Man-in-the-middle attack, Arp detection mechanism, Ip-to-mac bindings – H3C Technologies H3C S5120 Series Switches User Manual
Page 232
2-4
Man-in-the-middle attack
According to the ARP design, after receiving an ARP reply, a host adds the IP-to-MAC mapping of the
sender to its ARP mapping table. This design reduces the ARP traffic on the network, but also makes
ARP spoofing possible.
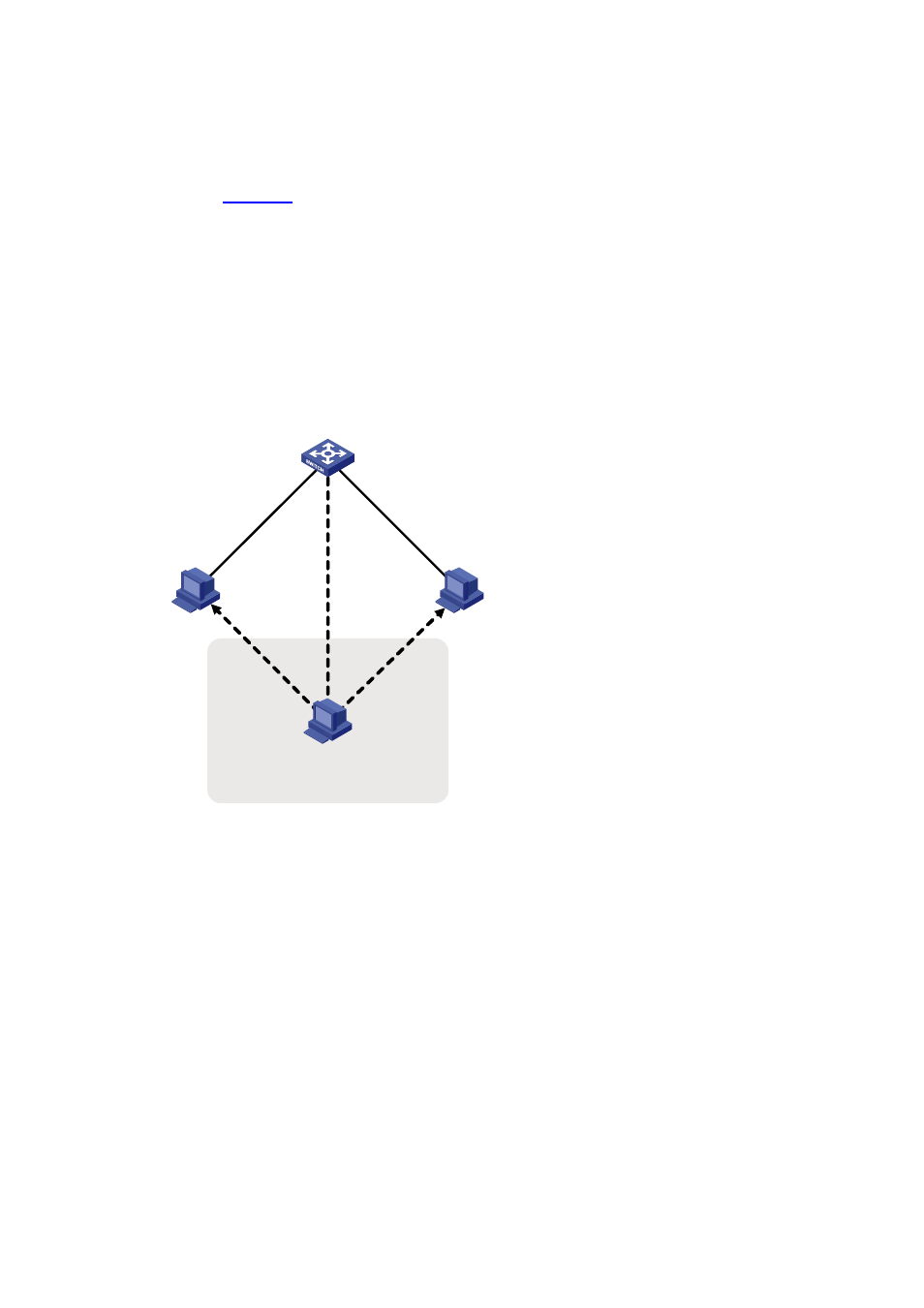
As shown in
, Host A communicates with Host C through a switch. After intercepting the traffic
between Host A and Host C, a hacker (Host B) forwards forged ARP replies to Host A and Host C
respectively. Upon receiving the ARP replies, the two hosts update the MAC address corresponding to
the peer IP address in their ARP tables with the MAC address of Host B (MAC_B). After that, Host B
establishes independent connections with Host A and Host C and relays messages between them,
deceiving them into believing that they are talking directly to each other over a private connection, while
the entire conversation is actually controlled by Host B. Host B may intercept and modify the
communication data. Such an attack is called a man-in-the-middle attack.
Figure 2-1 Man-in-the-middle attack
Switch
Host A
Host B
IP_ A
MAC_ A
IP_B
MAC_B
IP_C
MAC_C
Host C
Forged
ARP reply
Forged
ARP reply
ARP detection mechanism
With ARP detection enabled for a specific VLAN, ARP messages arrived on any interface in the VLAN
are redirected to the CPU to have their MAC and IP addresses checked. ARP messages that pass the
check are forwarded, and other ARP messages are discarded.
Enabling ARP Detection Based on DHCP Snooping Entries/802.1X Security
Entries/Static IP-to-MAC Bindings
With this feature enabled, the device compares the source IP and MAC addresses of an ARP packet
received from the VLAN against the DHCP snooping entries, 802.1X security entries, or static
IP-to-MAC binding entries. You can specify a detection type or types as needed.
1) After you enable ARP detection based on DHCP snooping entries for a VLAN,
z
Upon receiving an ARP packet from an ARP untrusted port, the device compares the ARP packet
against the DHCP snooping entries. If a match is found, that is, the parameters (such as IP address,