Layer 2 multicast protocols, Multicast packet forwarding mechanism – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 304
1-10
mature intra-domain multicast routing protocols, protocol independent multicast (PIM) is a popular
one. Based on the forwarding mechanism, PIM comes in two modes – dense mode (often referred
to as PIM-DM) and sparse mode (often referred to as PIM-SM).
z
An inter-domain multicast routing protocol is used for delivery of multicast information between two
ASs. So far, mature solutions include multicast source discovery protocol (MSDP) and multicast
border gateway protocol (MBGP). MSDP is used to propagate multicast source information among
different ASs, while MBGP, an extension of the Multi-protocol Border Gateway Protocol (MP-BGP),
is used for exchanging multicast routing information among different ASs.
For the SSM model, multicast routes are not divided into inter-domain routes and intra-domain routes.
Since receivers know the position of the multicast source, channels established through PIM-SM are
sufficient for multicast information transport.
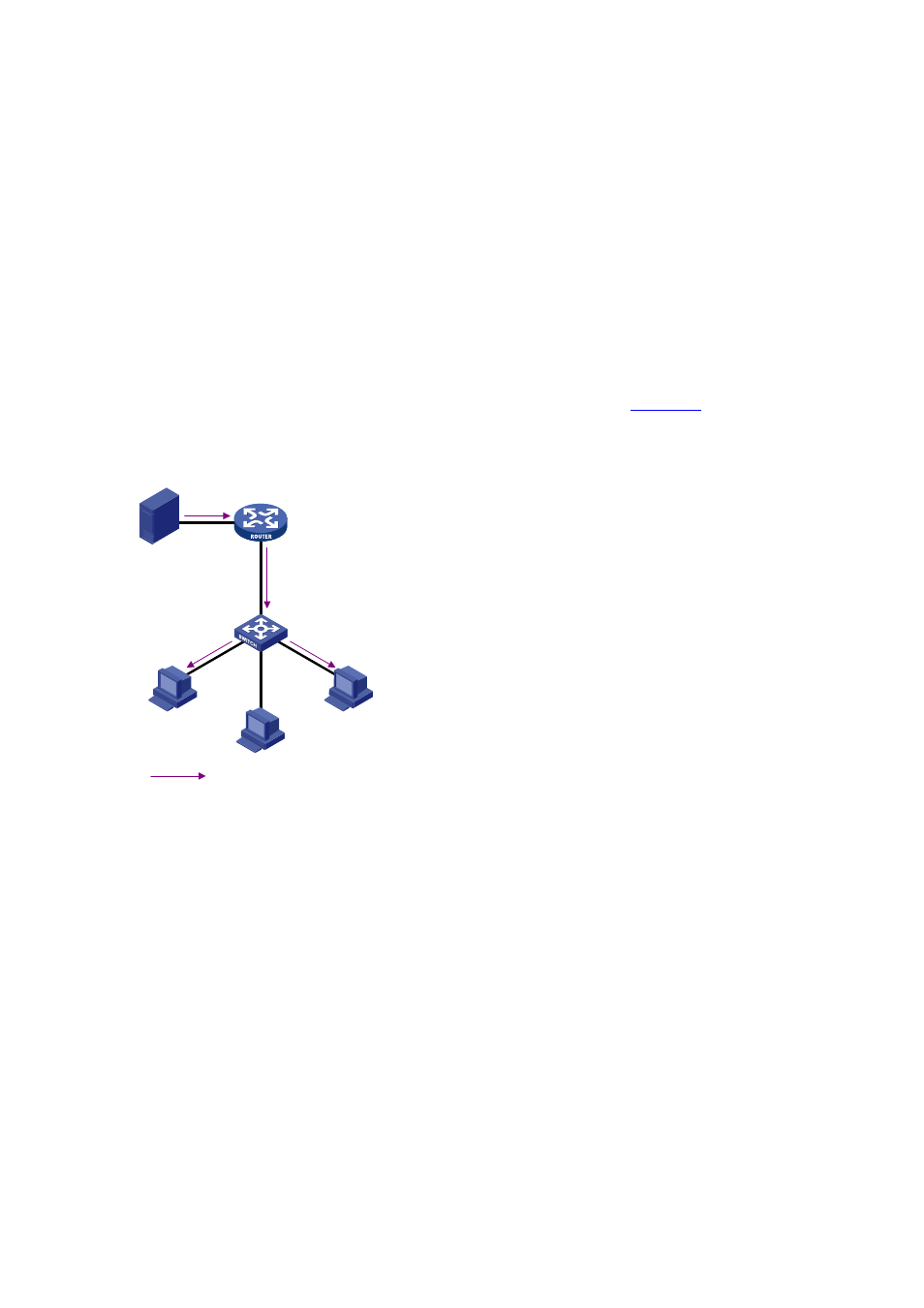
Layer 2 multicast protocols
Layer 2 multicast protocols include IGMP Snooping and multicast VLAN.
shows where these
protocols are in the network.
Figure 1-6 Position of Layer 2 multicast protocols
Source
Receiver
Receiver
IPv4 multicast packets
IGMP Snooping
Multicast VLAN
1) IGMP
Snooping
Running on Layer 2 devices, Internet Group Management Protocol Snooping (IGMP Snooping) is
multicast constraining mechanisms that manage and control multicast groups by listening to and
analyzing IGMP messages exchanged between the hosts and Layer 3 multicast devices, thus
effectively controlling the flooding of multicast data in a Layer 2 network.
2) Multicast
VLAN
In the traditional multicast-on-demand mode, when users in different VLANs on a Layer 2 device need
multicast information, the upstream Layer 3 device needs to forward a separate copy of the multicast
data to each VLAN of the Layer 2 device. With the multicast VLAN feature enabled on the Layer 2
device, the Layer 3 multicast device needs to send only one copy of multicast to the multicast VLAN on
the Layer 2 device. This avoids waste of network bandwidth and extra burden on the Layer 3 device.
Multicast Packet Forwarding Mechanism
In a multicast model, a multicast source sends information to the host group identified by the multicast
group address in the destination address field of IP multicast packets. Therefore, to deliver multicast