Bestlogic application hints, Bestlogic application hints -9 – Basler Electric BE1-BPR User Manual
Page 115
9272000990 Rev J
BE1-BPR BESTlogic Programmable Logic
5-9
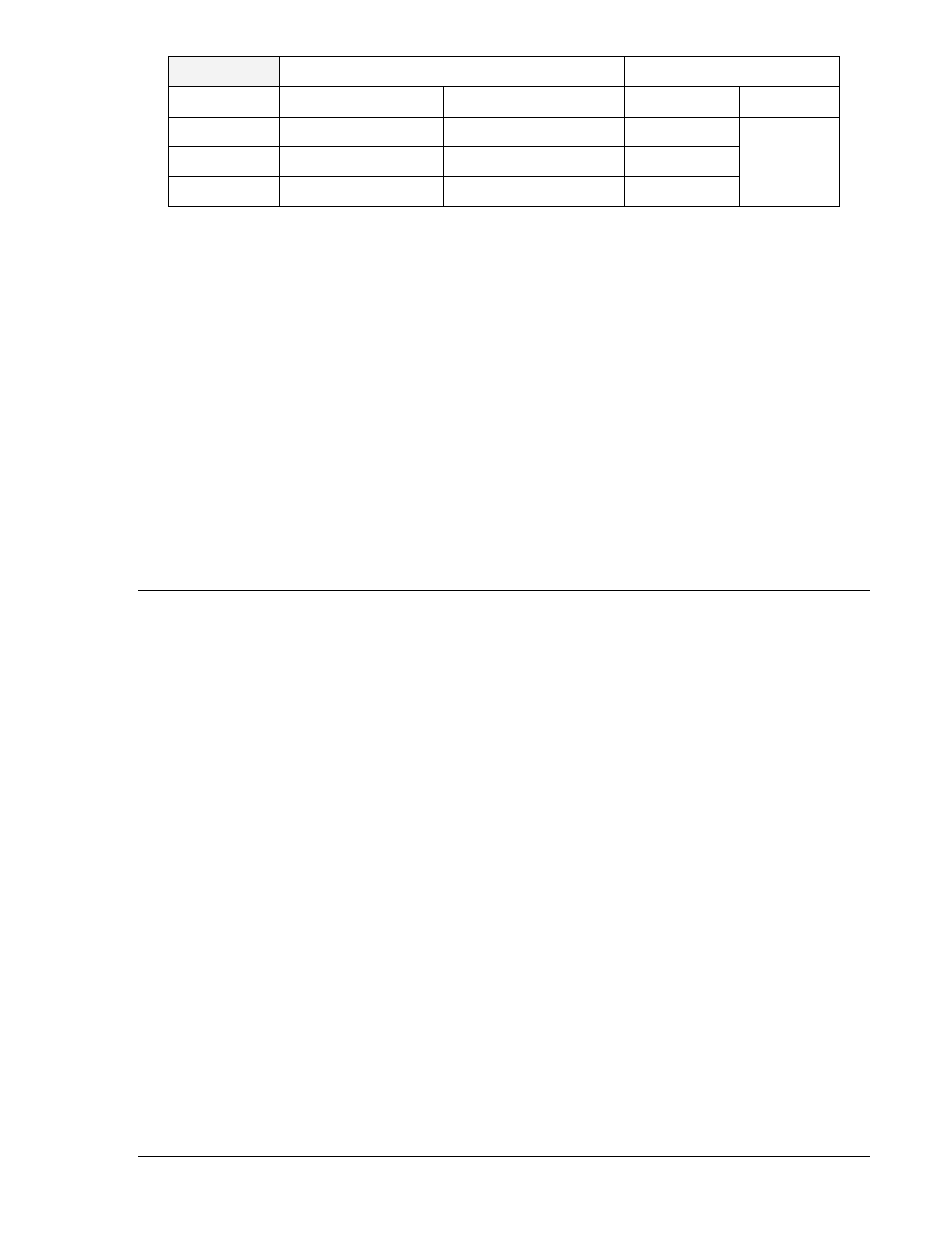
LI
Contact input logic
HMI Menu Branch: N/A
Parameter
Unit of Measure
Range
Increment
Default
#
N/A
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7
N/A
LI#=4,12
r
milliseconds
4 - 255
1
db
milliseconds
4 - 255
1
LI Command
Purpose:
Reads or programs contact input logic.
Syntax:
LI[#[=<r>,<db>]]
Comments:
Access area one password is required to change settings.
LI Command Example:
Configure input 3 for a contact recognition time of 10 milliseconds and a debounce time of 20
milliseconds.
LI3=10,20
The state of the contact sensing inputs is scanned twelve times per cycle. The time settings are converted
to the nearest multiple of the scan interval, which is determined by the nominal frequency setting (1.39
milliseconds at 60 hertz or 1.67 milliseconds at 50 hertz). For example, if the nominal frequency is 60
hertz, a recognition time setting of 4 milliseconds is rounded to 4.17 milliseconds, which is the nearest
multiple of the scan interval. In this case, a contact closure must be present on three consecutive scans of
the input state for it to be recognized and the BESTlogic input variable to change state from a 0 to 1.
BESTLOGIC APPLICATION HINTS
Preprogrammed protection schemes may provide additional inputs, outputs, or features that are not
needed for all applications. This is done so that a few schemes can be used in a large number of
applications with no special programming required. The unneeded inputs or outputs may be left open to
disable the function. Unused CT inputs should be shorted to minimize noise pickup.
Additional Breaker Failure inputs have been provided in many schemes for diagnostic reasons. Target
information can be provided for inputs as well as outputs, therefore the relay that caused the breaker
operation may be identified by requesting target information through the communications port. This is
especially useful when trying to remotely determine the cause of a problem when the relay that tripped
the breaker is an older, non-communicating relay.
When designing new protection schemes, avoid unnecessary confusion by maintaining consistency
wherever possible between function of the inputs and outputs in the new scheme and the preprogrammed
schemes. The preprogrammed schemes are consistent in the following functions:
IN1 (I1) = Breaker status contact (isolated input)
IN3 (I3) = Primary BFI (isolated input)
IN7 (I7) = External fault trigger to record fault records on enhanced relays
F1 = Always associated with phase fault detector
F2 = Always associated with neutral fault detector
ALM (OA) = Alarm output
OUT1 (O1) = Primary BFO - high speed (1/4 cycle pickup)
OUT2 (O2) = Secondary BFO
OUT3 (O5) = Retrip Output
TIMER1 (T1) = Always associated with primary BFO delay timer
TIMER2 (T2) = Always associated with alternate BFO delay timer
TIMER3 (T3) = Always associated with the control timer