H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 204
7-3
Router A and Router B are MSDP peers on common multicast routers. Such MSDP peers just forward
received SA messages.
In a PIM-SM network running the BSR mechanism, the RP is dynamically elected from C-RPs. To
enhance network robustness, a PIM-SM network typically has more than one C-RP. As the RP
election result is unpredictable, MSDP peering relationships should be built among all C-RPs so that
the winner C-RP is always on the "MSDP interconnection map”, while loser C-RPs will assume the
role of common PIM-SM routers on the “MSDP interconnection map”.
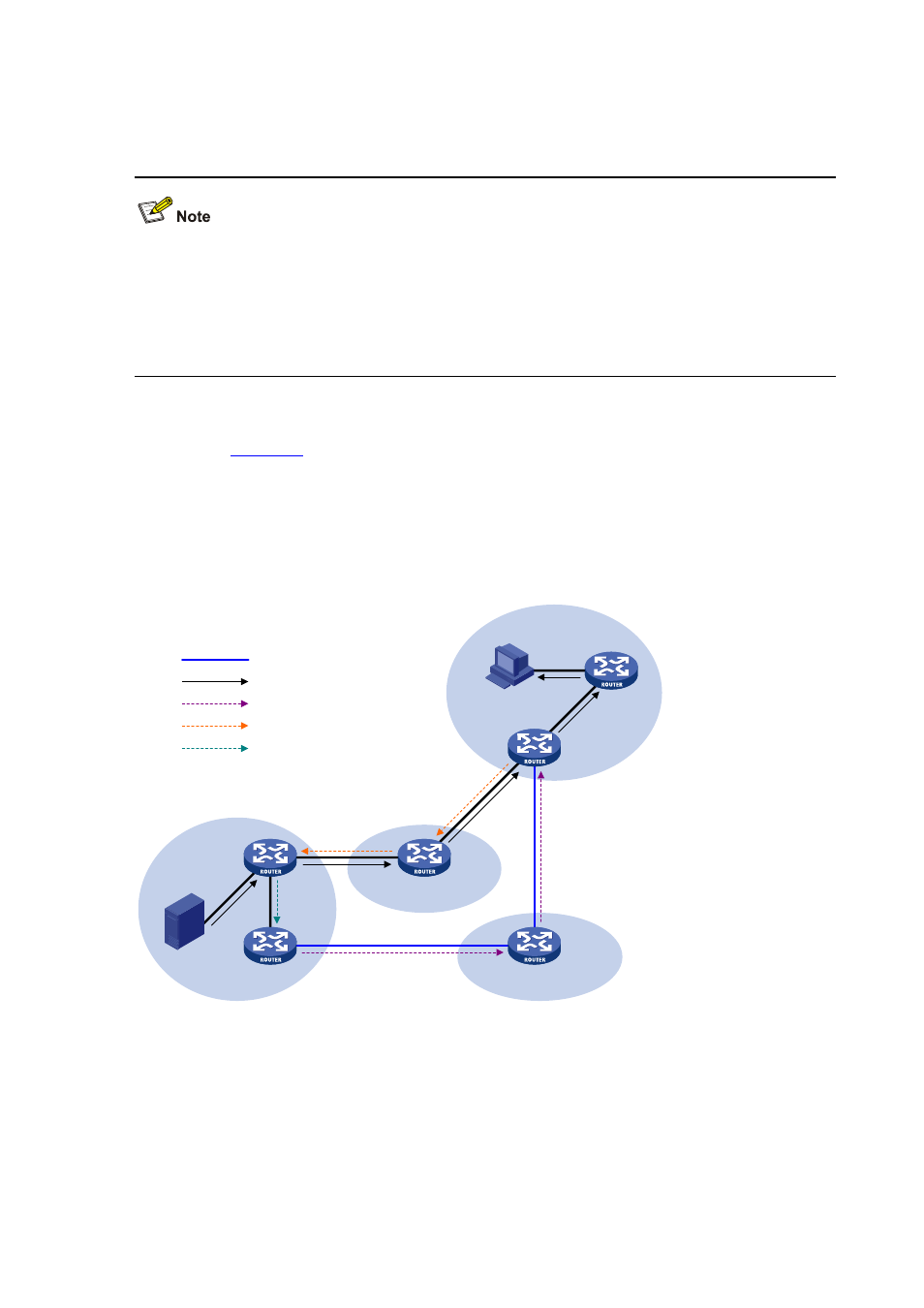
Implementing inter-domain multicast delivery by leveraging MSDP peers
As shown in
, an active source (Source) exists in the domain PIM-SM 1, and RP 1 has
learned the existence of Source through multicast source registration. If RPs in PIM-SM 2 and
PIM-SM 3 also wish to know the specific location of Source so that receiver hosts can receive
multicast traffic originated from it, MSDP peering relationships should be established between RP 1
and RP 3 and between RP 3 and RP 2 respectively.
Figure 7-2 MSDP peering relationships
RP 1
DR 1
Source
PIM-SM 1
PIM-SM 3
PIM-SM 2
PIM-SM 4
RP 3
RP 2
DR 2
MSDP peers
SA message
Join message
Multicast packets
Register message
Receiver
The process of implementing inter-domain multicast delivery by leveraging MSDP peers is as follows:
1) When the multicast source in PIM-SM 1 sends the first multicast packet to multicast group G, DR
1 encapsulates the multicast data within a register message and sends the register message to
RP 1. Then, RP 1 gets aware of the information related to the multicast source.