3 ipv6 dcscm typical examples – PLANET XGS3-24040 User Manual
Page 426
Chapter 44 IPv6 Multicast Protocol
44-24
44.5.3 IPv6 DCSCM Typical Examples
1. Source control
In order to prevent an edge switch sends multicast data at will, we configure on the edge switch that only the
switch whose port is Ethernet1/5 can send multicast data, and the group of data should be ff1e::1. The uplink
port Ethernet1/25 can forward multicast data without being restricted, so we can configure as follows.
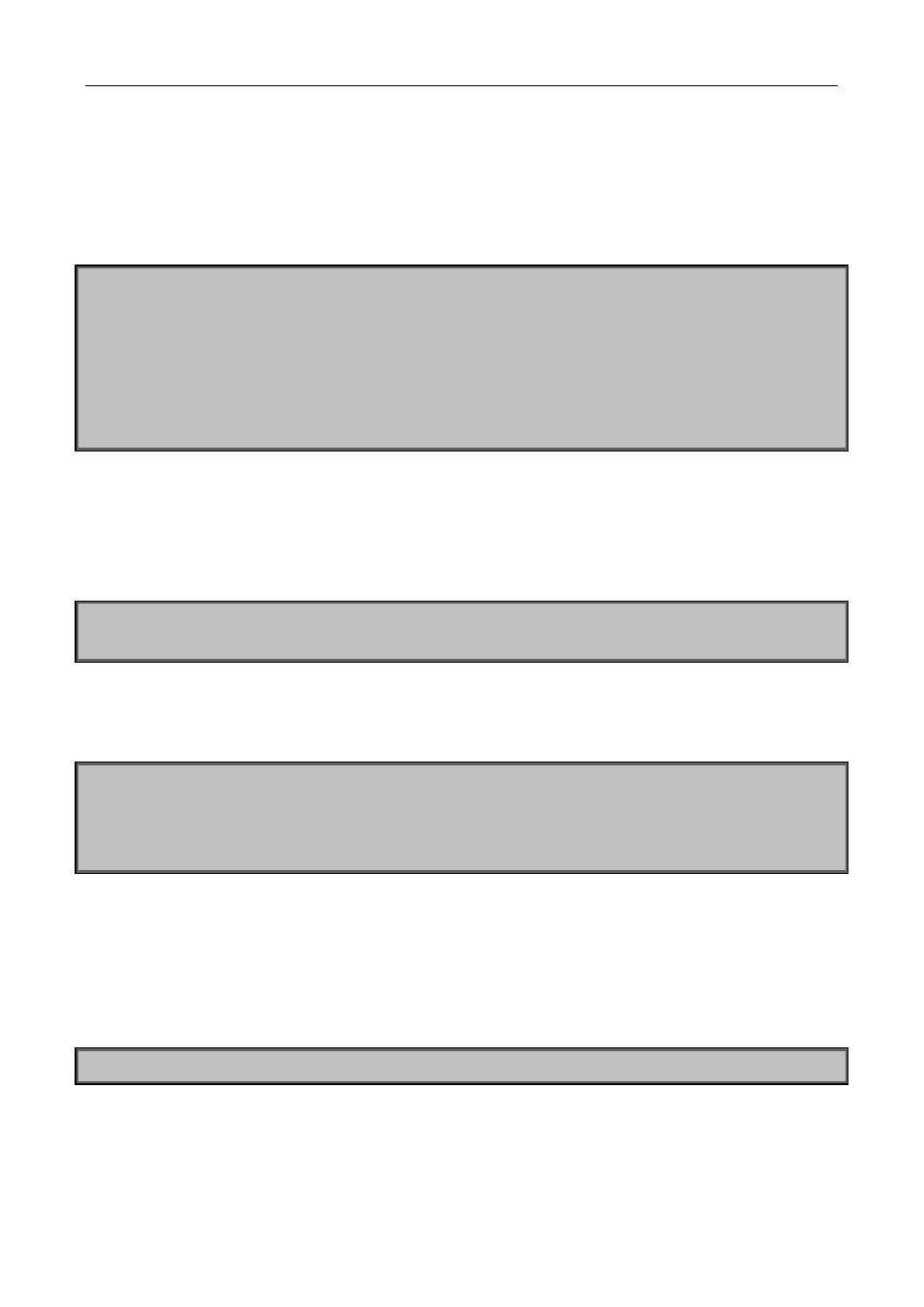
Switch(config)#ipv6 access-list 8000 permit any-source ff1e::1
Switch(config)#ipv6 access-list 8001 permit any any
Switch(config)#ipv6 multicast source-control
Switch(config)#interface Ethernet1/5
Switch(Config-If-Ethernet1/5)#ipv6 multicast source-control access-group 8000
Switch(config)#interface Ethernet1/25
Switch(Config-If-Ethernet1/25)#ipv6 multicast source-control access-group 8001
2. Destination control
We want to confine that the users of the segment whose address is fe80::203:fff:fe01:228a/64 can not join the
ff1e::1/64 group, so we can configure as follows:
First, enable MLD Snooping in the VLAN where it locates (in this example, it is VLAN2).
Switch(config)#ipv6 mld snooping
Switch(config)#ipv6 mld snooping vlan 2
Then configure relative destination control access list and configure specified IPv6 address to use this access
list.
Switch(config)#ipv6 access-list 9000 deny any ff1e::1/64
Switch(config)#ipv6 access-list 9000 permit any any
Switch(config)#multicast destination-control
Switch(config)#ipv6 multicast destination-control fe80::203:fff:fe01:228a/64 access-group 9000
Thus, the users of this segment can only join groups other than 2ff1e::1/64.
3.Multicast policy
Server 2008::1 is sending important multicast data in group ff1e::1, we can configure on its access switch as
follows:
Switch(config)#ipv6 multicast policy 2008::1/128 ff1e::1/128 cos 4
Thus this multicast flow will have a priority of 4, when it passes the TRUNK port of this switch to another
switch (generally speaking, it is a relatively high priority, the data with higher priority might be protocol data, if
a higher priority is set, when there is too much multicast data, the switch protocol might operate abnormally).