Diffserv model, Qos techniques overview, Applying qos techniques in a network – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 349
1-2
small-sized or edge networks, but not large-sized networks, for example, the core layer of the Internet,
where billions of flows are present.
DiffServ Model
The differentiated service (DiffServ) model is a multiple-service model that can satisfy diverse QoS
requirements. Unlike IntServ, DiffServ does not require an application to signal the network to reserve
resources before sending data. DiffServ is easy to implement and extend.
All QoS techniques in this document are based on the Diff-Serv model.
QoS Techniques Overview
The QoS techniques fall into traffic classification, traffic policing, traffic shaping, line rate, congestion
management, and congestion avoidance. The following part briefly introduces these QoS techniques.
Applying QoS Techniques in a Network
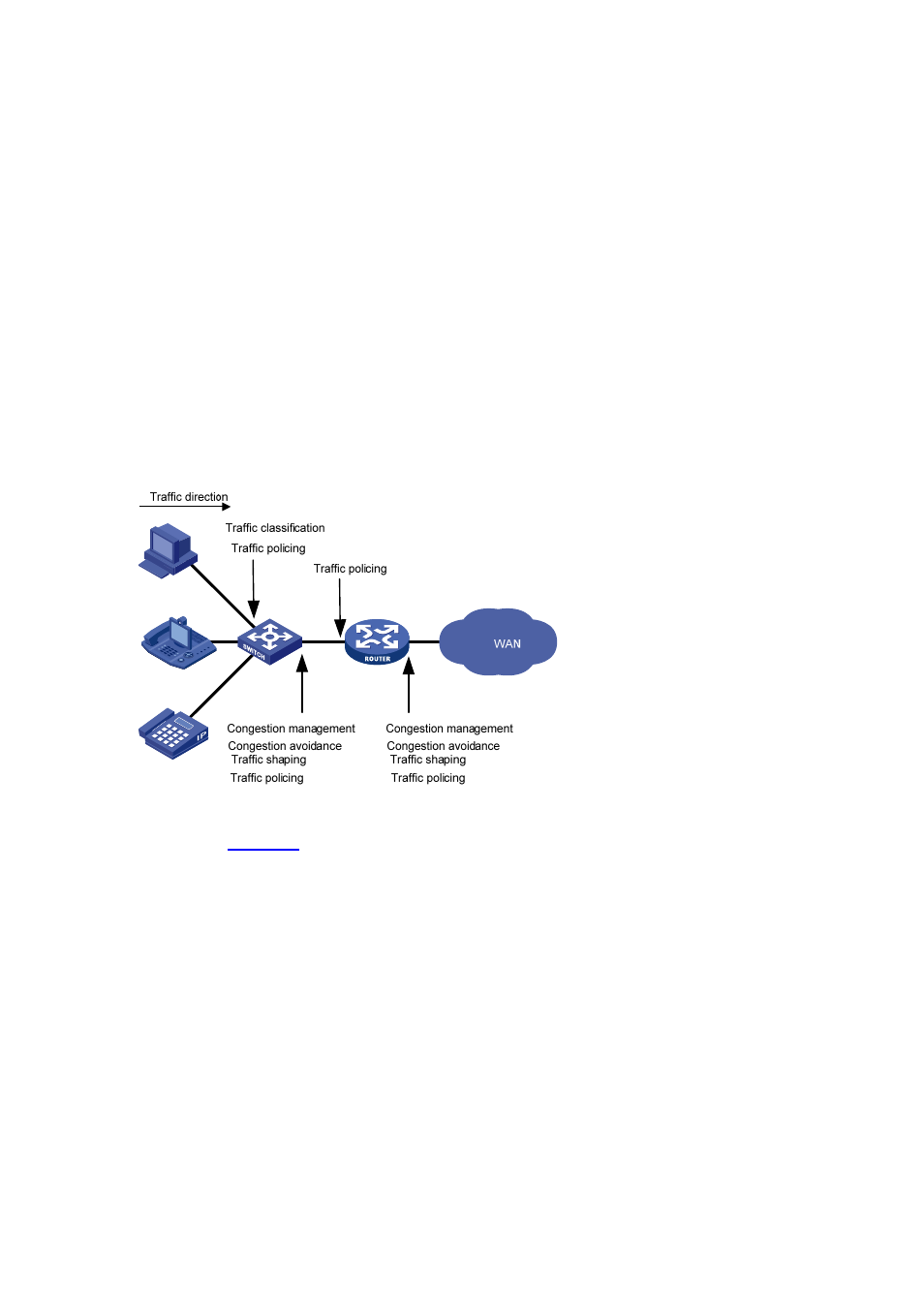
Figure 1-1 Position of the QoS techniques in a network
As shown in
, traffic classification, traffic shaping, traffic policing, congestion management,
and congestion avoidance mainly implement the following functions:
z
Traffic classification uses certain match criteria to assign packets with the same characteristics to a
class. Based on classes, you can provide differentiated services.
z
Traffic policing polices flows entering or leaving a device, and imposes penalties on traffic flows
that exceed the pre-set threshold to prevent aggressive use of network resources. You can apply
traffic policing to both incoming and outgoing traffic of a port.
z
Traffic shaping proactively adapts the output rate of traffic to the network resources available on
the downstream device to eliminate packet drops. Traffic shaping usually applies to the outgoing
traffic of a port.
z
Congestion management provides a resource scheduling policy to determine the packet
forwarding sequence when congestion occurs. Congestion management usually applies to the
outgoing traffic of a port.
z
Congestion avoidance monitors the network resource usage and is usually applied to the outgoing
traffic of a port. As congestion worsens, congestion avoidance actively reduces the queue length
by dropping packets.