Configuring vlans, Overview, Vlan fundamentals – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 14
1
Configuring VLANs
In this documentation, EB and EC2 cards refer to the interface cards prefixed with EB and EC2,
respectively.
Overview
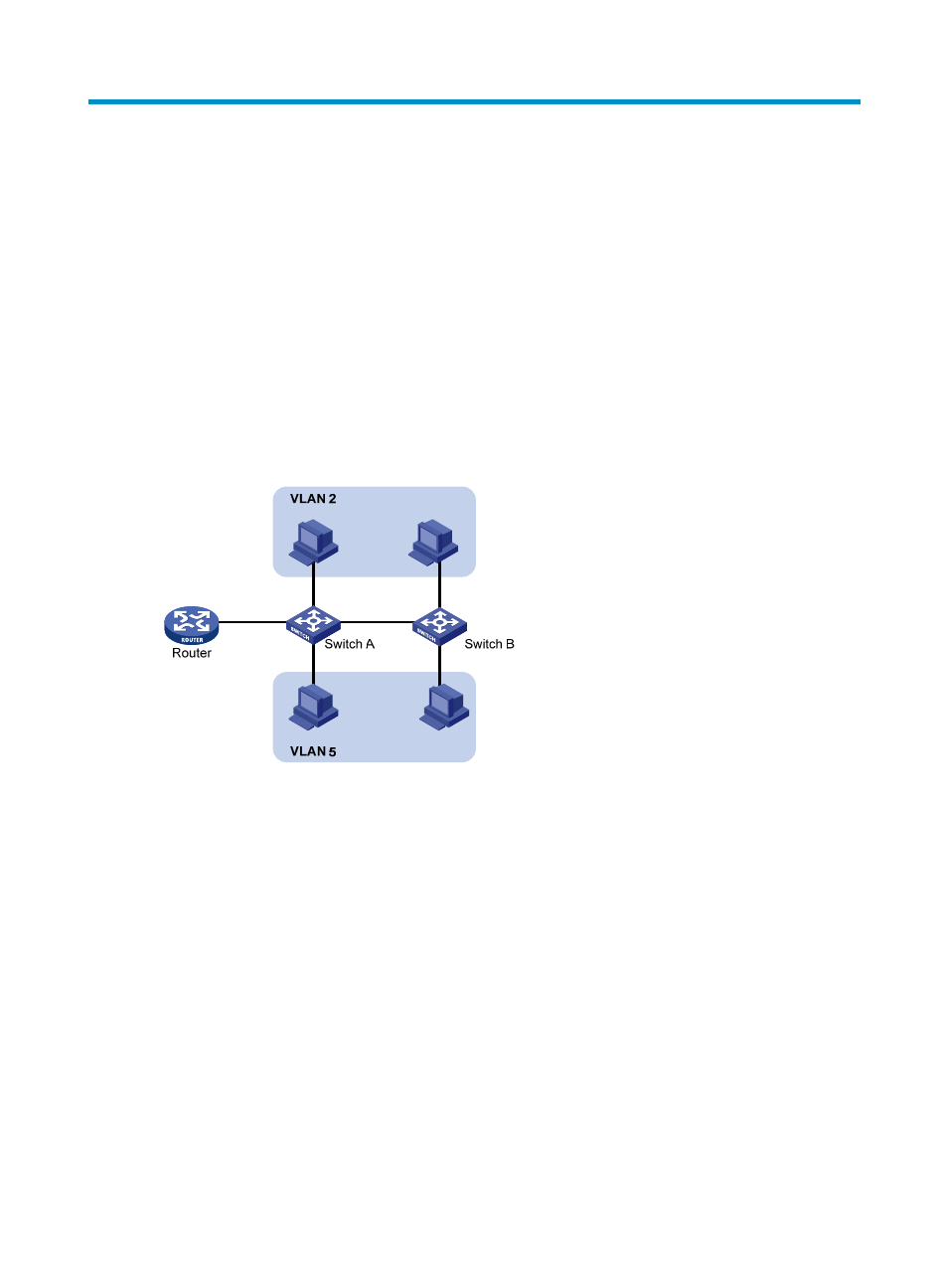
Ethernet is a network technology based on the Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect
(CSMA/CD) mechanism. As the medium is shared, collisions and excessive broadcasts are common on
Ethernet networks. To address the issue, virtual LAN (VLAN) was introduced to break a LAN down into
separate VLANs. VLANs are isolated from each other at Layer 2. A VLAN is a bridging domain, and all
broadcast traffic is contained within it, as shown in
Figure 1 A VLAN diagram
A VLAN is logically divided on an organizational basis rather than on a physical basis. For example, all
workstations and servers used by a particular workgroup can be connected to the same LAN, regardless
of their physical locations.
VLAN technology delivers the following benefits:
•
Confining broadcast traffic within individual VLANs. This reduces bandwidth waste and improves
network performance.
•
Improving LAN security. By assigning user groups to different VLANs, you can isolate them at Layer
2. To enable communication between VLANs, routers or Layer 3 switches are required.
•
Flexible virtual workgroup creation. As users from the same workgroup can be assigned to the same
VLAN regardless of their physical locations, network construction and maintenance is much easier
and more flexible.
VLAN fundamentals
To enable a switch to identify frames of different VLANs, a VLAN tag field is inserted into the data link
layer encapsulation.