H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 33
1-19
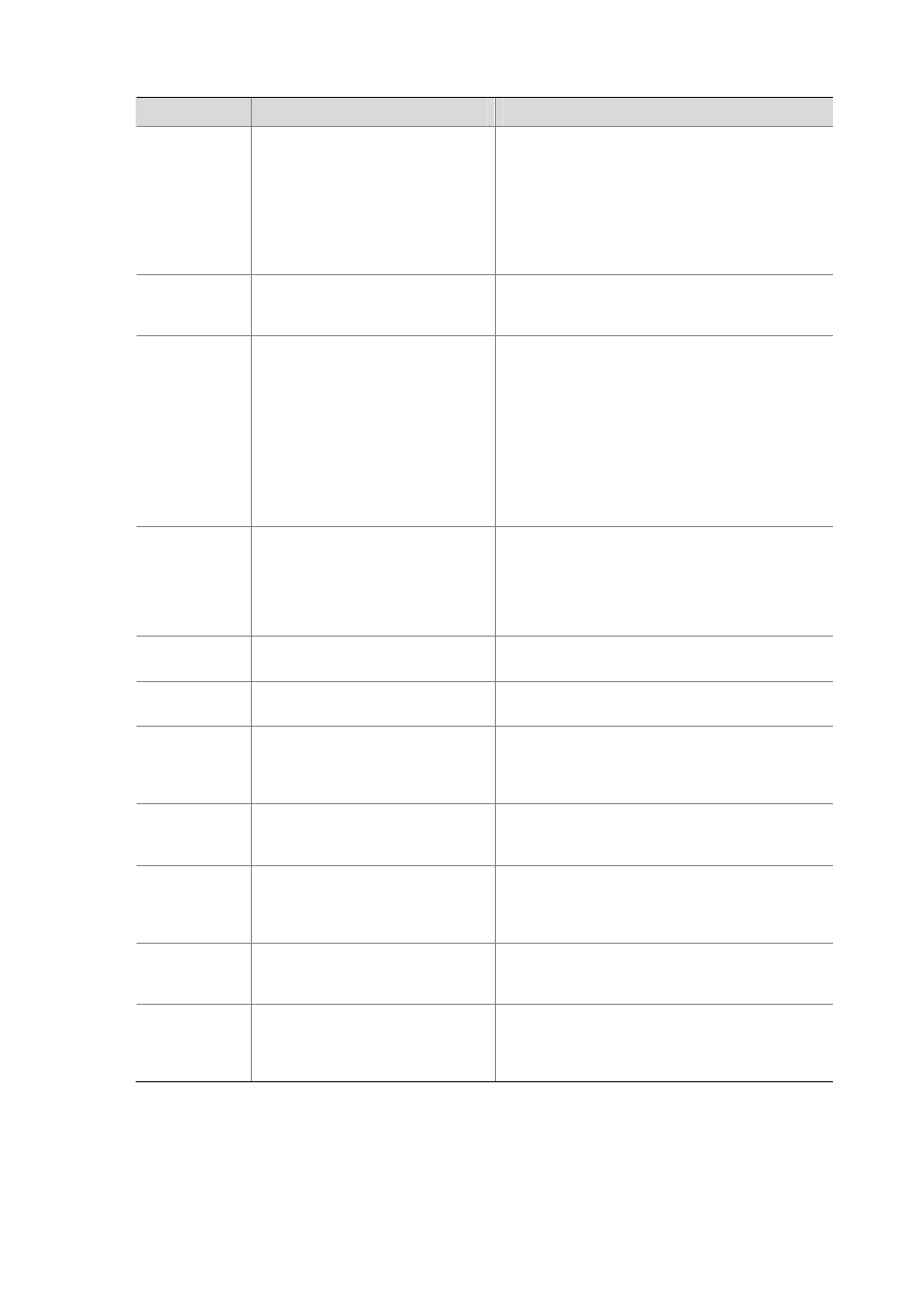
Character
Meaning
Remarks
[ ]
Matches a single character
contained within the brackets.
For example, [16A] matches a string containing any
character among 1, 6, and A; [1-36A] matches a
string containing any character among 1, 2, 3, 6, and
A (- is a hyphen).
“]” can be matched as a common character only
when it is put at the beginning of characters within
the brackets, for example [ ]string]. There is no such
limit on “[”.
( )
A character group. It is usually used
with “+” or “*”.
For example, (123A) means a character group
“123A”; “408(12)+” matches 40812 or 408121212.
But it does not match 408.
\index
Repeats the character string
specified by the index. A character
string refers to the string within ()
before \. index refers to the
sequence number (starting from 1
from left to right) of the character
group before \. If only one character
group appears before \, index can
only be 1; if n character groups
appear before index, index can be
any integer from 1 to n.
For example, (string)\1 repeats string, and thus a
matching string must contain stringstring.
(string1)(string2)\2 repeats string2, and thus a
matching string must contain string1string2string2.
(string1)(string2)\1\2 repeats string1 and string2
respectively, and thus a matching string must
contain string1string2string1string2.
[^]
Matches a single character not
contained within the brackets.
For example, [^16A] means to match a string
containing any character except 1, 6 or A, and the
matching string can also contain 1, 6 or A, but cannot
contain these three characters only. For example,
[^16A] matches “abc” and “m16”, but not 1, 16, or
16A.
\<string
Matches a character string starting
with string.
For example, “\<do” matches word “domain” and
string “doa”.
string\>
Matches a character string ending
with string.
For example, “do\>” matches word “undo” and string
“abcdo”.
\bcharacter2
Matches character1character2.
character1 can be any character
except number, letter or underline,
and \b equals [^A-Za-z0-9_].
For example, “\ba” matches “-a” with “-“ being
character1, and “a” being character2, but it does not
match “2a” or “ba”.
\Bcharacter
Matches a string containing
character, and no space is allowed
before character.
For example, “\Bt” matches “t” in “install”, but not “t”
in “big top”.
character1\w
Matches character1character2.
character2 must be a number, letter,
or underline, and \w equals
[^A-Za-z0-9_].
For example, “v\w” matches “vlan”, with “v” being
character1, and “l” being character2. v\w also
matches “service”, with “i” being character2.
\W Equals
\b.
For example, “\Wa” matches “-a”, with “-” being
character1, and “a” being character2, but does not
match “2a” or “ba”.
\
Escape character. If a special
character listed in this table follows \,
the specific meaning of the character
is removed.
For example, “\\” matches a string containing “\”, “\^”
matches a string containing “^”, and “\\b” matches a
string containing “\b”.