Shutdown, Pid loop setup – Super Systems 9130 Series User Manual
Page 24
Series 9130 Operations Manual Rev -
23
Shutdown
The Shutdown selection will display a screen asking whether or not to shutdown the interface of the SERIES
9130. When the operator interface is shutdown, the SERIES 9130 controller is still functioning. IT can be
monitored by connecting the ETHERNET connection to a laptop computer, using Internet Explorer, and
assigning a legitimate IP address. Choosing Yes displays a typical computer desktop screen with the Start
button in the bottom left-hand corner. The power to the operator interface can now be turned off without
upsetting any of the settings. Choosing No displays the initial Status Screen.
Note -Shutting down the
Operator Interface does not shutdown the SERIES 9130 Controller
.
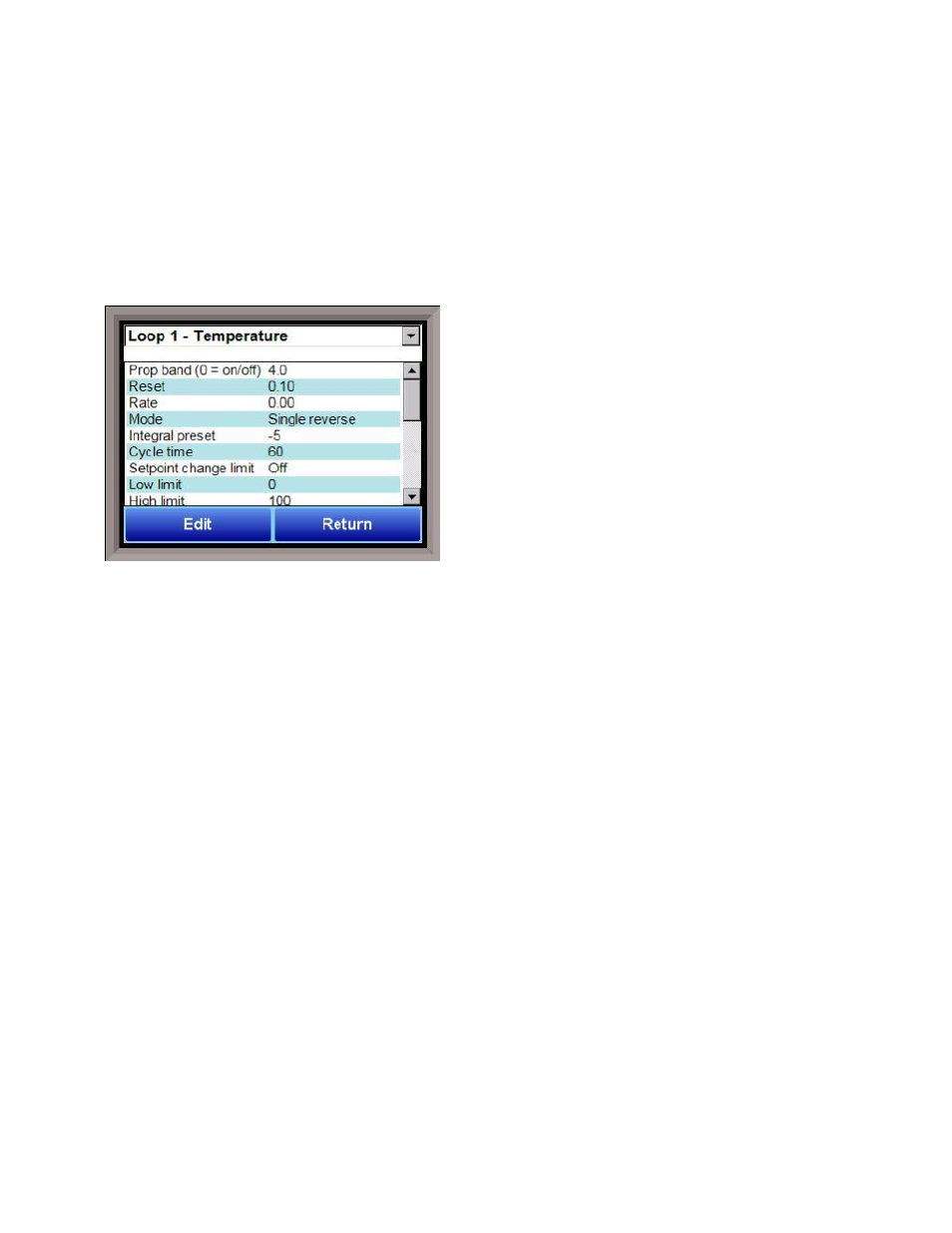
PID Loop Setup
PID is the tuning parameters entered for each Process
Variable loop.
Prop Band (0 for On/Off)
This is the proportional band field. P = Proportional
(Prop Band). This is a field in which you want to stay
around the setpoint. The range 0 – 3276.0.
Reset
This is the reset field. I = Integral (Reset). This is the
actual temperature being monitored over a period of
time and then averaged to keep within the Proportional
band. The reset is in repeats per minute. This affects the
output of the controller. It will be proportional to the
amount of time the error is present. This helps to eliminate offset. The range 0 – 327.67.
Rate
This is the rate field. D = Derivative (Rate). This is the sudden change or rate in the temperature. This rate
is in minutes. This affects the controller output which is proportional to the rate of change of the
measurement and will control the amount of output by time restraints. Thus derivative takes action to
inhibit more rapid changes of the measurement than proportional action. Derivative is often used to avoid
overshoot. The range 0 – 327.67. The rate is not typically used for heating/carbon.
Mode
This is the mode of the loop. The values are: Dual Reverse, Single Reverse, Dual Direct, or Single Direct.
Dual – This has two output relays which can increase and decrease to achieve the SP.
Single – This has one relay which works in only one direction to achieve the SP.
Direct - If the PV - SP equals a positive number and the output would bring the PV down toward setpoint
that is direct.
Reverse – If the PV - SP equals a negative number and the output would bring the PV up toward setpoint
then that is reverse
Example: If a 12 mA output drives a 0 degree F temperature (PV)
UP
to a 1200 degree F temperature (SP),
this would be
REVERSE
, and since this would take a
SINGLE
output from the controller, the Mode for the
Temperature Loop is Single Reverse.
Integral Preset
This field provides an offset for the starting point for PID control, also referred to as “Load Line” or “Manual
Reset”. The range is –100 to 100.
Cycle Time
This field is typically set to the valve travel time multiplied by 1.5. The range is 0 – 500.