Area based ospf network partition, Network partition, Backbone area and virtual links – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 78
62
Adjacency: Two OSPF neighbors establish an adjacency relationship to synchronize their LSDBs.
Therefore, any two neighbors without exchanging route information do not establish an adjacency.
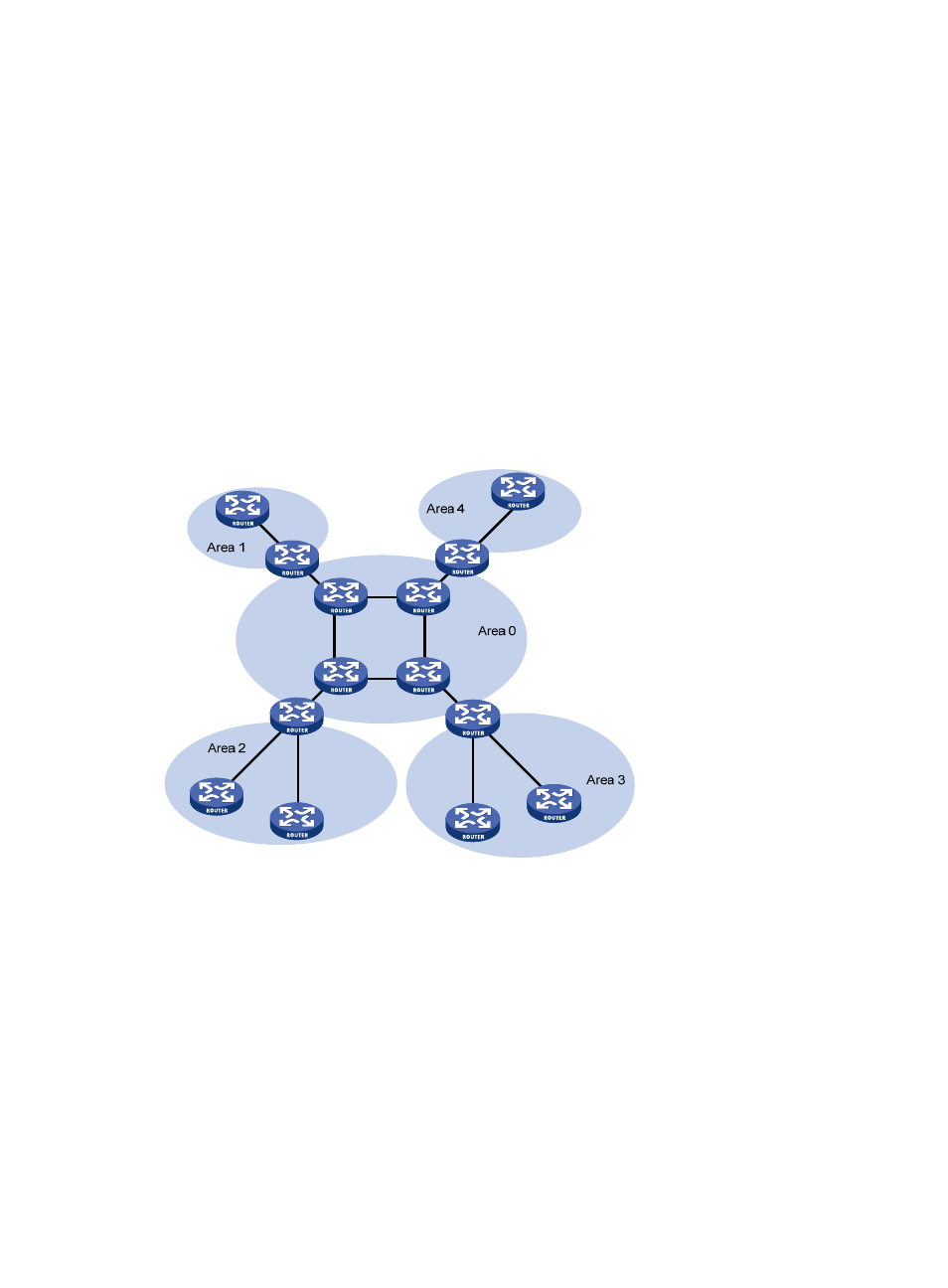
Area based OSPF network partition
Network partition
In a large OSPF routing domain, the LSDB becomes very huge and SPF computation consumes many
storage and CPU resources.
In addition, because topology changes can easily occur, OSPF packets generated for route information
synchronization are enormous, occupying excessive bandwidth.
To solve these problems, OSPF splits an AS into multiple areas, each of which is identified by an area ID.
The boundaries between areas are routers rather than links. A network segment (or a link) can only
reside in one area. An OSPF interface must be specified to belong to its attached area, as shown
in
Figure 17 Area based OSPF network partition
After network partition, ABRs perform route summarization to reduce the number of LSAs advertised to
other areas and minimize the effect of topology changes.
Backbone area and virtual links
Each AS has a backbone area that distributes routing information between none-backbone areas.
Routing information between non-backbone areas must be forwarded by the backbone area. OSPF
requires that:
•
All non-backbone areas must maintain connectivity to the backbone area.
•
The backbone area must maintain connectivity within itself.
In practice, the requirements may not be satisfied due to lack of physical links. OSPF virtual links can
solve this problem.