priority and MAC address of the root bridge.
z
Root path cost: the cost of the path to the root bridge denoted by the root identifier from the
transmitting bridge.
z
Designated bridge ID: consisting of the priority and MAC address of the designated bridge.
z
Designated port ID: designated port priority plus port name.
z
Message age: age of the configuration BPDU while it propagates in the network.
z
Max age: maximum age of the configuration BPDU.
z
Hello time: configuration BPDU transmission interval.
z
Forward delay: the delay used by STP bridges to transit the state of the root and designated ports
to forwarding.
For simplicity, the descriptions and examples below involve only four fields of configuration BPDUs:
z
Root bridge ID (represented by device priority)
z
Root path cost (related to the rate of the link connecting the port)
z
Designated bridge ID (represented by device priority)
z
Designated port ID (represented by port name)