Ethernet multicast mac addresses – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 27
1-10
Value
Meaning
2 Link-local
scope
3 Subnet-local
scope
4 Admin-local
scope
5 Site-local
scope
6, 7, 9 through D
Unassigned
8 Organization-local
scope
E Global
scope
z
Group ID: 112 bits, IPv6 multicast group identifier that uniquely identifies an IPv6 multicast
group in the scope defined by the Scope field.
Ethernet multicast MAC addresses
When a unicast IP packet is transmitted over Ethernet, the destination MAC address is the MAC
address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transmitted over Ethernet, however, the
destination address is a multicast MAC address because the packet is directed to a group formed by
a number of receivers, rather than to one specific receiver.
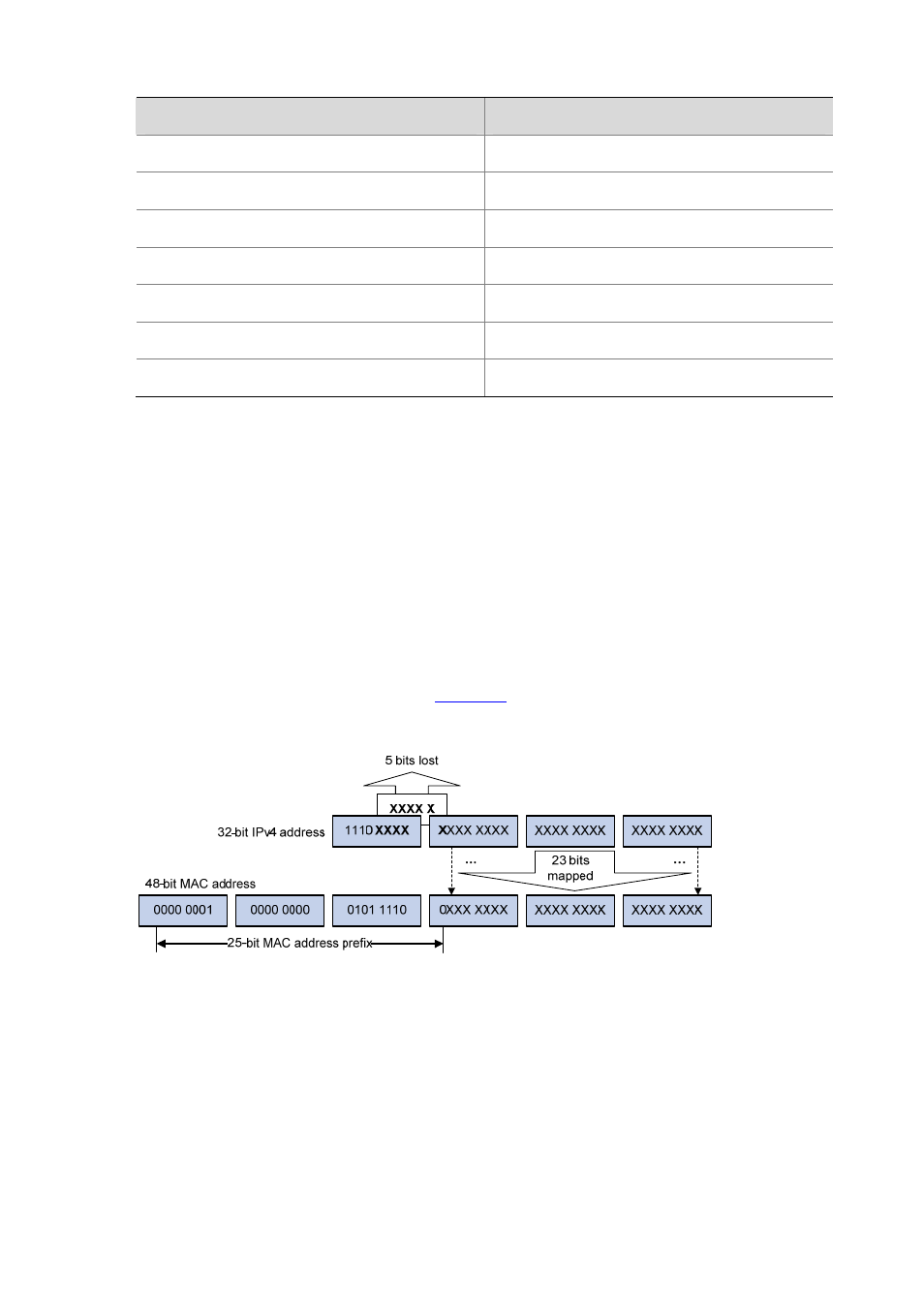
1) IPv4 multicast MAC addresses
As defined by IANA, the high-order 24 bits of an IPv4 multicast MAC address are 0x01005E, bit 25
is 0, and the low-order 23 bits are the low-order 23 bits of a multicast IPv4 address. The
IPv4-to-MAC mapping relation is shown in
.
Figure 1-6 IPv4-to-MAC address mapping
The high-order four bits of a multicast IPv4 address are 1110, indicating that this address is a
multicast address, and only 23 bits of the remaining 28 bits are mapped to a MAC address, so five
bits of the multicast IPv4 address are lost. As a result, 32 multicast IPv4 addresses map to the same
MAC address. Therefore, in Layer 2 multicast forwarding, a device may receive some multicast data
addressed for other IPv4 multicast groups, and such redundant data needs to be filtered by the
upper layer.
2) IPv6 multicast MAC addresses